Abstract
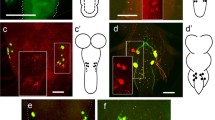
Although the corazonin gene (Crz) has been molecularly characterized, little is known concerning the function of this neuropeptide in Drosophila melanogaster. To gain insight into Crz function in Drosophila, we have investigated the developmental regulation of Crz expression and the morphology of corazonergic neurons. From late embryo to larva, Crz expression is consistently detected in three neuronal groups: dorso-lateral Crz neurons (DL), dorso-medial Crz neurons (DM), and Crz neurons in the ventral nerve cord (vCrz). Both the vCrz and DM groups die via programmed cell death during metamorphosis, whereas the DL neurons persist to adulthood. In adults, Crz is expressed in a cluster of six to eight neurons per lobe in the pars lateralis (DLP), in numerous neuronal cells in the optic lobes, and in a novel group of four abdominal ganglionic neurons present only in males (ms-aCrz). The DLP group consists of two subsets of cells having different developmental origins: embryo and pupa. In the optic lobes, we have detected both Crz transcripts and Crz promoter activity, but no Crz-immunoreactive products, suggesting a post-transcriptional regulation of Crz mRNA. Projections of the ms-aCrz neurons terminate within the ventral nerve cord, implying a role as interneurons. Terminals of the DLP neurons are found in the retrocerebral complex that produces juvenile hormone and adipokinetic hormone. Significant reduction of trehalose levels in adults lacking DLP neurons suggests that DLP neurons are involved in the regulation of trehalose metabolism. Thus, the tissue-, stage-, and sex-specific expression of Crz and the association of Crz with the function of the retrocerebral complex suggest diverse roles for this neuropeptide in Drosophila.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AE:
-
After eclosion
- AEL:
-
After egg laying
- Akh:
-
Adipokinetic hormone
- APF:
-
After puparium formation
- CA:
-
Corpora allata
- CC:
-
Corpora cardiaca
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- Crz:
-
Corazonin
- DL:
-
Dorso-lateral Crz neurons
- DM:
-
Dorso-medial Crz neurons
- DLP:
-
Dorso-lateral posterior Crz neurons
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- ISH:
-
In situ hybridization
- ir:
-
Immunoreactive
- JH:
-
Juvenile hormone
- OL:
-
Optic lobe
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- PLT:
-
Posterior lateral tract
- TRITC:
-
Tetramethylrhodamine isothiocyanate
- vCrz:
-
Crz neurons in the ventral nerve cord
- VNC:
-
Ventral nerve cord
- X-gal:
-
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl β-D-galactoside
References
Amare A, Hummon AB, Southey BR, Zimmerman TA, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Sweedler JV (2006) Bridging neuropeptidomics and genomics with bioinformatics: prediction of mammalian neuropeptide prohormone processing. J Proteome Res 5:1162–1167
Baggerman G, Cerstiaens A, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2002) Peptidomics of the larval Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system. J Biol Chem 277:40368–40374
Baggerman G, Boonen K, Verleyen P, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2005) Peptidomic analysis of the larval Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system by two-dimensional capillary liquid chromatography quadruple time of flight mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 40:250–260
Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993) Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118:401–415
Campbell G, Goring H, Lin T, Spana E, Andersson S, Doe CQ, Tomlinson A (1994) RJ2, a glial-specific homeodomain protein required for embryonic nerve cord condensation and viability in Drosophila. Development 120:2957–2966
Cantera R, Veenstra JA, Nässel DR (1994) Postembryonic development of corazonin-containing neurons and neurosecretory cells in the blowfly, Phormia terraenovae. J Comp Neurol 350:559–572
Chen Q, Ma E, Behar KL, Xu T, Haddad GG (2002) Role of trehalose phosphate synthase in anoxia tolerance and development in Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem 277:3274–3279
Choi YJ, Lee G, Hall JC, Park JH (2005) Comparative analysis of Corazonin-encoding genes (Crz’s) in Drosophila species and functional insights into Crz-expressing neurons. J Comp Neurol 482:372–385
Choi YJ, Lee G, Park JH (2006) Programmed cell death mechanisms of identifiable peptidergic neurons in Drosophila melanogaster. Development 133:2223–2232
Clark IE, Dobi KC, Duchow HK, Vlasak AN, Gavis ER (2002) A common translational control mechanism functions in axial patterning and neuroendocrine signaling in Drosophila. Development 129:3325–3334
Consoulas C, Duch C, Bayline RJ, Levine RB (2000) Behavioral transformations during metamorphosis: remodeling of neural and motor systems. Brain Res Bull 53:571–583
Dai JL, Gilbert LI (1991) Metamorphosis of the corpus allatum and degeneration of the prothoracic glands during the larval-pupal-adult transformation of Drosophila melanogaster: a cytophysiological analysis of the ring gland. Dev Biol 144:309–326
Dewey EM, McNabb SL, Ewer J, Kuo GR, Takanishi CL, Truman JW, Honegger HW (2004) Identification of the gene encoding bursicon, an insect neuropeptide responsible for cuticle sclerotization and wing spreading. Curr Biol 14:1208–1213
Dierick HA, Greenspan RJ (2007) Serotonin and neuropeptide F have opposite modulatory effects on fly aggression. Nat Genet 39:678–682
Draizen TA, Ewer J, Robinow S (1999) Genetic and hormonal regulation of the death of peptidergic neurons in the Drosophila central nervous system. J Neurobiol 38:455–465
Feany MB, Quinn WG (1995) A neuropeptide gene defined by the Drosophila memory mutant amnesiac. Science 268:869–873
Flatt T, Tu M-P, Tatar M (2005) Hormonal pleiotropy and the juvenile hormone regulation of Drosophila development and life history. BioEssays 27:999–1010
Halter DA, Urban J, Rickert C, Ner SS, Ito K, Travers AA, Technau GM (1995) The homeobox gene repo is required for the differentiation and maintenance of glia function in the embryonic nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. Development 121:317–332
Hamanaka Y, Yasuyama K, Numata H, Shiga S (2005) Synaptic connections between pigment-dispersing factor-immunoreactive neurons and neurons in the pars lateralis of the blow fly Protophormia terraenovae. J Comp Neurol 491:390–399
Hansen IA, Sehnal F, Meyer SR, Scheller K (2001) Corazonin gene expression in the waxmoth Galleria mellonella. Insect Mol Biol 10:341–346
Hassan BA, Bermingham NA, He Y, Sun Y, Jan YN, Zoghbi HY, Bellen HJ (2000) atonal regulates neurite arborization but does not act as a proneural gene in the Drosophila brain. Neuron 25:549–561
Hawkins CJ, Yoo SJ, Peterson EP, Wang SL, Vernooy SY, Hay BA (2000) The Drosophila caspase DRONC cleaves following glutamate or aspartate and is regulated by DIAP1, HID, and GRIM. J Biol Chem 275:27084–27093
Hay BA, Wolff T, Rubin GM (1994) Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development 120:2121–2129
Helfrich-Förster C (2003) The neuroarchitecture of the circadian clock in the brain of Drosophila melanogaster. Microsc Res Tech 62:94–102
Helfrich-Förster C, Täuber M, Park JH, Mühlig-Versen M, Schneuwly S, Hofbauer A (2000) Ectopic expression of the neuropeptide pigment-dispersing factor alters behavioral rhythms in Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurosci 20:3339–3353
Hewes RS, Taghert PH (2001) Neuropeptides and neuropeptide receptors in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genome Res 11:1126–1142
Hua Y-J, Ishibashi J, Saito H, Tawfik AI, Sakakibara M, Tanaka Y, Derua R, Waelkens E, Baggerman G, De Loof A, Schoofs L, Tanaka S (2000) Identification of [Arg7] corazonin in the silkworm, Bombyx mori, and the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus, as a factor inducing dark color in an albino strain of the locust, Locusta migratoria. J Insect Physiol 46:853–859
Isshiki T, Pearson B, Holbrook S, Doe CQ (2001) Drosophila neuroblasts sequentially express transcription factors which specify the temporal identity of their neuronal progeny. Cell 106:511–521
Johnson EC, Shafer OT, Trigg JS, Park JH, Schooley DA, Dow JA, Taghert PH (2005) A novel diuretic hormone receptor in Drosophila: evidence for conservation of CGRP signaling. J Exp Biol 208:1239–1246
Kaneko M, Hall JC (2000) Neuroanatomy of cell expressing clock genes in Drosophila: transgenic manipulation of the period and timeless genes to mark the perikarya of circadian pacemaker neurons and their projections. J Comp Neurol 422:66–94
Kim SK, Rulifson EJ (2004) Conserved mechanisms of glucose sensing and regulation by Drosophila corpora cardiaca cells. Nature 431:316–320
Kim Y-J, Spalovská-Valachová I, Cho K-H, Zitnanova I, Park Y, Adams ME, Zitnan D (2004) Corazonin receptor signaling in ecdysis initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6704–6709
Kim Y-J, Zitnan D, Galizia CG, Cho K-H, Adams ME (2006) A command chemical triggers an innate behavior by sequential activation of multiple peptidergic ensembles. Curr Biol 16:1395–1407
Klann E, Antion MD, Banko JL, Hou L (2004) Synaptic plasticity and translation initiation. Learn Mem 11:365–372
Kuersten S, Goodwin EB (2003) The power of the 3′-UTR: translational control and development. Nat Rev Genet 4:626–637
Lee G, Park JH (2004) Hemolymph sugar homeostasis and starvation-induced hyperactivity affected by genetic manipulations of the adipokinetic hormone-encoding gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 167:311–323
Lee G, Bahn JH, Park JH (2006) Sex- and clock-controlled expression of the neuropeptide F gene in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12580–12585
Lee T, Luo L (1999) Mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker for studies of gene function in neuronal morphogenesis. Neuron 22:451–461
Levine RB, Morton DB, Restifo LL (1995) Remodeling of the insect nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:28–35
Li C, Kim K, Nelson LS (1999) FMRFamide-related neuropeptide gene family in Caenorhabditis elegans. Brain Res 8848:26–34
Liu F, Baggerman G, D’Hertog W, Verleyen P, Schoofs L, Wets G (2006) In silico identification of new secretory peptide genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:510–522
Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z (2004) Caspase-independent cell death? Oncogene 23: 2766–2773
Lundell MJ, Lee HK, Perez E, Chadwell L (2003) The regulation of apoptosis by Numb/Notch signaling in the serotonin lineage of Drosophila. Development 130:4109–21
Maeno K, Tanaka S (2004) Hormonal control of phase-related changes in the number of antennal sensilla in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria: possible involvement of [His7]-corazonin. J Insect Physiol 50:855–865
Merighi A (2002) Costorage and coexistence of neuropeptides in the mammalian CNS. Prog Neurobiol 66:161–190
Moore MS, DeZazzo J, Luk AY, Tully T, Singh CM, Heberlein U (1998) Ethanol intoxication in Drosophila: genetic and pharmacological evidence for regulation by the cAMP signaling pathway. Cell 93:997–1007
Nässel DR (2002) Neuropeptides in the nervous system of Drosophila and other insects: multiple roles as neuromodulators and neurohormones. Prog Neurobiol 68:1–84
Nässel DR, Homberg U (2006) Neuropeptides in interneurons of the insect brain. Cell Tissue Res 326:1–24
Novotny T, Eiselt R, Urban J (2002) Hunchback is required for the specification of the early sublineage neuroblast 7–3 in the Drosophila central nervous system. Development 129:1027–1036
Noyes BE, Katz FN, Schaffer MH (1995) Identification and expression of the Drosophila adipokinetic hormone gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol 109:133–141
Park JH, Schroeder AJ, Helfrich-Förster C, Jackson FR, Ewer J (2003) Targeted ablation of CCAP neuropeptide-containing neurons of Drosophila causes specific defects in execution and circadian timing of ecdysis behavior. Development 130:2645–2656
Park Y, Filippov V, Gill SS, Adams ME (2002) Deletion of the ecdysis-triggering hormone gene leads to lethal ecdysis deficiency. Development 129:493–503
Porras MG, De Loof A, Breuer M, Aréchiga H (2003) Corazonin promotes tegumentary pigment migration in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Peptides 24:1581–1589
Predel R, Agricola H, Linde D, Wollweber L, Veenstra JA, Penzlin H (1994) The insect neuropeptide corazonin: physiological and immunocytochemical studies in Blattariae. Zoology 98:35–50
Predel R, Kellner R, Gäde G (1999) Myotropic neuropeptides from the retrocerebral complex of the stick insect, Carausius morosus (Phasmatodea: Lonchodidae). Eur J Entomol 96:275–278
Renn SCP, Park JH, Rosbash M, Hall JC, Taghert PH (1999) A pdf neuropeptide gene mutation and ablation of PDF neurons each cause severe abnormalities of behavioral circadian rhythms in Drosophila. Cell 99:791–802
Roller L, Tanaka Y, Tanaka S (2003) Corazonin and corazonin-like substances in the central nervous system of the Pterygote and Apterygote insects. Cell Tissue Res 312:393–406
Roller L, Tanaka S, Kimura K, Satake H, Tanaka Y (2006) Molecular cloning of [Thr4, His7]-corazonin (Apime-corazonin) and its distribution in the central nervous system of the honey bee Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera : Apidiae). Appl Entomol Zool 41:331–338
Rulifson EJ, Kim SK, Nusse R (2002) Ablation of insulin-producing neurons in flies: growth and diabetic phenotypes. Science 296:1118–1120
Salio C, Lossi L, Ferrini F, Merighi A (2006) Neuropeptides as synaptic transmitters. Cell Tissue Res 326:583–598
Sandman CA, Strand FL, Beckwith B, Chronwall BM, Flynn FW, Nachman RJ (1999) Neuropeptides: structure and function in biology and behavior. New York Academy of Sciences, New York
Shiga S (2003) Anatomy and functions of brain neurosecretory cells in Diptera. Microsc Res Tech 62:114–131
Shiga S, Davis NT, Hildebrand JG (2003) Role of neurosecretory cells in the photoperiodic induction of pupal diapause of the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 462:275–285
Siegmund T, Korge G (2001) Innervation of the ring gland of Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 431:481–491
Slama K, Sakai T, Takeda M (2006) Effect of corazonin and cardioactive peptide on heartbeat in the adult American cockroach (Periplaneta americana). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 62:91–103
Spradling AC, Rubin GM (1982) Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science 218:341–347
Spradling AC, Rubin GM (1983) The effect of chromosomal position on the expression of the Drosophila xanthine dehydrogenase. Cell 34:47–57
Svensson M, Skold K, Svenningsson P, Andren PE (2003) Peptidomics-based discovery of novel neuropeptides. J Proteome Res 2:213–219
Taghert PH, Veenstra JA (2003) Drosophila neuropeptide signaling. Adv Genet 49:1–65
Tanaka S, Pener MP (1994) A neuropeptide controlling the dark pigmentation in color polymorphism of the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. J Insect Physiol 40:997–1005
Tanaka S, Zhu DH, Hoste B, Breuer M (2002a) The dark-color inducing neuropeptide, His7-corazonin, causes a shift in morphometric characteristics towards the gregarious phase in isolated-reared (solitarious) Locusta migratoria. J Insect Physiol 48:1065–1074
Tanaka Y, Hua Y, Roller L, Tanaka S (2002b) Corazonin reduces the spinning rate in the silk worm, Bombyx mori. J Insect Physiol 48:707–714
Tawfik IA, Tanaka S, De Loof A, Schoofs L, Baggerman G, Waelkens E, Derura R, Milner Y, Yerushalmi Y, Pener MP (1999) Identification of the gregarization-associated dark-pigmentotropin in locusts through an albino mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7083–7087
Tissot M, Stocker RF (2000) Metamorphosis in Drosophila and other insects: the fate of neurons throughout the stages. Prog Neurobiol 62:89–111
Truman JW, Taylor BJ, Awad TA (1993) Formation of the adult nervous system. In: Bate M, Martinez A (ed) The development of Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp 1245–1275
Vanden Broeck J (2001) Neuropeptides and their precursors in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster. Peptides 22:241–254
Veenstra J (1989) Isolation and structure of corazonin, a cardio-active peptide from the American cockroach. FEBS Lett 250:231–234
Veenstra J (1991) Presence of corazonin in three insect species, and isolation and identification of [His7] corazonin from Schistocerca americana. Peptides 12:1285–1289
Veenstra J (1994) Isolation and structure of the Drosophila corazonin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 204:292–296
Veenstra JA, Davis NT (1993) Localization of corazonin in the nervous system of the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 274:57–64
Verleyen P, Baggerman G, Mertens I, Vandersmissen T, Huybrechts J, Van Lommel A, De Loof A, Schoofs L (2006) Cloning and characterization of a third isoform of corazonin in the honey bee Apis mellifera. Peptides 27:493–499
Wegener C, Reinl T, Jansch L, Predel R (2006) Direct mass spectrometric peptide profiling and fragmentation of larval peptide hormone release sites in Drosophila melanogaster reveals tagma-specific peptide expression and differential processing. J Neurochem 96:1362–1374
Wen T, Parrish CA, Xu D, Wu Q, Shen P (2005) Drosophila neuropeptide F and its receptor, NPFR1, define a signaling pathway that acutely modulates alcohol sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2141–2146
White K, Grether ME, Abrams JM, Young, L, Farrell K, Steller H (1994) Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila. Science 264:677–683
White K, Tahaoglu E, Steller H (1996) Cell killing by the Drosophila reaper. Science 271:805–807
Wilkie GS, Dickson KS, Gray NK (2003) Regulation of mRNA translation by 5′- and 3′-UTR-binding factors. Trends Biochem Sci 28:182−188
Wise S, Davis, NT, Tyndale E, Noveral J, Folwell MG, Bedian V, Emery IF, Siwicki KK (2002) Neuroanatomical studies of period gene expression in the hawk moth, Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 447:366−380
Wu Q, Wen T, Lee G, Park JH, Cai HN, Shen P (2003) Developmental control of foraging and social behavior by the Drosophila neuropeptide Y (NPY) like system. Neuron 39:147–161
Yao K-M, Samson M-L, Reeves R, White K (1993) Gene elav of Drosophila melanogaster; a prototype for neuronal-specific binding protein gene family that is conserved in flies and humans. J Neurobiol 24:723–739
Xiong WC, Okano H, Patel NH, Blendy JA, Montell C (1994) Repo encodes a glial-specific homeodomain protein required in the Drosophila nervous system. Genes Dev 8:981–994
Acknowledgments
We thank Bruce Hay (Caltech) for the UAS-p35 transgenic line and Jeff Hall (Brandeis University) for the tim-gal4 transgenic line. We are also grateful to Jim Hall and Tom Dockendorff for proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a USA National Science Foundation grant to J.H.P. (IBN-0133538) and, in part, by the Basic Research Program of the Korean Science and Engineering Foundation to K.-M.K. (R05-2004-000-10770-0).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G., Kim, KM., Kikuno, K. et al. Developmental regulation and functions of the expression of the neuropeptide corazonin in Drosophila melanogaster . Cell Tissue Res 331, 659–673 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0549-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0549-5