Abstract
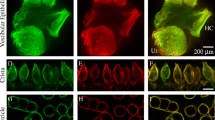
The immunohistochemical localization of α1A, α1B, α1C, α1D, and α1E voltage-gated calcium channel subunits was investigated in the chinchilla organ of Corti and spiral ganglia with the use of specific antipeptide antibodies. The inner and outer hair cells were immunoreactive for α1A and α1D subunit antibodies. α1C immunoreactivity localized to the nerve terminals innervating inner hair cells and the basal pole of the outer hair cell. There was only non-specific staining to α1B and α1E. Supporting cells were non-immunoreactive. Spiral ganglia neurons were α1B, α1C, and α1D immunoreactive. A few spiral ganglia neurons were α1E immunoreactive. The importance of α1D, the pore-forming subunit of the L-type channel, in outer and inner hair cell function has been clearly demonstrated in electrophysiological, molecular biological, and knockout models. The presence of α1A, the pore-forming subunit of the P/Q type channels, has not previously been demonstrated in inner and outer hair cells, and its function in the cochlear hair cell is unknown.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Art JJ, Wu YC, Fettiplace R (1995) The calcium-activated potassium channels of turtle hair cells. J Gen Physiol 105:49–72
Beisel KW, Deffenbacher KE, Drescher MJ, Drescher DG (1998) Expression of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) in cochlear hair cells. 21st ARO, Midwinter Research Meeting, Abs #77
Catterall WA (1998) Structure and function of neuronal Ca2+ channels and their role in neurotransmitter release. Cell Calcium 24:307–323
Engel J, Michna M, Platzer J, Striessnig J (2002) Calcium channels in mouse hair cells: function, properties and pharmacology. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 59:35–41
Fechter LD, Liu Y (1995) Elevation of intracellular calcium levels in spiral ganglion cells by trimethyltin. Hear Res 91:101–109
Fisher TE, Bourque CW (2001) The function of calcium channel subtypes in exocytotic secretion: new perspectives from synaptic and non-synaptic release. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 77:269–303
Fletcher CF, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1998) Genetic analysis of voltage-dependent calcium channels. J Bioenerg Biomembr 30:387–398
Fuchs PA (1996) Synaptic transmission at vertebrate hair cells. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6:514–519
Fuchs PA, Evans MG (1988) Voltage oscillations and ionic conductances in hair cells isolated from the alligator cochlea. J Comp Physiol [A] 164:151–163
Fuchs PA, Nagai T, Evans MG (1988) Electrical tuning in hair cells isolated from the chick cochlea. J Neurosci 8:2460–2467
Green GE, Khan KM, Beisel DW, Drescher MJ, Hatfield JS, Drescher DJ (1996) Calcium channel subunits in the mouse cochlea. J Neurochem 67:37–45
Gummer AW, Meyer J, Frank G, Scherrer MP, Preyer S (2002) Mechanical transduction in outer hair cells. Audiol Neurootol 7:13–16
Hawkins JF, Johnsson LG (1976) Microdissection and surface preparations of the inner ear. In: Smith CA, Vernon JA (eds) Handbook of auditory and vestibular research methods. Thomas, Springfield, Ill, pp 5–51
Heinrich UR, Maurer J, Mann W (1997) Alteration of loosely bound calcium in the organ of Corti of the guinea pig after application of the calcium channel blocker diltiazem. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 254:223–229
Heinrich UR, Maurer J, Mann W (1999) Ultrastructural evidence for protection of the outer hair cells of the inner ear during intense noise exposure by application of the organic calcium channel blocker diltiazem. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 61:321–327
Hell JW, Westenbroek RE, Warner C, Ahlijanian MK, Prystary W, Gilbert MM, Snutch TP, Catteral WA (1993) Identification and differential subcellular localization of the neuronal class C and class D L-type Ca2+ channel α1 subunits. J Cell Biol 123:949–962
Hillman DE, Avital I, Weiser M, Rudy B, Cherksey B, Llinas R (1995) Immunohistochemical localization of ionic channel on hair cells. 18th ARO, Midwinter Research Meeting, Abs #632
Hoffmann F, Biel M, Flockerzi V (1994) Molecular basis for Ca 2+ diversity. Annu Rev Neurosci 17:399–418
Hudspeth AJ (1985) The cellular basis of hearing: the biophysics of hair cells. Science 230:745–752
Hudspeth AJ (1989) How the ear's works work. Nature 341:397–404
Hudspeth AJ (1997) How hearing happens. Neuron 19:947–950
Jimenez C, Gireldez F, Represa J, Garcia-Diaz JF (1997) Calcium currents in dissociated cochlear neurons from the chick embryo and their modification by neurotrophin-3. Neuroscience 77:673–682
Kollmar R, Fak J, Montgomery LG, Hudspeth AJ (1997a) Hair cell-specific splicing of mRNA for the α-1D subunit of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the chicken's cochlea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:14889–14893
Kollmar R, Montgomery LG, Fak J, Henry LJ, Hudspeth AJ (1997b) Predominance of the α-1D subunit in L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels of hair cells in the chicken's cochlea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:14883–14888
Koschak A, Reimer D, Huber I, Grabner M, Blossmann H, Engel J, Striessnig J (2001) Alpha 1D (Cav1.3) subunits can form L-type Ca2+ channels activating at negative voltages. J Biol Chem 276:22100–22106
Lenzi D, Roberts W (1994) Calcium signalling in hair cells: multiple roles in a compact cell. Curr Biol 4:496–502
Lim DJ, Kalinec F (1998) Cell and molecular basis of hearing. Kidney Int 53(suppl 65):104–113
Lopez I, Ishiyama G, Ishiyama A, Jen JC, Liu F, Baloh R (1999) Differential subcellular immunolocalization of voltage-gated calcium channel 1 subunits in the chinchilla cristae ampullaris. Neuroscience 92:773–782
Lory P, Ophoff RA, Nahmias J (1997) Towards a unified nomenclature describing voltage-gated calcium channel genes. Hum Genet 100:149–150
Martinez-Dunst C, Michaels RL, Fuchs PA (1997) Release sites and calcium channels in hair cells of the chick's cochlea. J Neurosci 17:9133–9144
Maurer J, Heinrich UR, Hinni M, Mann W (1999) Alteration of the calcium content in inner hair cells of the cochlea of the guinea pig after acute noise trauma with and without application of the organic calcium channel blocker diltiazem. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 61:328–333
Nakagawa T, Kakehata S, Akaike N, Komune S, Takasaka T, Uemura T (1994) Voltage-dependent channels in dissociated outer hair cells of the guinea pig. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol: 251(suppl 1):S57–S60
Nilles R (1995) Direct evidence of a protective effect of calcium antagonists on the inner ear. Inhibition of a toxic increase in the calcium level in hair cells of the guinea pig. HNO 43:716–723
Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouwe MN, van Eijk R, Oefner PJ, Hoffman SM, Lamerdin JE, Mohrenweiser HW, Bulman DE, Ferrari M, Haan J, Lindhouth D, van Ommen GJ, Hofker MH, Ferrari MD, Frants RR (1996) Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell 7:543–552
Parsons TD, Lenzi D, Almers W, Roberts WM (1994) Calcium-triggered exocytosis and endocytosis in an isolated presynaptic cell: capacitance measurements in saccular hair cells. Neuron 13:875–883
Perez-Reyes E, Schneider T (1995) Molecular biology of calcium channels. Kidney Int 48:1111–1124
Platzer J, Engel J, Schrott-Fischer A, Stephan K, Bova S, Chen H, Zheng H, Striessnig J (2000) Congenital deafness and sinoatrial node dysfunction in mice lacking class D L-type Ca2+ channels. Cell 102:89–97
Ramanathan K, Michael TH, Jiang GJ, Hiel H, Fuchs PA (1999) A molecular mechanism for electrical tuning of cochlear hair cells. Science 283:215–217
Roberts WM, Jacobs RA, Hudspeth AJ (1990) Colocalization of ion channels involved in frequency selectivity and synaptic transmission at presynaptic active zones of hair cells. J Neurosci 10:3664–3684
Roberts WM, Jacobs RA, Hudspeth AJ (1991) The hair cell as a presynaptic terminal. Ann N Y Acad Sci 635:221–233
Robertson D, Paki B (2002) Role of L-type Ca2+ channels in transmitter release from mammalian inner hair cells. II. Single-neuron activity. J Neurophysiol 87:2734–2740
Slepecky N (1996) Structure of the mammalian cochlea. In: Dallos P, Popper AN, Fay R (eds) The cochlea. Springer handbook of auditory research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 44–129
Spassova M, Eisen MD, Saunders JC, Parsons TD (2001) Chick cochlear hair cell exocytosis mediated by dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels. J Physiol 535:689–696
Su ZL, Jiang SC, Gu R, Yang WP (1995) Two types of calcium channels in bullfrog saccular hair cells. Hear Res 7:62–68
Triggle DJ (1999) Molecular pharmacology of voltage-gated calcium channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 267–281
Tsien RW (1998) Key clockwork component cloned. Nature 391:839–840
Tucker TR, Fettiplace R (1996) Monitoring calcium in turtle hair cells with a calcium-activated potassium channel. J Physiol 494:613–626
Volsen SG, Day NC, McCormack AL, Smith W, Craig PJ, Beattie R, Ince PG, Shaw, PJ, Ellis SB, Gillespie A, Harpold MM, Lodge D (1995) The expression of neuronal voltage-dependent calcium channels in human cerebellum. Mol Brain Res 34:271–282
Westenbroek RE, Hell JW, Warner C, Dubel SJ, Snutch TP, Catterall WA (1992) Biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of an N-type calcium channel alfa1 antibody. Neuron 9:1099–1115
Westenbroek RE, Sakurai T, Elliot EM, Hell JW, Starr TV, Snutch TP, Catterall WA (1995) Immunohistochemical localization and subcellular distribution of the alfa-1A subunits of brain calcium channels. J Neurosci 15:6403–6418
Williams ME, Brust PF, Feldman DH, Saraswathi P, Simerson S, Maroufi A, McCue AF, Velicebi G, Ellis SB, Harpold MM (1992) Structure and functional expression of an ω-conotoxin-sensitive human N-type calcium channel. Science 257:389–395
Williams ME, Marubio LM, Deal CR, Hans M, Brust PF, Philipson LH, Miller RJ, Johnson EC, Harpold MM, Ellis SB (1994) Structure and functional characterization of neuronal α1E calcium channel subtypes. J Biol Chem 269:22347–22357
Wu YC, Art JJ, Goodman MB, Fettiplace R (1995) A kinetic description of the calcium-activated potassium channel and its application to electrical tuning of hair cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 63:131–158
Yokoyama CT, Westenbroek RE, Hell JW, Soong TW, Snutch TP, Catterall WA (1995) Biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of the neuronal class E calcium channel alpha 1 subunit. J Neurosci 15:6419–6432
Yue Q, Jen JC, Thwe MM, Nelson SF, Baloh RW (1998) De novo mutation in CACNA1A caused acetazolamide-responsive episodic ataxia. Am J Med Genet 77:298–301
Zhang SY, Robertson D, Yates G, Everett A (1999) Role of L-type Ca (2+) channels in transmitter release from mammalian inner hair cells. I. Gross sound-evoked potentials. J Neurophysiol 82:3307–3315
Zidanic M, Fuchs P (1995) Kinetic analysis of barium currents in chick cochlear hair cells. Biophys J 68:1323–1336
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Richard Altschuler from the Kresge Hearing Research Institute, Ann Arbor Michigan, for his assistance in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The National Institutes of Health grants AG09693-10, DC005224, 00140-02, and DC05187-01 supported this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez, I., Ishiyama, G., Acuna, D. et al. Immunolocalization of voltage-gated calcium channel α1 subunits in the chinchilla cochlea. Cell Tissue Res 313, 177–186 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0759-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0759-4