Abstract
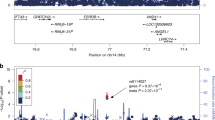
Although epidemiological evidence suggests a human genetic basis of pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) susceptibility, the identification of specific genes and alleles influencing PTB risk has proven to be difficult. Previous genome-wide association (GWA) studies have identified only three novel loci with modest effect sizes in sub-Saharan African and Russian populations. We performed a GWA study of 550,352 autosomal SNPs in a family-based discovery Moroccan sample (on the full population and on the subset with PTB diagnosis at <25 years), which identified 143 SNPs with p < 1 × 10−4. The replication study in an independent case/control sample identified four SNPs displaying a p < 0.01 implicating the same risk allele. In the combined sample including 556 PTB subjects and 650 controls these four SNPs showed suggestive association (2 × 10−6 < p < 4 × 10−5): rs358793 and rs17590261 were intergenic, while rs6786408 and rs916943 were located in introns of FOXP1 and AGMO, respectively. Both genes are involved in the function of macrophages, which are the site of latency and reactivation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The most significant finding (p = 2 × 10−6) was obtained for the AGMO SNP in an early (<25 years) age-at-onset subset, confirming the importance of considering age-at-onset to decipher the genetic basis of PTB. Although only suggestive, these findings highlight several avenues for future research in the human genetics of PTB.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel L, Alcaïs A, Schurr E (2014a) The dissection of complex susceptibility to infectious disease: bacterial, viral and parasitic infections. Curr Opin Immunol 30C:72–78. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2014.07.002
Abel L, El-Baghdadi J, Bousfiha AA et al (2014b) Human genetics of tuberculosis: a long and winding road. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369:20130428. doi:10.1098/rstb.2013.0428
Alcaïs A, Fieschi C, Abel L, Casanova J-L (2005) Tuberculosis in children and adults: two distinct genetic diseases. J Exp Med 202:1617–1621. doi:10.1084/jem.20052302
Azad AK, Sadee W, Schlesinger LS (2012) Innate immune gene polymorphisms in tuberculosis. Infect Immun 80:3343–3359. doi:10.1128/IAI.00443-12
Baghdadi JE, Orlova M, Alter A et al (2006) An autosomal dominant major gene confers predisposition to pulmonary tuberculosis in adults. J Exp Med 203:1679–1684. doi:10.1084/jem.20060269
Barreiro LB, Tailleux L, Pai AA et al (2012) Deciphering the genetic architecture of variation in the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:1204–1209. doi:10.1073/pnas.1115761109
Bellamy R, Ruwende C, Corrah T et al (1998) Variations in the NRAMP1 gene and susceptibility to tuberculosis in West Africans. N Engl J Med 338:640–644. doi:10.1056/NEJM199803053381002
Berry MPR, Graham CM, McNab FW et al (2010) An interferon-inducible neutrophil-driven blood transcriptional signature in human tuberculosis. Nature 466:973–977. doi:10.1038/nature09247
Boisson-Dupuis S, El Baghdadi J, Parvaneh N et al (2011) IL-12Rβ1 deficiency in two of fifty children with severe tuberculosis from Iran, Morocco, and Turkey. PLoS One 6:e18524. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018524
Boisson-Dupuis S, Bustamante J, El-Baghdadi J et al (2015) Inherited and acquired immunodeficiencies underlying tuberculosis in childhood. Immunol Rev 264:103–120. doi:10.1111/imr.12272
Casanova J-L, Abel L (2002) Genetic dissection of immunity to mycobacteria: the human model. Annu Rev Immunol 20:581–620. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.081501.125851
Chimusa ER, Zaitlen N, Daya M et al (2014) Genome-wide association study of ancestry-specific TB risk in the South African Coloured population. Hum Mol Genet 23:796–809. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddt462
Cobat A, Gallant CJ, Simkin L et al (2009) Two loci control tuberculin skin test reactivity in an area hyperendemic for tuberculosis. J Exp Med 206:2583–2591. doi:10.1084/jem.20090892
Cobat A, Gallant CJ, Simkin L et al (2010) High heritability of antimycobacterial immunity in an area of hyperendemicity for tuberculosis disease. J Infect Dis 201:15–19. doi:10.1086/648611
Cobat A, Barrera LF, Henao H et al (2012) Tuberculin skin test reactivity is dependent on host genetic background in Colombian tuberculosis household contacts. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am 54:968–971. doi:10.1093/cid/cir972
Cobat A, Abel L, Alcaïs A, Schurr E (2014a) A general efficient and flexible approach for genome-wide association analyses of imputed genotypes in family-based designs. Genet Epidemiol 38:560–571. doi:10.1002/gepi.21842
Cobat A, Poirier C, Hoal E et al (2014b) Tuberculin skin test negativity is under tight genetic control of the chromosomal region 11p14-15 in settings of different TB endemicity. J Infect Dis. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiu446
Cochran WG (1954) The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 10:101–129
Curtis J, Luo Y, Zenner HL et al (2015) Susceptibility to tuberculosis is associated with variants in the ASAP1 gene encoding a regulator of dendritic cell migration. Nat Genet. doi:10.1038/ng.3248
Dai Y, Zhang X, Pan H et al (2011) Fine mapping of genetic polymorphisms of pulmonary tuberculosis within chromosome 18q11.2 in the Chinese population: a case-control study. BMC Infect Dis 11:282. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-282
Ernst JD (2012) The immunological life cycle of tuberculosis. Nat Rev Immunol 12:581–591. doi:10.1038/nri3259
Grant AV, El Baghdadi J, Sabri A et al (2013) Age-dependent association between pulmonary tuberculosis and common TOX variants in the 8q12-13 linkage region. Am J Hum Genet 92:407–414. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.01.013
Hamdan FF, Daoud H, Rochefort D et al (2010) De novo mutations in FOXP1 in cases with intellectual disability, autism, and language impairment. Am J Hum Genet 87:671–678. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.09.017
Horvath S, Xu X, Laird NM (2001) The family based association test method: strategies for studying general genotype–phenotype associations. Eur J Hum Genet EJHG 9:301–306. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200625
Jepson A, Fowler A, Banya W et al (2001) Genetic regulation of acquired immune responses to antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a study of twins in West Africa. Infect Immun 69:3989–3994. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.6.3989-3994.2001
Kaufmann SHE, Lange C, Rao M et al (2014) Progress in tuberculosis vaccine development and host-directed therapies—a state of the art review. Lancet Respir Med 2:301–320. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70033-5
Mägi R, Morris AP (2010) GWAMA: software for genome-wide association meta-analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 11:288. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-288
Mahasirimongkol S, Yanai H, Mushiroda T et al (2012) Genome-wide association studies of tuberculosis in Asians identify distinct at-risk locus for young tuberculosis. J Hum Genet 57:363–367. doi:10.1038/jhg.2012.35
Malik S, Abel L, Tooker H et al (2005) Alleles of the NRAMP1 gene are risk factors for pediatric tuberculosis disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12183–12188. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503368102
Meyer CG, Thye T (2014) Host genetic studies in adult pulmonary tuberculosis. Semin Immunol 26:445–453. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2014.09.005
Möller M, Hoal EG (2010) Current findings, challenges and novel approaches in human genetic susceptibility to tuberculosis. Tuberc Edinb Scotl 90:71–83. doi:10.1016/j.tube.2010.02.002
O’Garra A, Redford PS, McNab FW et al (2013) The immune response in tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol 31:475–527. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095939
Png E, Alisjahbana B, Sahiratmadja E et al (2012) A genome wide association study of pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility in Indonesians. BMC Med Genet 13:5. doi:10.1186/1471-2350-13-5
Puffer RR (1944) Familial susceptibility to tuberculosis: its importance as a public health problem. Harvard University Press
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575. doi:10.1086/519795
Sabri A, Grant AV, Cosker K et al (2014) Association study of genes controlling IL-12-dependent IFN-γ immunity: STAT4 alleles increase risk of pulmonary tuberculosis in Morocco. J Infect Dis 210:611–618. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiu140
Sepulveda RL, Heiba IM, Navarrete C et al (1994) Tuberculin reactivity after newborn BCG immunization in mono- and dizygotic twins. Tuber Lung Dis Off J Int Union Tuberc Lung Dis 75:138–143. doi:10.1016/0962-8479(94)90043-4
Shi C, Sakuma M, Mooroka T et al (2008) Down-regulation of the forkhead transcription factor Foxp1 is required for monocyte differentiation and macrophage function. Blood 112:4699–4711. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-01-137018
Thye T, Vannberg FO, Wong SH et al (2010) Genome-wide association analyses identifies a susceptibility locus for tuberculosis on chromosome 18q11.2. Nat Genet 42:739–741. doi:10.1038/ng.639
Thye T, Owusu-Dabo E, Vannberg FO et al (2012) Common variants at 11p13 are associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis. Nat Genet 44:257–259. doi:10.1038/ng.1080
Tokuoka SM, Kita Y, Shindou H, Shimizu T (2013) Alkylglycerol monooxygenase as a potential modulator for PAF synthesis in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 436:306–312. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.099
Vidal SM, Malo D, Vogan K et al (1993) Natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites: isolation of a candidate for Bcg. Cell 73:469–485
Wang X, Tang NLS, Leung CC et al (2013) Association of polymorphisms in the Chr18q11.2 locus with tuberculosis in Chinese population. Hum Genet 132:691–695. doi:10.1007/s00439-013-1282-7
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011) Global tuberculosis control 2011. In: WHO. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed 23 Apr 2012
World Health Organization (WHO) (2013) Global tuberculosis report 2013. In: WHO. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed 7 Aug 2014
Acknowledgments
We thank all patients and family members from Morocco and all the healthy Moroccan subjects for their participation in this study. We thank the late Dr M. Chentoufi from the TB Diagnostic Center (CDST) of Hay Mohammadi. We are grateful to Fatima El Bordi, the nurse from the CDTMR of Salé and to Amal Rzioui of Pneumology department of Hospital Mohammed V. We thank the Centre National de Génotypage for carrying out the genotyping. This work was supported by grants from Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, University Paris Descartes, the European Research Council (grant n°ERC-2010-AdG-268777), the EU-grant HOMITB (HEALTH-F3-2008-200732), the French National Research Agency (ANR) under the “Investments for the future” program (grant n°ANR-10-IAHU-01), the St. Giles Foundation, the National Center for Research Resources and the National Center for Advancing Sciences (NCATS) of the National Institute of Health (grant n°8ULTR000043), the Rockefeller University, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (grant n°U01AI088685). AVG was supported by the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale and Fondation BNP Paribas.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study (as stated in supplemental methods).
Additional information
J. El Baghdadi and L. Abel contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grant, A.V., Sabri, A., Abid, A. et al. A genome-wide association study of pulmonary tuberculosis in Morocco. Hum Genet 135, 299–307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1633-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1633-2