Abstract
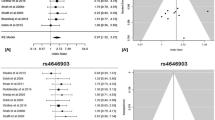
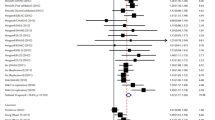
To explore the real association between p53 codon 72 polymorphism and lung cancer risk, a pooled analysis of 32 case–control studies involving 19,255 subjects was conducted. When all 32 studies were pooled into the analysis, significantly elevated lung cancer risks were associated with variant genotypes in all genetic models (for Pro/Arg vs. Arg/Arg: OR 1.21, 95% CI 1.01–1.23; for Pro/Pro vs. Arg/Arg: OR 1.20, 95% CI 1.03–1.39; for Pro/Pro + Pro/Arg vs. Arg/Arg: OR 1.14, 95% CI 1.03–1.25; for Pro/Pro vs. Arg/Arg + Pro/Arg: OR 1.06, 95% CI 1.01–1.12). In the subgroup analysis by ethnicity, histological type, or smoking status, significantly increased risks were found in subgroups such as Asians, Caucasians, lung adenocarcinoma patients, or smokers, respectively. In conclusion, our results suggest that the Pro allele at p53 codon 72 is emerging as a low-penetrance susceptibility allele for lung cancer development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agorastos T, Masouridou S, Lambropoulos AF, Chrisafi S, Miliaras D, Pantazis K (2004) P53 codon 72 polymorphism and correlation with ovarian and endometrial cancer in Greek women. Eur J Cancer Prev 13:277–280
Amos CI, Wu X, Broderick P, Gorlov IP, Gu J (2008) Genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility locus for lung cancer at 15q25.1. Nat Genet 40:616–622
Belyavskaya VA, Vardosanidze VK, Smirnova OY, Karakin EI, Sav-kin IV, Gervas PA (2006) Genetic status of p53 in stomach cancer: somatic mutations and polymorphism of codon 72. Bull Exp Biol Med 141:243–246
Birgander R, Sjaelander A, Rannug A, Alexandrie AK, Ingelman Sundberg M, Seidegard J (1995) P53 polymorphisms and haplotypes in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 16:2233–2236
Biros E, Kalina I, Biros I, Kohut A, Bogyiova E, Salagovic J (2001a) Polymorphism of the p53 gene within the codon 72 in lung cancer patients. Neoplasma 48:407–411
Biros E, Kalina I, Kohut A, Stubna J, Salagovic J (2001b) Germ line polymorphisms of the tumor suppressor gene p53 and lung cancer. Lung Cancer 31:157–162
Chen WC, Tsai FJ, Wu JY, Wu HC, Lu HF, Li CW (2000) Distributions of p53 codon 72 polymorphism in bladder cancerdproline form is prominent in invasive tumour. Urol Res 28:293–296
Egger M, Smith DG, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in metaanalysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Fan R, Wu MT, Miller D, Wain JC, Kelsey KT, Wiencke JK (2000) The p53 codon 72 polymorphism and lung cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 9:1037–1042
Fernandez-Rubio A, López-Cima MF, González-Arriaga P, García-Castro L, Pascual T, Marrón MG (2008) The P53 Arg72Pro polymorphism and lung cancer risk in a population of Northern Spain. Lung Cancer 61:309–316
Giuliani L, Jaxmar T, Casadio C, Gariglio M, Manna A, Dantonio D (2007) Detection of oncogenic viruses SV40, BKV, JCV, HCMV, HPV and p53 codon 72 polymorphism in lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 57:273–281
Hiraki A, Matsuo K, Hamajima N, Ito H, Hatooka S, Suyama M (2003) Different risk relations with smoking for non-small-cell lung cancer: comparison of P53 and TP73 genotypes. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 4:107–112
Honma HN, De Capitani EM, Perroud MW, Barbeiroa AS, Toro IF, Costa DB (2008) Influence of p53 codon 72 exon 4, GSTM1, GSTT1 and GSTP1*B polymorphisms in lung cancer risk in a Brazilian population. Lung Cancer 62:152–162
Hung RJ, McKay JD, Gaborieau V, Boffetta P, Hashibe M (2008) A susceptibility locus for lung cancer maps to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes on 15q25. Nature 452:633–637
Irarrazabal CE, Rojas C, Aracena R, Marquez C, Gil L (2003) Chilean pilot study on the risk of lung cancer associated with codon 72 polymorphism in the gene of protein p53. Toxicol Lett 144:69–76
Jain N, Singh V, Hedau S, Kumar S, Daga MK, Dewan R (2005) Infection of human papillomavirus type 18 and p53 codon 72 polymorphism in lung cancer patients from India. Chest 128:3999–4007
Jin X, Wu X, Roth JA, Amos CI, King TM, Branch C (1995) Higher lung cancer risk for younger African–Americans with the Pro/Pro p53 genotype. Carcinogenesis 16:2205–2208
Jung HY, Whang YM, Sung JS, Shin HD, Park BL, Kim JS (2008) Association study of TP53 polymorphisms with lung cancer in a Korean population. J Hum Genet 53:508–514
Lee JM, Lee YC, Yang SY, Shi WL, Lee CJ, Luh SP (2000) Genetic polymorphisms of p53 and GSTP1, but not NAT2, are associated with susceptibility to squamous-cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Int J Cancer 89:458–464
Levine AJ (1997) P53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Liu G, Miller DP, Zhou W, Thurston SW, Fan R, Xu LL (2001) Differential association of the codon 72 p53 and GSTM1 polymorphisms on the histological subtype of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 61:8718–8722
Mechanic LE, Bowman ED, Welsh JA, Khan MA, Hagiwara N, Enewold L (2007) Common genetic variation in TP53 is associated with lung cancer risk and prognosis in African Americans and somatic mutations in lung tumors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:214–222
Miller DP, Liu G, De L, Lynch TJ, Wain JC, Su L (2002) Combinations of the variant genotypes of GSTP1, GSTM1 and p53 are associated with an increased lung cancer risk. Cancer Res 62:2819–2823
Murata M, Tagawa M, Kimura M, Kimura H, Watanabe S, Saisho H (1996) Analysis of a germ line polymorphism of the p53 gene in lung cancer patients discrete results with smoking history. Carcinogenesis 17:261–264
Murata M, Tagawa M, Kimura H, Kakisawa K, Shirasawa H, Fujisawa T (1998) Correlation of the mutation of p53 gene and the polymorphism at codon 72 in smoking-related non-small lung cancer patients. Int J Oncol 12:577–581
Nadji SA, Mahmoodi M, Ziaee AA, Naghshvar F, Torabizadeh J, Yahyapour Y (2007) An increased lung cancer risk associated with codon 72 polymorphism in the TP53 gene and human papillomavirus infection in Mazandaran province, Iran. Lung Cancer 56:145–151
Papadakis ED, Soulitzis N, Spandidos DA (2002) Association of p53 codon 72 polymorphism with advanced lung cancer: the Arg allele is preferentially retained in tumours arising in Arg/Pro germline heterozygotes. Br J Cancer 87:1013–1018
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Pierce LM, Sivaraman L, Chang W, Lum A, Donlon T, Seifried A (2000) Relationships of TP53 codon 72 and HRAS1 polymorphisms with lung cancer risk in an ethnically diverse population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 9:1199–1204
Popanda O, Edler L, Waas P, Schattenberg T, Butkiewicz D, Muley T (2007) Elevated risk of squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung in heavy smokers carrying the variant alleles of the TP53 Arg72Pro and p21 Ser31Arg polymorphisms. Lung Cancer 55:25–34
Robles AI, Linke SP, Harris CC (2002) The p53 network in lung carcinogenesis. Oncogene 21:6898–6907
Rodin SN, Rodin AS (2000) Human lung cancer and p53: the interplay between mutagenesis and selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12244–12249
Saccone SF, Hinrichs AL, Saccone NL, Chase GA, Konvicka K (2007) Cholinergic nicotinic receptor genes implicated in a nicotine dependence association study targeting 348 candidate genes with 3713 SNPs. Hum Mol Genet 16:36–49
Sakiyama T, Kohno T, Mimaki S, Ohta T, Yanagitani N, Sobue T, Kunitoh H (2005) Association of amino acid substitution polymorphisms in DNA repair genes TP53, POLI, REV1 and LIG4 with lung cancer risk. Int J Cancer 114:730–737
Sato S, Nakamura Y, Tsuchiya E (1994) Difference of allelotype between squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer Res 54:5652–5655
Sreeja L, Syamala V, Raveendran PB, Santhi S, Madhavan J, Ankathil R (2008) p53 Arg72Pro polymorphism predicts survival outcome in lung cancer patients in Indian population. Cancer Invest 26:41–46
Szymanowska A, Jassem E, Dziadziuszko R, Borg A, Limon J, Kobierska-Gulida G (2006) Increased risk of non-small cell lung cancer and frequency of somatic TP53 gene mutations in Pro72 carriers of TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism. Lung Cancer 52:9–14
Tardon A, Lee W, Delgado M, Dosemeci M, Albanes D, Hoover R (2005) Leisure-time physical activity and lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 16:389–397
Thomas M, Kalita A, Labrecque S, Pim D, Banks L, Matlashewski G (1999) Two polymorphic variants of wild-type p53 differ biochemically and biologically. Mol Cell Biol 19:1092–1100
Tobias A (1999) Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Tech Bull 8:15–17
To-Figueras J, Gene M, Gomez-Catalan J, Galan C, Firvida J, Fuentes M (1996) Glutathione-Stransferase M1 and codon 72 p53 polymorphisms in a northwestern Mediterranean population and their relation to lung cancer susceptibility. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 5:337–342
Wang YC, Chen CY, Chen SK, Chang YY, Lin P (1999) P53 codon 72 polymorphism in Taiwanese lung cancer patients: association with lung cancer susceptibility and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 5:129–134
Weiss RB, Baker TB, Cannon DS, von Niederhausern A, Dunn DM (2008) A candidate gene approach identifies the CHRNA5-A3-B4 region as a risk factor for age-dependent nicotine addiction. PLoS Genet 4:e1000125
Weston A, Perrin LS, Forrester K, Hoover RN, Trump BF, Harris CC (1992) Allelic frequency of a p53 polymorphism in human lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 1:481–483
Weston A, Ling-Cawley HM, Caporaso NE, Bowman ED, Hoover RN, Trump BF (1994) Determination of the allelic frequencies of an L-myc and a p53 polymorphism in human lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 15:583–587
Wu X, Zhao H, Amos CI, Shete S, Makan N, Hong WK (2002) P53 genotypes and haplotypes associated with lung cancer susceptibility and ethnicity. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:681–690
Zehbe I, Voglino G, Wilander E, Delius H, Marongiu A, Edler L (2001) p53 codon 72 polymorphism and various human papillomavirus 16 E6 genotypes are risk factors for cervical References cancer development. Cancer Res 61:608–611
Zhang JH, Li Y, Wang R, Wen DG, Wu ML, He M (2003) P53 gene polymorphism with susceptibility to esophageal cancer and lung cancer in Chinese population. Chin J Oncol 25:365–367
Zhang XM, Miao X, Guo Y, Tan W, Zhou Y, Sun T (2006) Genetic polymorphisms in cell cycle regulatory genes MDM2 and TP53 are associated with susceptibility to lung cancer. Hum Mutat 27:110–117
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from “Nature Science Foundation of Liuzhou, Guangxi, PR China” (20050336).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Dai, C. Mao and L. Jiang contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, S., Mao, C., Jiang, L. et al. P53 polymorphism and lung cancer susceptibility: a pooled analysis of 32 case–control studies. Hum Genet 125, 633–638 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-009-0664-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-009-0664-3