Abstract
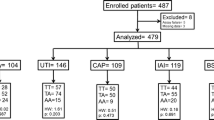
Meningococcal disease may present as sepsis, meningitis or a combination of both. Protein C (PC) is an important regulator of thrombin activity. Two polymorphisms in the promoter region of PC (C-1654T, A-1641G) have been shown to affect PC levels. In patients with meningococcal sepsis, low PC levels have been correlated with increased severity and poor outcome. We established a multicenter case–control study to determine whether PC promoter polymorphisms are associated with occurrence and outcome of meningococcal disease and sepsis. 288 previously healthy children with meningococcal infection from 97 pediatric hospitals in Germany, Switzerland, Italy, and Austria and 309 healthy controls were included in the study. A strong age-dependant effect was found. Patients younger than 1 year carried significantly more often the CG–CG genotype than healthy controls (28.6% vs. 17.8%, P = 0.04). Carriers of the CG allele showed a 3.43-fold increased odds ratio (OR) to develop sepsis (95% CI: 1.05–11.20; 85.7% vs. 63.6%, P = 0.036). The TA–TA genotype conferred a protective role for the development of sepsis (P = 0.017) with a Haldane OR of 0.09 (95% CI: 0.01–0.94). Systolic blood pressure values were significantly decreased in patients carrying the CG–CG genotype (70 vs. 86 mmHg, P = 0.005), and the need for adrenergic support significantly higher (70% vs. 26%, P = 0.018), resulting in an OR of 6.61 (95% CI: 1.28–34.14). These findings show that in young children PC promoter genotype is associated with susceptibility for meningococcal disease, the development of meningococcal sepsis, lower blood pressure, and need for adrenergic support.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PC:
-
Protein C
- APC:
-
Activated protein C
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- HWE:
-
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium
- CEMR:
-
Central European Meningococcal Research
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
References
Achtmann M (1995) Global epidemiology of meningococcal disease. In: Cartwright K (ed) Meningococcal disease. Wiley, Chichester, pp 159–177
Aiach M, Nicaud V, Alhenc-Gelas M, Gandrille S, Arnaud E, Amiral J, Guize L, Fiessinger JN, Emmerich J (1999) Complex association of protein C gene promoter polymorphism with circulating protein C levels and thrombotic risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:1573–1576
Andrew M, Vegh P, Johnston M, Bowker J, Ofosu F, Mitchell L (1992) Maturation of the hemostatic system during childhood. Blood 80:1998–2005
Annane D, Bellissant E, Bollaert PE, Briegel J, Keh D, Kupfer Y (2004) Corticosteroids for severe sepsis and septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 329:480
Annane D, Bellissant E, Cavaillon JM (2005) Septic shock. Lancet 365:63–78
Bernard GR, Vincent JL, Laterre PF, LaRosa SP, Dhainaut JF, Lopez-Rodriguez A, Steingrub JS, Garber GE, Helterbrand JD, Ely EW, Fisher CJ Jr (2001) Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 344:699–709
Binder A (2006) Identification of genes for a complex trait: examples from hypertension. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 7:1–13
Brandtzaeg P, Sandset PM, Joo GB, Ovstebo R, Abildgaard U, Kierulf P (1989) The quantitative association of plasma endotoxin, antithrombin, protein C, extrinsic pathway inhibitor and fibrinopeptide A in systemic meningococcal disease. Thromb Res 55:459–470
Cheng T, Liu D, Griffin JH, Fernandez JA, Castellino F, Rosen ED, Fukudome K, Zlokovic BV (2003) Activated protein C blocks p53-mediated apoptosis in ischemic human brain endothelium and is neuroprotective. Nat Med 9:338–342
Conkling PR, Greenberg CS, Weinberg JB (1988) Tumor necrosis factor induces tissue factor-like activity in human leukemia cell line U937 and peripheral blood monocytes. Blood 72:128–133
Corrigan JJ Jr, Ray WL, May N (1968) Changes in the blood coagulation system associated with septicemia. N Engl J Med 279:851–856
Dahlback B, Villoutreix BO (2005) The anticoagulant protein C pathway. FEBS Lett 579:3310–3316
de Kleijn ED, de Groot R, Hack CE, Mulder PG, Engl W, Moritz B, Joosten KF, Hazelzet JA (2003) Activation of protein C following infusion of protein C concentrate in children with severe meningococcal sepsis and purpura fulminans: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study. Crit Care Med 31:1839–1847
Esmon CT (1989) The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem 264:4743–4746
Faust SN, Heyderman RS, Levin M (2001a) Coagulation in severe sepsis: a central role for thrombomodulin and activated protein C (discussion S67–S68). Crit Care Med 29:S62–S67
Faust SN, Levin M, Harrison OB, Goldin RD, Lockhart MS, Kondaveeti S, Laszik Z, Esmon CT, Heyderman RS (2001b) Dysfunction of endothelial protein C activation in severe meningococcal sepsis. N Engl J Med 345:408–416
Fijnvandraat K, Derkx B, Peters M, Bijlmer R, Sturk A, Prins MH, van Deventer SJ, ten Cate JW (1995) Coagulation activation and tissue necrosis in meningococcal septic shock: severely reduced protein C levels predict a high mortality. Thromb Haemost 73:15–20
Fisher CJ Jr, Yan SB (2000) Protein C levels as a prognostic indicator of outcome in sepsis and related diseases. Crit Care Med 28:S49–S56
Foster DC, Yoshitake S, Davie EW (1985) The nucleotide sequence of the gene for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4673–4677
Fourrier F, Lestavel P, Chopin C, Marey A, Goudemand J, Rime A, Mangalaboyi J (1990) Meningococcemia and purpura fulminans in adults: acute deficiencies of proteins C and S and early treatment with antithrombin III concentrates. Intensive Care Med 16:121–124
Geishofer G, Binder A, Muller M, Zohrer B, Resch B, Muller W, Faber J, Finn A, Endler G, Mannhalter C, Zenz W (2005) 4G/5G promoter polymorphism in the plasminogen-activator-inhibitor-1 gene in children with systemic meningococcaemia. Eur J Pediatr 164:486–490
Gregory SA, Morrissey JH, Edgington TS (1989) Regulation of tissue factor gene expression in the monocyte procoagulant response to endotoxin. Mol Cell Biol 9:2752–2755
Guo H, Liu D, Gelbard H, Cheng T, Insalaco R, Fernandez JA, Griffin JH, Zlokovic BV (2004) Activated protein C prevents neuronal apoptosis via protease activated receptors 1 and 3. Neuron 41:563–572
Haralambous E, Weiss HA, Radalowicz A, Hibberd ML, Booy R, Levin M (2003) Sibling familial risk ratio of meningococcal disease in UK Caucasians. Epidemiol Infect 130:413–418
Hesselvik JF, Malm J, Dahlback B, Blomback M (1991) Protein C, protein S and C4b-binding protein in severe infection and septic shock. Thromb Haemost 65:126–129
Heyderman RS, Klein NJ, Shennan GI, Levin M (1991) Deficiency of prostacyclin production in meningococcal shock. Arch Dis Child 66:1296–1299
Kalil AC, Coyle SM, Um JY, LaRosa SP, Turlo MA, Calvano SE, Sundin DP, Nelson DR, Lowry SF (2004) Effects of drotrecogin alfa (activated) in human endotoxemia. Shock 21:222–229
Kato A, Miura O, Sumi Y, Aoki N (1988) Assignment of the human protein C gene (PROC) to chromosome region 2q14–q21 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 47:46–47
Leclerc F, Hazelzet J, Jude B, Hofhuis W, Hue V, Martinot A, Van der Voort E (1992) Protein C and S deficiency in severe infectious purpura of children: a collaborative study of 40 cases. Intensive Care Med 18:202–205
Lorente JA, Garcia-Frade LJ, Landin L, de Pablo R, Torrado C, Renes E, Garcia-Avello A (1993) Time course of hemostatic abnormalities in sepsis and its relation to outcome. Chest 103:1536–1542
Macias WL, Yan SB, Williams MD, Um SL, Sandusky GE, Ballard DW, Planquois JM (2005) New insights into the protein C pathway: potential implications for the biological activities of drotrecogin alfa (activated). Crit Care 9(Suppl 4):S38–S45
Mackman N (1995) Regulation of the tissue factor gene. Faseb J 9:883–889
Moore KL, Andreoli SP, Esmon NL, Esmon CT, Bang NU (1987) Endotoxin enhances tissue factor and suppresses thrombomodulin expression of human vascular endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest 79:124–130
Patracchini P, Aiello V, Palazzi P, Calzolari E, Bernardi F (1989) Sublocalization of the human protein C gene on chromosome 2q13–q14. Hum Genet 81:191–192
Powars DR, Rogers ZR, Patch MJ, McGehee WG, Francis RBJ (1987) Purpura fulminans in meningococcemia: association with acquired deficiencies of proteins C and S. N Engl J Med 317:571–572
Saez-Llorens X, McCracken GH Jr (1993) Sepsis syndrome and septic shock in pediatrics: current concepts of terminology, pathophysiology, and management. J Pediatr 123:497–508
Scopes D, Berg LP, Krawczak M, Kakkar VV, Cooper DN (1995) Polymorphic variation in the human protein C (PROC) gene promoter can influence transcriptional efficiency in vitro. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 6:317–321
Shibata M, Kumar SR, Amar A, Fernandez JA, Hofman F, Griffin JH, Zlokovic BV (2001) Anti-inflammatory, antithrombotic, and neuroprotective effects of activated protein C in a murine model of focal ischemic stroke. Circulation 103:1799–1805
Sorensen TI, Nielsen GG, Andersen PK, Teasdale TW (1988) Genetic and environmental influences on premature death in adult adoptees. N Engl J Med 318:727–732
Spek CA, Poort SR, Bertina RM, Reitsma PH (1994) Determination of the allelic and haplotype frequencies of three polymorphisms in the promoter region of the human protein C gene. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 5:309–311
Spek CA, Greengard JS, Griffin JH, Bertina RM, Reitsma PH (1995a) Two mutations in the promoter region of the human protein C gene both cause type I protein C deficiency by disruption of two HNF-3 binding sites. J Biol Chem 270:24216–24221
Spek CA, Koster T, Rosendaal FR, Bertina RM, Reitsma PH (1995b) Genotypic variation in the promoter region of the protein C gene is associated with plasma protein C levels and thrombotic risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 15:214–218
Taylor FB Jr, Chang A, Esmon CT, D’Angelo A, Vigano-D’Angelo S, Blick KE (1987) Protein C prevents the coagulopathic and lethal effects of Escherichia coli infusion in the baboon. J Clin Invest 79:918–925
Taylor FB Jr, Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Kurosawa S, Ferrell G, Chang AC, Laszik Z, Kosanke S, Peer G, Esmon CT (2000) The endothelial cell protein C receptor aids in host defense against Escherichia coli sepsis. Blood 95:1680–1686
Texereau J, Pene F, Chiche JD, Rousseau C, Mira JP (2004) Importance of hemostatic gene polymorphisms for susceptibility to and outcome of severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 32:S313–S319
Toews WH, Bass JW (1974) Skin manifestations of meningococcal infection; an immediate indicator of prognosis. Am J Dis Child 127:173–176
van Teunenbroek A, Peters M, Sturk A, Borm JJ, Breederveld C (1990) Protein C activity and antigen levels in childhood. Eur J Pediatr 149:774–778
Vincent JL, Angus DC, Artigas A, Kalil A, Basson BR, Jamal HH, Johnson G 3rd, Bernard GR (2003) Effects of drotrecogin alfa (activated) on organ dysfunction in the PROWESS trial. Crit Care Med 31:834–840
Walker FJ (1981) Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem 256:11128–11131
Walley KR, Russell JA (2007) Protein C -1641 AA is associated with decreased survival and more organ dysfunction in severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 35:12–17
Westendorp RG, Reitsma PH, Bertina RM (1996) Inherited prethrombotic disorders and infectious purpura. Thromb Haemost 75:899–901
Zenz W, Zoehrer B, Levin M, Fanconi S, Hatzis TD, Knight G, Müllner M, Faust SN (2004) Use of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in children with meningococcal purpura fulminans: a retrospective study. Crit Care Med 32:1777–1780
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding Sources: This study was supported by the Jubiläumsfond der Österreichischen Nationalbank, grant 8842 and 10112.
Additional Investigators Participating in the Central European Meningococcal Study Group
Additional Investigators Participating in the Central European Meningococcal Study Group
Bärbel Töpke (Ostalb-Klinikum, Aalen, Austria), Peter Fucik (Krankenhaus Amstetten, Amstetten, Austria), Johann M. Penzien (Zentralklinikum Kinderkliniken, Augsburg, Germany), Gedeon Diab (Kreiskrankenhaus Bad Hersfeld, Bad Hersfeld, Germany), Robert Miething (Diakonie-Krankenhaus, Bad Kreuznach, Germany), K.H. Deeg (Klinikum Bamberg, Bamberg, Germany), Jürg Hammer (Universitäts-Kinderspital beider Basel, Pädiatrische Intensivmedizin, Basel, Switzerland), Ulrich Heininger (Universitäts-Kinderspital beider Basel, Abt für Infektiologie, Basel, Switzerland), Verena Varnholt (Uni-Klinikum Charité, Campus Virchow Klinikum, Berlin, Germany), Andreas Schmidt (St.-Agnes-Hospital, Bocholt, Germany), Lutz Bindl (Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität, Bonn, Germany), Ursula Sillaber (Landeskrankenhaus Bregenz, Abt für Innere Medizin, Bregenz, Austria), Christian Huemer (Landeskrankenhaus Bregenz, Abt für Kinderheilkunde, Bregenz, Austria), Primrose Meier (Zentralkrankenhaus Links d. Weser, Bremen, Germany), G. Simic-Schleicher (Zentralkrankenhaus Bremen-Nord, Bremen, Germany), Markus Markart (Ospedale di Bressanone, Brixen, Italy), Eberhard Pfau (DRK-Krankenhaus Chemnitz-Rabenstein, Chemnitz, Germany), Hans Broede (Klinikum Lippe-Detmold GmbH, Detmold, Germany), Bernd Ausserer (Krankenhaus Dornbirn, Dornbirn, Austria), Hermann Kalhoff (Städt. Kliniken Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany), Volker Arpe (St. Marien-Hospital Düren-Birkesdorf, Düren, Germany), Susanne Schweitzer-Krantz (Evangelisches Krankenhaus, Düsseldorf, Germany), Johannes-Martin Kasper (St. Georg Klinikum Eisenach gGmbH, Eisenach, Germany), Kathrin Loranth (Krankenhaus der Barmherzigen Brüder, Eisenstadt, Austria), Hans J. Bittrich (Helios Klinikum Erfurt, Erfurt, Germany), Burkhard Simmer (Landeskrankenhaus Feldkirch, Feldkirch, Austria), Nicola Weigand (Klinikum Justus-Liebig-Uni-O, Gießen, Germany), Egbert Herting (Georg-August Universitäts-Kinderklinik, Göttingen, Germany), Karl-Heinz Smolle (Medizinische Universitätsklinik, Graz, Austria), Regina Grube (Neurologische Universitätsklinik, Graz, Austria), Christoph Fusch (Klinikum d. Ernst-Moritz-Arndt- Universität, Greifswald, Germany), Alois Gruber (Krankenhaus der Schulschwestern Grieskirchen, Grieskirchen, Austria), Ulf Schimmel (Allg. Krankenhaus Hagen GmbH, Hagen, Germany), Suzanne Knaufer-Schiefer (Ohrekreis-Klinikum, Haldensleben, Germany), Wolfgang Lässig (Städt. Krankenhaus Martha-Maria Halle-Dölau gGmbH, Halle, Germany), Axel Hennenberger (Kinderkrankenhaus Wilhelmstift, Hamburg, Germany), Axel von der Wense (Altonaer Kinderkrankenhaus, Hamburg, Germany), Roland Tillmann (Klinikum Kreis Herford, Herford, Germany), Jürgen Schwarick (Kreiskrankenhaus Herzberg, Herzberg, Germany), F.C. Sitzmann (Univ. Klinik für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin, Homburg/Saar, Germany), Herbert Müller (Klinik Robert-Weixler-Strasse, Kempten, Germany), Peter Kurnik (Landeskrankenhaus Klagenfurt, Klagenfurt, Austria), Peter Groneck (Kinderklinik der Stadt Köln, Köln, Germany), Helene Gröblacher-Roth (Landeskrankenhaus Krems a. d. Donau, Krems a.d. Donau, Austria), Jürgen Bensch (Vinzentius-Krankenhaus, Landau, Germany), Reinhard Moser (Landeskrankenhaus Leoben, Leoben, Austria), Rudolf Schwarz (Landes-Kinderklinik Linz, Linz, Austria), Kurt Lenz (Koventhospital der Barmherzigen Brüder, Linz, Austria), Thomas Hofmann (Evang. Krankenhaus, Lippstadt, Germany), Wolfgang Göpel (Med. Universität zu Lübeck, Lübeck, Germany), Thomas Berger (Kantonspital Luzern, Luzern, Switzerland), Erwin Hauser (Landeskrankenhaus Mödling, Mödling, Austria), Kai Martin Förster (Städt. Krankenhaus Harlaching, München, Germany), Jochen Peters (Kinderklinik der TU München, München, Germany), Thomas Nicolai (Klinikum Innenstadt v. Haunersches Kinderspital, München, Germany), Björn Kumlien (Kinderklinik des Dritten Ordens, München, Germany), Regina Beckmann (Dietrich-Bonhoeffer-Klinikum, Neubrandenburg, Germany), Christiane Seitz (FEK-Friedrich-Ebert-Krankenh. Neumünster GmbH, Neumünster, Germany), D. Hüseman (Ruppiner Kliniken GmbH, Neuruppin, Germany), Roland Schürmann (Städt. Kliniken Neuss Lukaskrankenhaus GmbH, Neuss, Germany), Van-Hop Ta (Evang. Krankenhaus, Oberhausen, Germany), Eckart Weikmann (Landeskrankenhaus Oberwart, Oberwart, Austria), W. Evert (Städt. Kliniken Offenbach, Offenbach, Germany), Jürgen Hautz (Klinikum Offenburg, Offenburg, Germany), Jürgen Seidenberg (Elisabeth-Kinderkrankenhaus, Oldenburg, Germany), Lucia Wocko (Krankenhaus Oranienburg, Oranienburg, Germany), Petra Luigs (St.Vincenz-Krankenhaus Frauen-u. Kinderklinik, Paderborn, Germany), Hans-Ludwig Reiter (Klinik für Kinder und Jugendliche am Städtischen Klinikum, Pforzheim, Germany), J. Quietzach (Vogtland-Klinikum Plauen GmbH, Plauen, Germany), Michael König (Oberschwaben Klinik gGmbH, Ravensburg, Germany), Johanna Herrmann (Kreiskrankenhaus Rendsburg, Rendsburg, Germany), Horst Mitter (Krankenhaus der Barmh. Schwestern Ried, Ried i. Innkreis, Austria), Ekkehard Seidler (Kreiskrankenhaus Obergöltzsch-Rodewisch, Rodewisch, Germany), Bernhard Maak (Thüringen-Klinik “Georgius Agricola” gGmbH, Saalfeld, Germany), Wolfgang Sperl (Landeskrankenanstalten Salzburg, Salzburg, Austria), Manfred Meissl (Landeskrankenhaus Schärding, Schärding, Austria), Reinhard Koch (Leopoldina-Krankenhaus, Schweinfurt, Germany), Manfred Cremer (DRK-Kinderklinik Siegen, Siegen, Germany), H.A. Breuer (Städt. Klinikum Solingen, Solingen, Germany), W. Görke (Johanniter Kinderklinik, Stendal, Germany), Robert Nossal (Olga Hospital Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany), Walter Pernice (Kreiskrankenhaus Torgau, Torgau, Germany), Ralf Brangenberg (Klinikum Traunstein, Traunstein, Germany), Hans R. Salzer (Landeskrankenhaus Tulln, Tulln, Austria), Hartmut Koch (St. Marien-Hospital, Vechta, Germany), Gerhard Schaller (Landeskrankenhaus Villach, Villach, Austria), Franz Paky (Landeskrankenhaus Vöcklabruck, Vöcklabruck, Austria), Friedrich Straßer (Klinikum Weiden, Weiden, Germany), Franz Eitelberger (Krankenhaus d. Barmh. Schwestern v. heiligen Kreuz, Wels, Austria), D. Sontheimer (Harz-Klinikum Wernigerode GmbH, Wernigerode, Germany), Andreas Lischka (Wilhelminenspital Wien, Wien, Austria), Alfred Dilch (Gottfried von Preyersches Kinderspital der Stadt Wien, Wien, Austria), Christian Scheibenpflug (Donauspital im SMZ-Ost der Stadt Wien, Wien, Austria), Robert Bruckner (Krankenhaus Wiener Neustadt, Wiener Neustadt, Austria), Klaus Runge (Zentrum für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin, Wuppertal, Germany), Wolfgang Kunze (Krankenhaus Muldentalkreis Wurzen, Wurzen, Germany), Peter Schermann (Krankenhaus Zwettl, Zwettl, Austria).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binder, A., Endler, G., Rieger, S. et al. Protein C promoter polymorphisms associate with sepsis in children with systemic meningococcemia. Hum Genet 122, 183–190 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0392-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0392-5