Abstract.
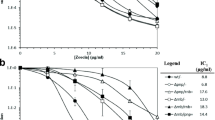
DNA polymerase IV (pol IV) in Escherichia coli is a member of a novel family of DNA polymerases (the DinB/UmuC/Rad30/Rev1 super-family or the DNA polymerase Y family). Although expression of the dinB gene encoding DNA pol IV is known to result in an enhancement of untargeted mutagenesis, it remains uncertain whether DNA pol IV is involved in a variety of lesion-induced mutagenesis (targeted mutagenesis), and the relationship between expression levels of dinB and the mutagenesis that DNA pol IV promotes has not been investigated thoroughly. Here, we report that DNA pol IV is involved in –1 frameshift mutagenesis induced by 4-nitroquinoline N-oxide (4-NQO) and that the expression level of the chromosomal pol IV gene is 6–12 times higher than those for other SOS-inducible DNA polymerases in E. coli, i.e., DNA pol II (PolB) or DNA pol V (UmuDC), respectively. Interestingly, the dinB gene is present not only on the chromosome but also on the F' plasmid in the E. coli CC108 strain. In this strain, 750 molecules of DNA pol IV are expressed from the F' dinB gene in the uninduced state and 250 molecules are expressed from the chromosomal gene. These cellular expression levels strongly affect –1 frameshifts induced by 4-NQO in runs of six guanine bases: mutagenicity was highest in the strain CC108, followed by strains YG2242 (chromosome ΔdinB/F' dinB +), YG2247 (chromosome dinB +/F' ΔdinB) and FC1243 (chromosome ΔdinB/F' ΔdinB). The incidence of untargeted –1 frameshifts was reduced by two-thirds on deletion of dinB from the F' episome. The chromosomal dinB gene appeared to have little or no effect on the untargeted mutagenesis. These results suggest that DNA pol IV efficiently mediates targeted mutagenesis by 4-NQO, and that the cellular levels of expression substantially affect targeted and untargeted mutagenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, .SR., Matsui, .K., Yamada, .M. et al. Roles of chromosomal and episomal dinB genes encoding DNA pol IV in targeted and untargeted mutagenesis in Escherichia coli . Mol Gen Genomics 266, 207–215 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380100541
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380100541