Abstract
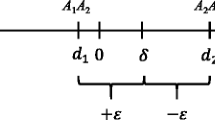
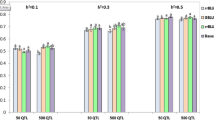
This study aimed to determine the effect of different rates of marker genotyping error on the accuracy of genomic prediction that was examined under distinct marker and quantitative trait loci (QTL) densities and different heritability estimates using a stochastic simulation approach. For each scenario of simulation, a reference population with phenotypic and genotypic records and a validation population with only genotypic records were considered. Marker effects were estimated in the reference population, and then their genotypic records were used to predict genomic breeding values in the validation population. The prediction accuracy was calculated as the correlation between estimated and true breeding values. The prediction bias was examined by computing the regression of true genomic breeding value on estimated genomic breeding value. The accuracy of the genomic evaluation was the highest in a scenario with no marker genotyping error and varied from 0.731 to 0.934. The accuracy of the genomic evaluation was the lowest in a scenario with marker genotyping error equal to 20% and changed from 0.517 to 0.762. The unbiased regression coefficients of true genomic breeding value on estimated genomic breeding value were obtained in the reference and validation populations when the rate of marker genotyping error was equal to zero. The results showed that marker genotyping error can reduce the accuracy of genomic evaluations. Moreover, marker genotyping error can provide biased estimates of genomic breeding values. Therefore, for obtaining accurate results it is recommended to minimize the marker genotyping errors to zero in genomic evaluation programs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cardon LR (2001) The impact of genotyping error on family-based analysis of quantitative traits. Eur J Hum Genet 9:130–134
Akey JM, Zhang K, Xiong M, Doris P, Jin L (2001) The effect that genotyping errors have on the robustness of common linkage-disequilibrium measures. Am J Human Genet 68:1447–1456
Atefi A, Shadparvar AA, Ghavi Hossein-Zadeh N (2016) Comparison of whole genome prediction accuracy across generations using parametric and semi parametric methods. Acta Sci Anim Sci 38(4):447–453
Barría A, Christensen KA, Yoshida G, Jedlicki A, Leong JS, Rondeau EB, Lhorente JP, Koop BF, Davidson WS, Yáñez JM (2019) Whole genome linkage disequilibrium and effective population size in a Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) breeding population using a high-density SNP array. Front Genet 10:498
Bonin A, Bellemain E, Bronken Eidesen P, Pompanon F, Brochmann C, Taberlet P (2004) How to track and assess genotyping errors in population genetics studies. Mol Ecol 13:3261–3273
Brito FV, Neto JB, Sargolzaei M, Cobuci JA, Schenkel FS (2011) Accuracy of genomic selection in simulated populations mimicking the extent of linkage disequilibrium in beef cattle. BMC Genet 12(1):80
Buetow KH (1991) Influence of aberrant observations on high- resolution linkage analysis outcomes. Am J Hum Genet 49:985–994
Calus MPL, De Roos APW, Veerkamp RF (2008) Accuracy of genomic selection using different methods to define haplotypes. Genetics 178(1):553–561
Cheng KF, Chen JH (2007) A simple and robust TDT-type test against genotyping error with error rates varying across families. Hum Hered 64:114–122
Combs E, Bernardo R (2013) Accuracy of genomewide selection for different traits with constant population size, heritability, and number of markers. Plant Genome 6(1):1–7
Daetwyler HD, Villanueva B, Woolliams JA (2008) Accuracy of predicting the genetic risk of disease using a genome-wide approach. PLoS ONE 3(10):3395
Daetwyler HD, Pong-Wong R, Villanueva B, Woolliams JA (2010) The impact of genetic architecture on genome-wide evaluation methods. Genetics 185(3):1021–1031
Dakin EE, Avise JC (2004) Microsatellite null alleles in parentage analysis. Heredity 93:504–509
De los Campos G, Rodriguez PP (2014) BGLR: Bayesian Generalized Linear Regressionversion 1.0.3.Rpackage version 2.15.0.
Douglas JA, Boehnke M, Lange K (2000) A multipoint method for detecting genotyping errors and mutations in sibling-pair linkage data. Am J Hum Genet 66(4):1287–1297
Fu WX, Dekkers JCM, Lee WR, Abasht B (2015) Linkage disequilibrium in crossbred and pure line chickens. Genet Sel Evol 47.
Goddard M (2009) Genomic selection: prediction of accuracy and maximisation of long term response. Genetica 136(2):245–257
Goddard ME, Hayes BJ (2007) Genomic selection. J Anim Breed Genet 124(6):323–230
Goldstein DR, Zhao H, Speed TP (1997) The effects of genotyping errors and interference on estimation of genetic distance. Human Hered 47(2):86–100
Gordon D, Heath SC, Ott J (1999) True pedigree errors more frequent than apparent errors for single nucleotide polymorphisms. Hum Hered 49:65–70
Gorgani Firozjah N, Atashi H, Dadpasand M, Zamiri MJ (2014) Effect of marker density and trait heritability on the accuracy of genomic prediction over three generations. J Livest Sci Technol 2(2):53–58
Govindarajulu US, Spiegelman D, Miller KL, Kraft P (2006) Quantifying bias due to allele misclassification in case-control studies of haplotypes. Genet Epidemiol 30:590–601
Habier D, Fernando RL, Kizilkaya K, Garrick DJ (2011) Extension of the Bayesian alphabet for genomic selection. BMC Bioinform 12:186–193
Hackett CA, Broadfott LB (2003) Effects of genotyping errors, missing values and segregation distortion in molecular marker data on the construction of linkage maps. Heredity 90:33–38
Hao K, Li C, Rosenow C, Wong WH (2004) Estimation of genotype error rate using samples with pedigree information—an application on the GeneChip Mapping 10K array. Genomics 84:623–630
Hayes BJ, Bowman PJ, Chamberlain AJ, Goddard ME (2009) Invited review: genomic selection in dairy cattle: progress and challenges. J Dairy Sci 92:433–443
Hill WG, Robertson A (1968) Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theoret Appl Genet 38:226–231
Hoerl AE, Kennard RW (1970) Ridge regression: biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 12(1):55–67
Howard R, Carriquiry AL, Beavis WD (2014) Parametric and nonparametric statistical methods for genomic selection of traits with additive and epistatic genetic architectures. G3: Genes Genom Genet 4(6):1027–1046
Kijas J, Elliot N, Kube P, Evans B, Botwright N, King H, Primmer CR, Verbyla K (2017) Diversity and linkage disequilibrium in farmed tasmanian atlantic salmon. Anim Genet 48:237–241
Kirk KM, Cardon LR (2002) The impact of genotyping error on haplotype reconstruction and frequency estimation. Eur J Hum Genet 10:616–622
Kolbehdari D, Schaeffer LR, Robinson JAB (2007) Estimation of genome wide haplotype effects in half-sib designs. J Anim Breed Genet 124(6):356–361
Lee SH, Cho YM, Lim D, Kim HC, Choi BH, Park HS, Kim OH, Kim S, Kim TH, Yoon D, Hong SK (2011) Linkage disequilibrium and efective population size in Hanwoo Korean cattle. Asian Aust J Anim Sci 24(12):1660–1665
Marquard V, Beckmann L, Heid IM, Claudia L, Chang-Claude J (2009) Impact of genotyping errors on the type I error rate and the power of haplotype-based association methods. BMC Genet 10:3
Meuwissen THE, Hayes BJ, Goddard M (2001) Prediction of total genetic value using genome-wide dense marker maps. Genetics 157(4):1819–1829
Piyasatian N, Dekkers J (2013) Accuracy of genomic Prediction when accounting for population structure and polygenic effects. Anim Indust Rep 659(1):68
Pompanon F, Bonin A, Bellemain E, Taberlet P (2005) Genotyping errors: causes, consequences and solutions. Nat Rev Genet 6:847–859
Sargolzaei M, Schenkel FS (2009) QMSim: a largescale genome simulator for livestock. Bioinformatics 25(5):680–681
Sargolzaei M., Schenkel FS (2013) QMSim user’s guide. Version. 1.10. Univ. Gulph, Canada.
Saunders IW, Brohede J, Hannan GN (2007) Estimating genotyping error rates from Mendelian errors in SNP array genotypes and their impact on inference. Genomics 90:291–296
Saura M, Tenesa A, Woolliams JA, Fernández A, Villanueva B (2015) Evaluation of the linkage-disequilibrium method for the estimation of effective population size when generations overlap: an empirical case. BMC Genom 16:922
Seo D, Lee DH, Choi N, Sudrajad P, Lee S-H, Lee J-H (2018) Estimation of linkage disequilibrium and analysis of genetic diversity in Korean chicken lines. PLoS ONE 13(2):e0192063
Sobel E, Lange K (1993) Metropolis sampling in pedigree analysis. Stat Methods Med Res 2:263–282
Solberg TR, Sonesson AK, Woolliams JA, Meuwissen THE (2008) Genomic selection using different marker types and densities. J Anim Sci 86:2447–2454
Tong L, Ma W, Liu H, Yuan C, Zhou Y (2015) Simultaneous estimation of QTL effects and positions when using genotype data with errors. J Genet 94(1):27–34
VanRaden PM (2008) Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci 91:4414–4423
Visscher PM, Haley CS (1998) Strategies for marker-assisted selection in pig breeding programs. In: 6th World Congr Genet Appl Livest Prod 23:503–510.
Vos PG, Paulo MJ, Voorrips RE, Visser RGF, van Eck HJ, van Eeuwijk FA (2017) Evaluation of LD decay and various LD-decay estimators in simulated and SNP-array data of tetraploid potato. Theor Appl Genet 130:123–135
Zhu WS, Fung WK, Guo J (2007) Incorporating genotyping uncertainty in haplotype frequency estimation in pedigree studies. Hum Hered 64:172–181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbarpour, T., Ghavi Hossein-Zadeh, N. & Shadparvar, A.A. Marker genotyping error effects on genomic predictions under different genetic architectures. Mol Genet Genomics 296, 79–89 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01728-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01728-z