Abstract
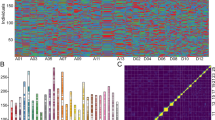
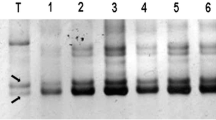
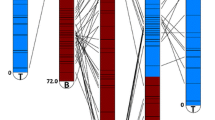
Fine mapping and positional cloning will eventually improve with the anchoring of additional markers derived from genomic clones such as BACs. From 2,603 new BAC-end genomic sequences from Gossypium hirsutum Acala ‘Maxxa’, 1,316 PCR primer pairs (designated as MUSB) were designed to flank microsatellite or simple sequence repeat motif sequences. Most (1164 or 88%) MUSB primer pairs successfully amplified DNA from three species of cotton with an average of three amplicons per marker and 365 markers (21%) were polymorphic between G. hirsutum and G. barbadense. An interspecific RIL population developed from the above two entries was used to map 433 marker loci and 46 linkage groups with a genetic distance of 2,126.3 cM covering approximately 45% of the cotton genome and an average distance between two loci of 4.9 cM. Based on genome-specific chromosomes identified in G. hirsutum tetraploid (A and D), 56.9% of the coverage was located on the A subgenome while 39.7% was assigned to the D subgenome in the genetic map, suggesting that the A subgenome may be more polymorphic and recombinationally active than originally thought. The linkage groups were assigned to 23 of the 26 chromosomes. This is the first genetic map in which the linkage groups A01 and A02/D03 have been assigned to specific chromosomes. In addition the MUSB-derived markers from BAC-end sequences markers allows fine genetic and QTL mapping of important traits and for the first time provides reconciliation of the genetic and physical maps. Limited QTL analyses suggested that loci on chromosomes 2, 3, 12, 15 and 18 may affect variation in fiber quality traits. The original BAC clones containing the newly mapped MUSB that tag the QTLs provide critical DNA regions for the discovery of gene sequences involved in biological processes such as fiber development and pest resistance in cotton.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Meyers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Anderson CG (1999) Cotton marketing. In: Smith CW, Cothren JT (eds) Cotton; origin, history, technology, and production. Wiley, New York, pp 659–679
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage map. Genome 36:181–186
Arpat AB, Waugh M, Sullivan JP, Gonzales M, Frisch D, Main D, Wood T, Leslie A, Wing RA, Wilkins TA (2004) Functional genomics of cell elongation in developing cotton fibers. Plant Mol Biol 54:911–929
Boissinot S, Entezam A, Young L, Munson PJ, Furano AV (2004) The insertional history of an active family of L1 retrotransposons in humans. Genome Res 14:1221–1231
Bolek Y, Kamal M El-Zik, Pepper AE, Bell AA, Magill CW, Thaxton PM, Reddy OUK (2005) Mapping of verticillium wilt resistance genes in cotton. Plant Sci 168:1581–1590
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Brubaker CL, Paterson AH, Wendell JF (1999) Comparative genetic mapping of allotetraploid cotton and its diploid progenitors. Genome 42:184–203
Cardle L, Ramsay L, Milbourne D, Macaulay M, Marshall D, Waugh R (2000) Computational and experimental characterization of physically clustered simple sequence repeats in plants. Genetics 156:847–854
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative traits mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
De Kock MJD, Brandwagt BF, Bonnema G, de Wit PJGM, Lindhout P (2005) The tomato Orion locus comprises a unique class of Hcr9 genes. Mol Breed 15:409–422
Fryxell PA (1992) A revised taxonomic interpretation of Gossypium L. (Malvaceae). Rheedea 2:108–165
Gill KS, Bill BS, Endo TR, Taylor T (1996) Identification and high density mapping of gene-rich regions in chromosome group 1 of wheat. Genetics 144:1883–1891
Gonzalez J, Nefedov M, Bosdet I, Casals F, Calvete O, Delprat A, Shin H, Readman C, Mathewson C, Wye N, Hoskins RA, Schein JE, deJong P, Ruiz A (2005) A BAC-based physical map of the Drosophila buzzatii genome. Genome Res 15:885–892
Gregory SR, Hernandez E, Savoy BR (1999) Cottonseed processing. In: Smith CW, Cothren JT (eds) Cotton; origin, history, technology, and production. Wiley, New York, pp 793–823
Gupta PK, Balyan HS, Sharma PC, Ramesh B (1996) Microsatellites in plants: a new class of molecular markers. Current Sci 70:45–53
Han Z, Guo W, Song X, Zhang T (2004) Genetic mapping of EST-derived microsatellites from the diploid Gossypium arboreum in allotetraploid cotton. Mol Genet Genomics 272:308–327
Hof JV, Saha S (1997) Cotton fibers can undergo cell division. Am J Bot 84(9):1231–1235
Hong CP, Lee SJ, Park JY, Plaha P, Park YS, Lee YK, Choi JE, Kim KY, Lee JH, Lee J, Jin H, Choi SR, Lim YP (2004) Construction of a BAC library of Korean ginseng and initial analysis of BAC-end sequences. Mol Genet Genomics 271:709–716
Islam-Faradi MN, Childs KL, Klein PE, Hodnett G, Menz MA, Klein RR, Rooney WL, Mullet JE, Stelly DM (2002) A molecular cytogenetic map of sorghum chromosome 1. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis with mapped bacterial artificial chromosomes. Genetics 161:345–353
Jiang C, Wright RJ, El-Zik KM, Paterson AH (1998) Polyploid formation created unique avenues for response to selection in Gossypium (cotton). Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:4419–4424
Kalendar R (2005) FastPCR: a PCR primer design and repeat sequence searching software with additional tools for the manipulation and analysis of DNA and protein (http://www.biocenter.helsinki.fi/bi/programs/fastpcr.htm)
Kilian A, Chen J, Han F, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (1997) Towards map-based cloning of the barley stem rust resistance genes Rpg1 and rpg4 using rice as an intergenomic cloning vehicle. Plant Mol Biol 35:187–195
Kim HJ, Triplett BA (2001) Cotton fiber growth in planta and in vitro. Models for plant cell elongation and cell wall biogenesis. Plant Phys 127:1361–1366
Kim J-S, Klein PE, Klein RR, Price HJ, Mullet JE, Stelly DM (2005) Molecular cytogenetic maps of Sorghum linkage groups 2 and 8. Genetics 169:955–965
Kohel RJ, Yu J, Park Y-H, Lazo GR (2001) Molecular mapping and characterization of traits controlling fiber quality in cotton. Euphytica 121:163–172
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lacape J-M, Nguyen T-B (2005) Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with leaf and stem pubescence in cotton. J Hered 96(4):441–444
Lacape J-M, Nguyen T-B, Thibivilliers S, Bojinov B, Courtois B, Cantrell RG (2003) A combined RFLP-SSR-AFLP map of tetraploid cotton based on a Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense backcross population. Genome 46:612–626
La Rota M, Kantety RV, Yu J-K, Sorrells ME (2005) Nonrandom distribution and frequencies of genomic and EST-derived microsatellites markers in rice, wheat, and barley. BMC Genomics 6:23 (http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2164/6/23) DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-23
Lin Z, He D, Zhang X, Nie Y, Guo X, Feng C, Stewart J McD (2005) Linkage map construction and mapping QTL for cotton fibre quality using SRAP, SSR and RAPD. Plant Breed 124:180–187
Liu S, Saha S, Stelly D, Burr B, Cantrell RG (2000) Chromosomal assignment of microsatellite loci in cotton. J Hered 91:326–332
Ma J, Devos KM, Bennetzen JL (2004) Analyses of LTR-retrotransposon structures reveal recent and rapid genomic DNA loss in rice. Genome Res 14:860–869
Mao L, Wood TC, Yu Y, Budiman MA, Tomkins J, Woo S, Sasinowski M, Presting G, Frisch D, Goff S, Dean RA, Wing RA (2000) Rice transposable elements: a survey of 73,000 sequence-tagged-connectors. Genome Res 10:982–990
Mei M, Syed NH, Gao W, Thaxton PM, Smith CW, Stelly DM, Chen ZJ (2004) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis of fiber-related traits in cotton (Gossypium). Theor Appl Genet 108:280–291
Metzgar D, Bytof J, Wills C (2000) Selection against frameshift mutation limits microsatellite expansion in coding DNA. Genome Res 10:72–80
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002) Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nature Genet 30:194–200
Nievergelt CM, Smith DW, Kohlenberg JB, Schork NJ (2004) Large-scale integration of human genetic and physical maps. Genome Res 14:1199–1205
Nguyen TB, Giband M, Brottier P, Risterucci A-M, Lacape J-M (2004) Wide coverage of the tetraploid cotton genome using newly developed microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:167–175
Palmer MB, Main D, Frelichowski JE, Tomkins JP, Ulloa M (2004) High-throughput development of new molecular markers for cotton. National Cotton Council Beltwide Cotton Conference p 1131
Park Y-H, Alabady MS, Ulloa M, Sickler B, Wilkins TA, Yu J, Stelly DM, Kohel RJ, El-Shihy OM, Cantrell RG (2005) Genetic mapping of new cotton fiber loci using EST-derived microsatellites in an interspecific recombinant inbred (RIL) cotton population. Mol Genet Genomics 274:428–441
Paterson AH (2002) What has QTL mapping taught us about plant domestication. New Phytol 154:591–608
Percival AE, Wendel JF, Stewart JM (1999) Taxonomy and germplasm resources. In: Smith CW, Cothren JT (eds) Cotton; origin, history, technology, and production. Wiley, New York, pp 33–63
Petes TD (2001) Meiotic recombination hot spots and cold spots. Nat Rev Genet 2:360–369
Qureshi SN, Saha S, Kantety RV, Jenkins JN (2004) EST-SSR: a new class of genetic markers in cotton. J Cotton Sci 8:112–123
Reinisch A, Dong J-M, Brubaker C, Stelly D, Wendel J, Paterson AH (1994) A detailed RFLP map of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum × G. barbadense); chromosome organization and evolution in a disomic polyploid genome. Genetics 138:829–847
Rong J, Abbey C, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chang C, Chee PW, Delmonte TA, Ding X, Garza JJ, Marler BS, Park C, Pierce GJ, Rainey KM, Rastogi VK, Schulze SR, Trolinder NL, Wendel JF, Wilkins TA, Williams-Coplin TD, Wing RA, Wright RJ, Zhao X, Zhu L, Paterson AH (2004) A 3347-locus genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites reveals features of genome organization, transmission and evolution of cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 166:389–417
Rong J, Bowers JE, Schulze SR, Waghmare VN, Rogers CJ, Pierce GJ, Zhang H, Estill JC, Paterson AH (2005) Comparative genomics of Gossypium and Arabidopsis: unraveling the consequences of both ancient and recent polyploidy. Genome Res 15:1198–1210
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols, in the series methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, pp 365–386. Code available at http://www.fokker.wi.mit.edu/primer3/
Saha S, Karaca M, Jenkins JN, Zipf AE, Reddy OUK, Kantety RV (2003) Simple sequence repeats as useful resources to study transcribed genes of cotton. Euphytica 130:355–364
Shen X, Guo W, Zhu X, Yuan Y, Yu JZ, Kohel RJ, Zhang T (2005) Molecular mapping of QTLs for qualities in three diverse lines in Upland cotton using SSR markers 15:169–181
Shizuya H, Birren B, Kim UJ, Mancino V, Slepak T, Tachirii Y, Simon M (1992) Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:8794–8797
Song X, Wang K, Guo W, Zhang J, Zhang T (2005) A comparison of genetic maps constructed from haploid and BC1 mapping populations from the same crossing between Gossypium hirsutum L. and Gossypium barbadense L. Genome 48:378–390
Stam P, Van Ooijen JW (1995) JoinMap™ version 2.0: software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. CPRO-DLO, Wageningen
Stelly DM (1993) Interfacing cytogenetics with the cotton genome mapping effort. In: Herber DJ, Richter DA (eds) Beltwide Cotton Conference, January 10–14, 1993, New Orleans, LA. Memphis, TN: National Cotton Council of America; pp 1545–1550
Taliercio EW, Ulloa M (2003) The DNA sequence of a Gypsy element from Gossypium hirsutum L. and characterization of Gypsy elements in three Gossypium species. DNA sequence V 14(4):319–325
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Miller L, Paterson AH, Pineda O, Roeder MS, Wing RA, Wu W, Young ND (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Tautz D, Schotterer C (1994) Simple sequences. Curr Opin Genet 4:832–837
Tomkins JP, Peterson DG, Yang TJ, Main D, Wilkins TA, Paterson AH, Wing RA (2001) Development of genomic resources for cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.): BAC library construction, preliminary STC analysis, and identification of clones associated with fiber development. Mol Breed 8(3):255–261
Ulloa M, Meredith WR Jr (2000) Genetic linkage map and QTL analysis of agronomic and fiber quality traits in an intraspecific population. J Cotton Sci 4:161–170
Ulloa M, Meredith WR Jr, Shappley ZW, Kahler AL (2002) RFLP genetic linkage maps from F2.3 populations and a joinmap of Gossypium hirsutum L. Theor Appl Genet 104:200–208
Ulloa M, Stewart J McD, Garcia CE, Godoy AS, Gaytan-MA, Acosta-NS (2006) Cotton genetic resources in the western states of Mexico; In situ conservation status and germplasm collection for ex situ preservation. Genet Resour Crop Evol (in press). DOI 10.1007/s10722-004-2988-0
Ulloa M, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Meredith WR, McCarty JC, Stelly MD (2005) Chromosomal assignment of RFLP linkage groups harboring important QTLs on an intraspecific cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) joinmap. J Hered 96:132–144
Van Ooijen JW, Maliepaard C (1996) MapQTL™ Version 3.0, software for the calculation of QTL positions on genetic maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55
Wang S, Wang J-W, Yu N, Li C-H, Luo B, Gou J-Y, Wang L-J, Chen X-Y (2004) Control of plant trichome development by a cotton fiber MYB gene. The Plant Cell 16:2323–2334
Wang C, Ulloa M, Roberts PA (2005) Identification and mapping of microsatellite markers linked to the root-knot nematode resistance gene rkn1 in Acala NemX (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet (in press) DOI:10.1007/S00122-005-0183
Wilkins TA, Arpat AB (2005) The cotton fiber transcriptome. Physiologia Plantarum 124:295–300
Yu, J, Kohel RJ, Xu Z, Dong J, Zhang H, Stelly DM, Zhu Y, Covaleda L (2005) Physical mapping of fiber development genes in cotton [abstract]. Plant And Animal Genome XIII Conference p 225
Zaki EA, Ghany AAA (2004) Ty3/gypsy retro-transposons in Egyptian cotton (G. barbadense). J Cotton Sci 8:179–185
Zhao X, Si Y, Sason RE, Crane CF, Price HJ, Stelly DM, Wendell JF, Paterson AH (1998) Dispersed repetitive DNA has spread to new genomes since polyploidy formation in cotton. Genome Res 8:479–492
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge Cotton Inc. for its support on this project under a Cotton Incorporated Fellowship (Cary, NC) for James Frelichowski. The sequences of these markers are made public through the Cotton Microsatellite Database (CMD, http://www.mainlab.clemson.edu/cmd/projects/) as part of a community-wide initiative to increase coverage of the cotton genome. Names are necessary to report factually in available data; however, the USDA neither guarantees nor warrants the standard of products or service, and the use of the name by the USDA implies no approval of the products or service to the exclusion of others that may also be suitable. This research was supported in part, by Cotton Incorporated Project Number 05-704 (to MU) under the C.I. Fellowship program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frelichowski, J.E., Palmer, M.B., Main, D. et al. Cotton genome mapping with new microsatellites from Acala ‘Maxxa’ BAC-ends. Mol Genet Genomics 275, 479–491 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0106-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0106-z