Abstract
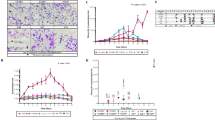
Fasciola hepatica are trematodes that reside in the bile ducts of mammals. Infection causes US$3 billion in losses annually in animal production and is considered a zoonosis of growing importance. An under-represented area in F. hepatica research has been the examination of the different immunomodulatory abilities of various parasite isolates on the host immune system. In this paper, this issue was explored, with the bovine macrophage cell line “BOMA”. The cells were matured by LPS treatment and stimulated with excretory/secretory antigens (ES) from two Fasciola hepatica isolates: a laboratory isolate “Weybridge” (Fh-WeyES) and a wild isolate (Fh-WildES). As expected, stimulation with antigen mixtures with highly similar compositions resulted in mild transcriptomic differences. However, there were significant differences in cytokine levels. Compared to Fh-WeyES, exposure to Fh-WildES upregulated 27 and downregulated 30 genes. Fh-ES from both isolates diminished the release of TNF-α, whereas only Fh-WildES decreased IL-10 secretion. Neither Fh-WeyES nor Fh-WildES had an impact on IL-12 release. Our results indicate that various isolates can have different immunomodulatory abilities and impacts on the bovine immune system.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bąska P, Zawistowska-Deniziak A, Zdziarska AM, Wasyl K, Wiśniewski M, Cywińska A, Klockiewicz M, Januszkiewicz K, Wędrychowicz H (2013) Fasciola hepatica—the pilot study of in vitro assessing immune response against native and recombinant antigens of the fluke. Acta Parasitol 58(4):453–462. doi:10.2478/s11686-013-0163-5
Bozinovski S, Jones J, Beavitt SJ, Cook AD, Hamilton JA, Anderson GP (2004) Innate immune responses to LPS in mouse lung are suppressed and reversed by neutralization of GM-CSF via repression of TLR-4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286(4):L877–L885
Brady MT, O'Neill SM, Dalton JP, Mills KH (1999) Fasciola hepatica suppresses a protective Th1 response against Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun 67:5372–5378
Brown WC, Woods VM, Chitko-McKown CG, Hash SM, Rice-Ficht AC (1994) Interleukin-10 is expressed by bovine type 1 helper, type 2 helper, and unrestricted parasite-specific T-cell clones and inhibits proliferation of all three subsets in an accessory-cell-dependent manner. Infect Immun 62(11):4697–4708
Cwiklinski K, O’Neill SM, Donnelly S, Dalton JP (2016) A prospective view of animal and human Fasciolosis. Parasite Immunol 38(9):558–568. doi:10.1111/pim.12343
Fairweather I (2011) Liver fluke isolates: a question of provenance. Vet Parasitol 6(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.12.011
Falcón C, Carranza F, Martínez FF, Knubel CP, Masih DT, Motrán CC, Cervi L (2010) Excretory-secretory products (ESP) from Fasciola hepatica induce tolerogenic properties in myeloid dendritic cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 137(1–2):36–46. doi:10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.04.007
Flynn RJ, Mulcahy G (2008a) The roles of IL-10 and TGF-beta in controlling IL-4 and IFN-gamma production during experimental Fasciola hepatica infection. Int J Parasitol 38(14):1673–1680. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2008.05.008
Flynn RJ, Mulcahy G (2008b) Possible role for toll-like receptors in interaction of Fasciola hepatica excretory/secretory products with bovine macrophages. Infect Immun 76(2):678–684
Flynn RJ, Mulcahy G, Welsh M, Cassidy JP, Corbett D, Milligan C, Andersen P, Strain S, McNair J (2009) Co-infection of cattle with Fasciola hepatica and Mycobacterium bovis—immunological consequences. Transbound Emerg Dis 56(6–7):269–274. doi:10.1111/j.1865-1682.2009.01075.x
Fu Y, Chryssafidis AL, Browne JA, O'Sullivan J, McGettigan PA, Mulcahy G (2016) Transcriptomic study on ovine immune responses to Fasciola hepatica infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10(9):e0005015. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0005015
Garza-Cuartero L, O'Sullivan J, Blanco A, McNair J, Welsh M, Flynn RJ, Williams D, Diggle P, Cassidy J, Mulcahy G (2016) Fasciola hepatica infection reduces Mycobacterium bovis burden and mycobacterial uptake and suppresses the pro-inflammatory response. Parasite Immunol 38(7):387–402. doi:10.1111/pim.12326
Gu H, Cui M, Bai Y, Chen F, Ma K, Zhou C, Guo L (2010) Angiopoietin-1/Tie2 signaling pathway inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 392(2):178–182. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.009
Guasconi L, Serradell MC, Garro AP, Iacobelli L, Masih DT (2011) C-type lectins on macrophages participate in the immunomodulatory response to Fasciola hepatica products. Immunology 133(3):386–396. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03449.x
Guasconi L, Serradell MC, Masih DT (2012) Fasciola hepatica products induce apoptosis of peritoneal macrophages. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 148(3–4):359–363. doi:10.1016/j.vetimm.2012.06.022
Haçariz O, Sayers G, Flynn RJ, Lejeune A, Mulcahy G (2009) IL-10 and TGF-beta1 are associated with variations in fluke burdens following experimental fasciolosis in sheep. Parasite Immunol 31(10):613–622. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01135.x
Hamilton CM, Dowling DJ, Loscher CE, Morphew RM, Brophy PM, O'Neill SM (2009) The Fasciola hepatica tegumental antigen suppresses dendritic cell maturation and function. Infect Immun 77(6):2488–2498. doi:10.1128/IAI.00919-08
Hill RD, Gouffon JS, Saxton AM, Su C (2012) Differential gene expression in mice infected with distinct Toxoplasma strains. Infect Immun 80(3):968–974. doi:10.1128/IAI.05421-11
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37(1):1–13
Januszkiewicz K, Norbury LJ, Wilkowski P, Zawistowska-Deniziak A, Wesołowska A, Wedrychowicz H (2015) Variations in cercarial production and the level of in vitro activation of metacercariae of two different isolates of Fasciola hepatica. Acta Parasitol 60(3):509–514. doi:10.1515/ap-2015-0072
Klementowicz JE, Travis MA, Grencis RK (2012) Trichuris muris: a model of gastrointestinal parasite infection. Semin Immunopathol 34(6):815–828. doi:10.1007/s00281-012-0348-2
Lu Y, Zhao X, Luo G, Shen G, Li K, Ren G, Pan Y, Wang X, Fan D (2015) Thioredoxin-like protein 2b facilitates colon cancer cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis via NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett 363(2):119–126. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.12.048
Lund ME, O'Brien BA, Hutchinson AT, Robinson MW, Simpson AM, Dalton JP, Donnelly S (2014) Secreted proteins from the helminth Fasciola hepatica inhibit the initiation of autoreactive T cell responses and prevent diabetes in the NOD mouse. PLoS One 9(1):e86289. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086289
Mi H, Poudel S, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT, Thomas PD (2016) PANTHER version 10: expanded protein families and functions, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D336–D342
Morrison LJ, McLellan S, Sweeney L, Chan CN, MacLeod A, Tait A, Turner CM (2010) Role for parasite genetic diversity in differential host responses to Trypanosoma brucei infection. Infect Immun 78(3):1096–1108. doi:10.1128/IAI.00943-09
Naranjo Lucena A, Garza Cuartero L, Mulcahy G, Zintl A (2017) The immunoregulatory effects of co-infection with Fasciola hepatica: from bovine tuberculosis to Johne’s disease. Vet J 222:9–16. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2017.02.007
Pannicke U, Baumann B, Fuchs S, Henneke P, Rensing-Ehl A, Rizzi M, Janda A, Hese K, Schlesier M, Holzmann K, Borte S, Laux C, Rump EM, Rosenberg A, Zelinski T, Schrezenmeier H, Wirth T, Ehl S, Schroeder ML, Schwarz K (2013) Deficiency of innate and acquired immunity caused by an IKBKB mutation. N Engl J Med 369(26):2504–2514. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1309199
Papavlassopoulos M, Stamme C, Thon L, Adam D, Hillemann D, Seydel U, Schromm AB (2006) MaxiK blockade selectively inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced I kappa B-alpha /NF-kappa B signaling pathway in macrophages. J Immunol 177(6):4086–4093
Risco AL, del Fresno C, Mambol A, Alsina-Beauchamp D, KF MK, Yang HT, Barber DF, Morcelle C, Arthur JS, Ley SC, Ardavin C, Cuenda A (2012) p38γ and p38δ kinases regulate the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-induced cytokine production by controlling ERK1/2 protein kinase pathway activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(28):11200–11205. doi:10.1073/pnas.1207290109
Rojas-Caraballo J, López-Abán J, Fernández-Soto P, Vicente B, Collía F, Muro A (2015) Gene expression profile in the liver of BALB/c mice infected with Fasciola hepatica. PLoS One 10(8):e0134910. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0134910
Scian R, Barrionuevo P, Giambartolomei GH, Fossati CA, Baldi PC, Delpino MV (2011) Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated matrix metalloproteinase production by human osteoblasts and monocytes after infection with Brucella abortus. Infect Immun 79(1):192–202. doi:10.1128/IAI.00934-10
Serradell MC, Guasconi L, Cervi L, Chiapello LS, Masih DT (2007) Excretory-secretory products from Fasciola hepatica induce eosinophil apoptosis by a caspase-dependent mechanism. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 117(3–4):197–208
Toet H, Piedrafita DM, Spithill TW (2014) Liver fluke vaccines in ruminants: strategies, progress and future opportunities. Int J Parasitol 15;44(12):915–927. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.07.011
Towne JE, Renshaw BR, Douangpanya J, Lipsky BP, Shen M, Gabel CA, Sims JE (2011) Interleukin-36 (IL-36) ligands require processing for full agonist (IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity. J Biol Chem 286(49):42594–42602. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.267922
Vukman KV, Adams PN, Metz M, Maurer M, O'Neill SM (2013) Fasciola hepatica tegumental coat impairs mast cells’ ability to drive Th1 immune responses. J Immunol 190(6):2873–2879. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203011
Walker SM, Hoey E, Fletcher H, Brennan G, Fairweather I, Trudgett A (2006) Stage-specific differences in fecundity over the life-cycle of two characterized isolates of the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 133(Pt 2):209–216
Walsh KP, Brady MT, Finlay CM, Boon L, Mills KH (2009) Infection with a helminth parasite attenuates autoimmunity through TGF-beta-mediated suppression of Th17 and Th1 responses. J Immunol 183(3):1577–1586. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803803
Wesołowska A, Jaros S, Norbury LJ, Jaros D, Zygner W, Wędrychowicz H (2013) Microarray analysis of rat immune responses to liver fluke infection following vaccination with Fasciola hepatica phosphoglycerate kinase. Exp Parasitol 134(1):33–38. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2013.01.013
Wu C, Yang Y, Ou J, Zhu L, Zhao W, Cui J (2016) LRRC14 attenuates toll-like receptor-mediated NF-κB signaling through disruption of IKK complex. Exp Cell Res 347(1):65–73. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.011
Yang Y, Kim SC, Yu T, Yi YS, Rhee MH, Sung GH, Yoo BC, Cho JY (2014) Functional roles of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. Mediat Inflamm 2014:352371. doi:10.1155/2014/352371
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Polish National Science Centre (Project no. N N304 156340). We are grateful to the Scientific Council of Białowieża National Park which gave us permission to collect biological material from bison from Białowieża National Park.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics statement
All experiments with animals followed institutional ethical guidelines and were approved by the Third Local Ethical Committee of Warsaw University of Life Sciences – SGGW (Permission no. 82/2010).
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bąska, P., Norbury, L.J., Zawistowska-Deniziak, A. et al. Excretory/secretory products from two Fasciola hepatica isolates induce different transcriptional changes and IL-10 release in LPS-activated bovine “BOMA” macrophages. Parasitol Res 116, 2775–2782 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5588-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5588-6