Abstract
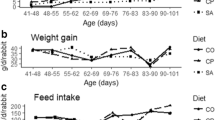
Recent research has suggested that plants containing condensed tannins may offer a promising alternative approach for the control of coccidiosis in lambs and goat kids. The present study aimed to examine the potential effect of condensed tannins in sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) and carob pods (Ceratonia siliqua) incorporated in sheep rations against lamb coccidiosis. The above tannin-rich sources were studied in three independent feeding trials in which the animals (naturally infected by Eimeria spp. ewes and their lambs) were allocated (i) in the control group and received a tannin-free diet (lucerne hay), or (ii) in the treatment groups and received a tannin-rich diet based on sainfoin hay (in trials 1 and 2), or in carob pod meal and a combination of carob pod meal and sainfoin hay (in trial 3). In total, 95 newborn lambs (and their 73 ewes) were enrolled in all trials which started a month before lambing and ended 8–10 weeks after lambs were born (at weaning). The course of coccidial infection was monitored in lambs by faecal oocyst counts and consistencies which were recorded at weekly intervals. Moreover, lambs total weight gain was evaluated at the end of each trial. During all trials, 100 % of the animals got naturally infected by Eimeria species and the infection burden was higher in trials 2 and 3 compared to trial 1 but in all cases, severe signs of diarrhoea were not observed. Tannin-rich diets were well accepted by the animals not affecting their feed intake and body weight gain when compared to the controls. The results suggest that incorporation of both tannin-rich resources (especially sainfoin) in sheep rations can reduce Eimeria oocyst excretion rates by the lambs, which can decrease subsequently the contamination of the farm environment with the parasite. However, the high variability noted on the results is not allowing us to draw any definite conclusions at least until the potential of those plants is further investigated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arroyo-Lopez C, Manolaraki F, Saratsis A, Saratsi K, Stefanakis A, Skampardonis V, Voutzourakis N, Hoste H, Sotiraki S (2014) Anthelmintic effect of carob pods and sainfoin hay when fed to lambs after experimental trickle infections with Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis. Parasite 21:71
Athanasiadou S, Kyriazakis I (2004) Plant secondary metabolites: antiparasitic effects and their role in ruminant production systems. Proc Nutr Soc 63(4):631–639
Bates D, Machler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67(1):1–48
Berriatua E, Green LE, Morgan KL (1994) A descriptive epidemiological study of coccidiosis in early lambing housed flocks. Vet Parasitol 54:337–351
Bretz F, Hothorn T, Westfall P (2010) Multiple comparisons using R. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Brunet S, Jackson F, Hoste H (2008) Effects of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) extract and monomers of condensed tannins on the association of abomasal nematode larvae with fundic explants. Int J Parasitol 38:783–790
Burke JM, Orlik S, Miller JE, Terrill TH, Mosjidis JA (2010) Using copper oxide wire particles or sericea lespedeza to prevent periparturient gastrointestinal nematode infection in sheep and goats. Livest Sci 132:13–18
Burke JM, Miller JE, Terrill TH, Orlik ST, Acharya M, Garza JJ, Mosjidis JA (2013) Sericea lespdeza as an aid in the control of Emeria spp. in lambs. Vet Parasitol 193:39–46
Chartier C, Paraud C (2012) Coccidiosis due to Eimeria in sheep and goats, a review. Small Rumin Res 103(1):84–92
Dakia PA, Wathelet B, Paquot M (2007) Isolation and chemical evaluation of carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) seed germ. Food Chem 102:1368–1374
Fraquelli C, Zanzani SA, Gazzonis AL, Rizzi R, Manfredi MT (2015) Effects of condensed tannin on natural coccidian infection in goat kids. Small Rumin Res 126(1):19–24
Frutos P, Moreno-Gonzalo J, Hervas G, García U, Ferreira LM, Celaya R, Toral PG, Ortega-Mora LM, Ferre I, Osoro K (2008) Is the anthelmintic effect of heather supplementation to grazing goats always accompanied by anti-nutritional effects? Animal 2:1449–1456
Gauly M, Reeg J, Bauer C, Erhardt G (2004) Influence of production systems in lambs on the Eimeria oocyst output and weight gain. Small Rumin Res 55:159–167
Gregory MW, Joyner LP, Catchpole J, Norton CC (1980) Ovine coccidiosis in England and Wales 1978–1979. Vet Rec 106:461–462
Hayot Carbonero C, Mueller-Harvey I, Brown TA, Smith L (2011) Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia): a beneficial forage legume. Plant Genet Resour 9:70–85
Heckendorn F, Haring DA, Maurer V, Zinsstag J, Langhans W, Hertzberg H (2006) Effect of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) silage and hay on established populations of Haemonchus contortus and Cooperia curticei in lambs. Vet Parasitol 142:293–300
Heckendorn F, Haring DA, Maurer V, Senn M, Hertzberg H (2007) Individual administration of three tanniferous forage plants to lambs artificially infected with Haemonchus contortus and Cooperia curticei. Vet Parasitol 146:123–134
Kommuru DS, Barker T, Desai S, Burke JM, Ramsay A, Mueller-Harvey I, Miller JE, Mosjidis JA, Kamisetti N, Terrill TH (2014) Use of pelleted sericea lespedeza (Lespedeza cuneata) for natural control of coccidia and gastrointestinal nematodes in weaned goats. Vet Parasitol 204:191–198
Kumazawa S, Taniguchi M, Suzuki Y, Shimura M, Kwon MS, Nakayama T (2002) Antioxidant activity of polyphenols in carob pods. J Agric Food Chem 50:373–377
Makris DP, Kefalas P (2004) Carob pods (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as a source of polyphenolic antioxidants. Food Technol Biotechnol 42(2):105–108
Manolaraki F, Sotiraki S, Stefanakis A, Skampardonis V, Volanis M, Hoste H (2010) Anthelmintic activity of some Mediterranean browse plants against parasitic nematodes. Parasitology 137:685–696
Markovics A, Cohen I, Muklada H, Glasser TA, Dvash L, Ungar ED, Azaizeh H, Landau SY (2012) Consumption of Pistacia lentiscus foliage alleviates coccidiosis in young goats. Vet Parasitol 186:165–169
Novobilsky A, Stringano E, Hayot Carbonero C, Smith LM, Enemark HL, Mueller-Harvey I, Thamsborg SM (2013) In vitro effects of extracts and purified tannins of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) against two cattle nematodes. Vet Parasitol 196:532–537
NRC (National Research Council) (2007) Nutrient requirements of small ruminants: sheep, goats, cervids, and new world camelids. The National Academies Press, Washington
Obeidat BS, Alrababah MA, Abdullah AY, Alhamad MN, Gharaibeh MA, Rababah TM, Abu Ishmais MA (2011) Growth performance and carcass characteristics of Awassi lambs fed diets containing carob pods (Ceratonia siliqua L.). Small Rumin Res 96:149–154
Obeidat BS, Alrababah MA, Alhamad MN, Gharaibeh MA, Ishmais MAA (2012) Effects of feeding carob pods (Ceratonia siliqua L.) on nursing performance of Awassi ewes and their lambs. Small Rumin Res 105:9–15
Papachristou TG, Dziba LE, Provenza FD (2005) Foraging ecology of goats and sheep on wooded rangelands. Small Rumin Res 59:141–156
Pinheiro JC, Bates DM (2000) Mixed-effects models in S and S-PLUS. Springer, New York
Pout DD, Ostler DC, Joyner LP, Norton CC (1966) The coccidial population in clinically normal sheep. Vet Rec 78:455–460
Priolo A, Lanza M, Biondi L, Pappalardo P, Young OA (1998) Effect of partially replacing dietary barley with 20 % carob pulp on post-weaning growth, and carcass and meat characteristics of Comisana lambs. Meat Sci 50:355–363
Priolo A, Waghorn GC, Lanza M, Biondi L, Pennisi P (2000) Polyethylene glycol as a means for reducing the impact of condensed tannins in carob pulp: effects on lamb growth performance and meat quality. J Anim Sci 78:810–816
Saratsis A, Joachim A, Alexandros S, Sotiraki S (2011) Lamb coccidiosis dynamics in different dairy production systems. Vet Parasitol 181:131–138
Saratsis A, Regos I, Tzanidakis N, Voutzourakis N, Stefanakis A, Treuter D, Joachim A, Sotiraki S (2012) In vivo and in vitro efficacy of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) against Eimeria spp in lambs. Vet Parasitol 188:1–9
Taylor MA, Catchpole J (1994) Review article: coccidiosis of domestic ruminants. Appl Parasitol 35:73–86
Team RC (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Vasta V, Nudda A, Cannas A, Lanza M, Priolo A (2008) Alternative feed resources and their effects on the quality of meat and milk from small ruminants. Anim Feed Sci Tech 147:223–246
Werne S, Perler E, Maurer V, Probst JK, Hoste H, Drewek A, Heckendorn F (2013) Effect of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) and faba bean (Vicia faba) on the periparturient rise in ewes infected with gastrointestinal nematodes. Small Rumin Res 113(2–3):454–460
Yousif AK, Alghzawi HM (2000) Processing and characterization of carob powder. Food Chem 69:283–287
Acknowledgments
This study has been supported by the financial funds of Marie Curie Research Fellow (Healthy Hay Project) and the European Community financial participation under the Seventh Framework Programme for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities, for the Integrated Project LOWINPUTBREEDS FP7-CP-IP 222623. The views expressed in this publication are the sole responsibility of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Commission. Neither the European Commission nor any person acting on behalf of the Commission is responsible for the use which might be made of the information contained herein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal-related procedures were in compliance with the national animal welfare regulations, as well as the animal experimentation ordinance, and the experimental protocols were approved by the responsible institutional authority.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saratsis, A., Voutzourakis, N., Theodosiou, T. et al. The effect of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) and carob pods (Ceratonia siliqua) feeding regimes on the control of lamb coccidiosis. Parasitol Res 115, 2233–2242 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4966-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4966-9