Abstract
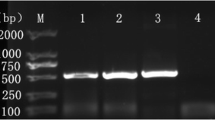
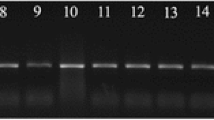
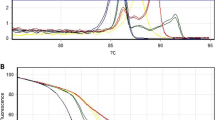
Giardia lamblia is a zoonotic flagellate protozoan in the intestine of human and many mammals including dogs. To assess a threat of dog-derived G. lamblia to humans, the common dog-derived G. lamblia assemblages A, C, and D were genotyped by high-resolution melting (HRM) technology. According to β-giardin gene sequence, the qPCR-HRM primers BG5 and BG7 were designed. A series of experiments on the stability, sensitivity, and accuracy of the HRM method were also tested. Results showed that the primers BG5 and BG7 could distinguish among three assemblages A, C, and D, which Tm value differences were about 1 °C to each other. The melting curves of intra-assay reproducibility were almost coincided, and those of inter-assay reproducibility were much the same shape. The lowest detection concentration was about 5 × 10−6-ng/μL sample. The genotyping results from 21 G. lamblia samples by the HRM method were in complete accordance with sequencing results. It is concluded that the HRM genotyping method is rapid, stable, specific, highly sensitive, and suitable for clinical detection and molecular epidemiological survey of dog-derived G. lamblia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adaszek L, Winiarczyk S (2010) Application of the SYBR Green real-time HRM PCR technique in the differentiation of the Babesia canis protozoa isolated in the areas of eastern Poland. Parasitol Res 106:1253–1256
Al-Mohammed HI (2011) Genotypes of Giardia intestinalis clinical isolates of gastrointestinal symptomatic and asymptomatic Saudi children. Parasitol Res 108(6):1375–1381
Cacciò SM, Ryan U (2008) Molecular epidemiology of giardiasis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 160(2):75–80
Cacciò SM, Thompson RC, McLauchlin J, Smith HV (2005) Unravelling Cryptosporidium and Giardia epidemiology. Trends Parasitol 21(9):430–437
Carlin EP, Bowman DD, Scarlett JM, Garrett J, Lorentzen L (2006) Prevalence of Giardia in symptomatic dogs and cats throughout the United States as determined by the IDEXX SNAP Giardia test. Vet Ther 7(3):199–206
Epe C, Rehkter G, Schnieder T, Lorentzen L, Kreienbrock L (2010) Giardia in symptomatic dogs and cats in Europe—results of a European study. Vet Parasitol 173(1-2):32–38
Erali M, Voelkerding KV, Witter CT (2008) High resolution melting applications for clinical laboratory medicine. Exp Mol Pathol 85:50–58
Flávio M, Paze S, Marina MM, Raimundo SL, João P, Jr A (2012) Molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis in dogs from Brazil. Parasitol Res 110:325–334
Gillin FD, Reiner DS, McCaffery JM (1996) Cell biology of the primitive eukaryote Giardia lamblia. Annu Rev Microbiol 50:679–705
Hoque ME, Hope VT, Kjellström T, Scragg R, Lay-Yee R (2002) Risk of giardiasis in Aucklanders: a case-control study. Int J Infect Dis 6(3):191–197
Hunter PR, Thompson RC (2005) The zoonotic transmission of Giardia and Cryptosporidium. Int J Parasitol 35(11-12):1181–1190
Koehler AV, Bradbury RS, Stevens MA, Haydon SR, Jex AR, Gasser RB (2013) Genetic characterization of selected parasites from people with histories of gastrointestinal disorders using a mutation scanning-coupled approach. Electrophoresis 34(12):1720
Lalle M, Pozio E, Capelli G, Bruschi F, Crotti D, Cacciò SM (2005) Genetic heterogeneity at the β-giardin locus among human and animal isolates of Giardia duodenalis and identification of potentially zoonotic subgenotypes. Int J Parasitol 35(2):207–213
Li J, Zhang P, Wang P, Alsarakibi M, Zhu H, Liu Y, Meng X, Li J, Guo J, Li G (2012) Genotype identification and prevalence of Giardia duodenalis in pet dogs of Guangzhou, Southern China. Vet Parasitol 188:368–371
Montgomery J, Wittwer CT, Palais R, Zhou L (2007) Simultaneous mutation scanning and genotyping by high-resolution DNA melting analysis. Nat Protoc 2:59–66
Provaznikova D, Kumstyrova T, Kotlin R, Salaj P, Matoska V, Hrachovinova I, Rittich S (2008) High-resolution melting analysis for detection of MYH9 mutations. Platelets 19(6):471–475
Radvánský J, Bazsalovicsová E, Králová-Hromadová I, Minárik G, Kádaši L (2011) Development of high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis for population studies of Fascioloides magna (Trematoda: Fasciolidae), the giant liver fluke of ruminants. Parasitol Res 108:201–209
Ryan U, Simone C (2013) Zoonotic potential of Giardia. Int J Parasitol 43(12-13):943
Sandhu H, Mahajan RC, Ganguly NK (2004) Flow cytometric assessment of the effect of drugs on Giardia lamblia trophozoites in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem 265(1-2):151–160
Tindall EA, Petersen DC, Woodbridge P, Schipany K, Hayes VM (2009) Assessing high-resolution melt curve analysis for accurate detection of gene variants in complex DNA fragments. Hum Mutat 30(6):876–883
Traub RJ, Monis PT, Robertson I, Irwin P, Mencke N, Thompson RC (2004) Epidemiological and molecular evidence supports the zoonotic transmission of Giardia among humans and dogs living in the same community. Parasitology 128(3):253–262
Vossen RH, Aten E, Roos A, den Dunnen JT (2009) High-resolution melting analysis (HRMA): More than just sequence variant screening. Hum Mutat 30(6):860–866
Wang Z, Vora GJ, Stenger DA (2004) Detection and genotyping of Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, Giardia lamblia, and Cryptosporidium parvum by oligonucleotide microarray. J Clin Microbiol 42(7):3262–3271
Zhang P, Liu Y, Alsarakibi M, Li J, Liu T, Li Y, Li G (2012) Application of HRM assays with EvaGreen dye for genotyping Giardia duodenalis zoonotic assemblages. Parasitol Res 111(5):2157–2163
Zheng G, Alsarakibi M, Liu Y, Hu W, Luo Q, Tan L, Li G (2014) Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis isolates from dogs in Guangdong, China based on multi-locus sequence. Korean J Parasitol 52(3):299–304
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31272551). The authors would like to thank the humane shelter’s personnel for helping to collect clinical samples and Miss Ping Kang for helping to draft the manuscript.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, L., Yu, X., Abdullahi, A.Y. et al. Development of a rapid HRM genotyping method for detection of dog-derived Giardia lamblia . Parasitol Res 114, 4081–4086 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4636-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4636-3