Abstract
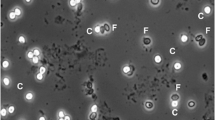
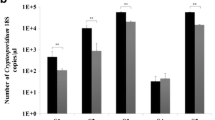
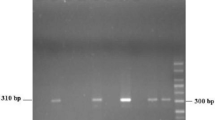
Detection of Blastocystis is routinely performed by microscopy, culture, and formyl-ether (ethyl acetate) concentration technique (FECT). Yet, these methods require special skilled personnel, are time consuming, and often involve processing that may cause misdiagnosis. The aim of this work is to demonstrate the usefulness of a newly introduced ELISA test for the detection of Blastocystis antigens in stool samples (CoproELISATM Blastocystis, Savyon Diagnostics) as a proper alternative to currently used methods, especially microscopy. A cohort of 179 fresh/frozen clinical stool samples was tested by the ELISA test, and results were compared to consensus methods comprised of microscopic examination of Lugol’s iodine staining, culture, and immunofluorescence assay (IFA). The new ELISA test was able to detect fewer than 103 cells, recognized subtypes 1, 2, 3, and 5 (comprising >95 % of human Blastocystis infections), and exhibited similar reactivity when comparing formalin-preserved samples to fresh/frozen samples. The test demonstrated 92 % sensitivity, 87 % specificity, and 89 % accuracy when culture, and IFA or microscopy consensus results were taken as reference. When the consensus was comprised of culture and IFA, the test demonstrated sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 82, 86, and 84 %, respectively. In contrast, the sensitivity of Lugol staining microscopy was only 18 %. This work presents a unique ELISA test that provides an alternative to the use of microscopy, currently most widely used method. The test enables high-throughput screening and diagnosis of Blastocystis, adaptation to automatic procedures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe N (2004) Molecular and phylogenetic analysis of Blastocystis isolates from various hosts. Vet Parasitol 25:235–242
Alfellani MA, Taner-Mulla D, Jacob AS, Imeede CA, Yoshikawa H, Stensvold CR, Clark CG (2013) Genetic diversity of Blastocystis in livestock and zoo animals. Protist 164:497–509
Ash LR, Orihel TC (1987) Parasites: a guide to laboratory procedures and identification. ASCP Press, Chicago, pp 121–122
Biedermann T, Hartmann K, Sing A, Przybilla B (2002) Hypersensitivity to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and chronic urticaria cured by treatment of Blastocystis hominis infection. Br J Dermatol 146:1113–1114
Chou CF, Tai JH (1996) Simultaneous extraction of DNA and RNA from nuclease-rich pathogenic protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis. Biotechniques 20:790–791
Dogruman-Al F, Kustimur S, Yoshikawa H, Tuncer C, Simsek Z, Tanyuksel M, Araz E, Boorom K (2009) Blastocystis subtypes in irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease in Ankara, Turkey. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104:724–727
Dogruman-Al F, Simsek Z, Boorom K, Ekici E, Sahin M, Tuncer C, Kustimur S, Altinbas A (2010) Comparison of methods for detection of Blastocystis infection in routinely submitted stool samples, and also in IBS/IBD patients in Ankara, Turkey. PLoS One 5:1–7
Eida AM, Eida MM (2008) Identification of Blastocystis hominis in patients with irritable bowel syndrome using microscopy and culture compare to PCR. Parasitol United J 2:87–92
Forsell J, Granlund M, Stensvold CR, Clark CG, Evengård B (2012) Subtype analysis of Blastocystis isolates in Swedish patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31:1689–1696
Krüger K, Kamilli I, Schattenkirchner M (1994) Blastocystis hominis as a rare arthritogenic pathogen. A case report. Z Rheumatol 53:83–85
Limor JR, Lal AA, Xiao L (2002) Detection and differentiation of Cryptosporidium parasites that are pathogenic for humans by real time PCR. J Clin Microbiol 40:2335–2338
Nasirudeen AM, Tan KS (2004) Caspase-3-like protease influence but is not essential for DNA fragmentation in Blastocystis undergoing apoptosis. Eur J Cell Biol 83:477–482
Noël C, Peyronnet C, Gerbod D, Edgcomb VP, Delgado-Viscogliosi P, Sogin ML, Capron M, Viscogliosi E, Zenner L (2003) Phylogenetic analysis of Blastocystis isolates from different hosts based on the comparison of small-subunit rRNA gene sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol 126:119–123
O’Gorman MA, Orenstein SR, Proujansky R, Wadowsky RM, Putnam PE, Kocoshis SA (1993) Prevalence and characteristics of Blastocystis hominis infection in children. Clin Pediatr 32:91–96
Parkar U, Traub RJ, Kumar S, Mungthin M, Vitali S, Leelayoova S, Morris K, Thompson RC (2007) Direct characterization of Blastocystis from faeces by PCR and evidence of zoonotic potential. Parasitology 134:359–367
Pasqui AL, Savini E, Saletti M, Guzzo C, Puccetti L, Auteri A (2004) Chronic urticaria and Blastocystis hominis infection: a case report. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 8:117–120
Peek R, Reedeker FR, van Gool T (2004) Direct amplification and genotyping of Dientamoeba fragilis from human stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 42:631–635
Qadri SM, al-Okaili GA, al-Dayel F (1989) Clinical significance of Blastocystis hominis. J Clin Microbiol 27:2407–2409
Rivera WL (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of Blastocystis isolates from animal and human hosts in the Philippines. Vet Parasitol 1:178–182
Rivera WL, Tan MA (2005) Molecular characterization of Blastocystis isolates in the Philippines by riboprinting. Parasitol Res 96:253–257
Roberts T, Barratt J, Harkness J, Ellis J, Stark D (2011) Comparison of microscopy, culture, and conventional polymerase chain reaction for detection of Blastocystis sp. in clinical stool samples. Am J Trop Med Hyg 84:308–312
Roberts T, Stark D, Harkness J, Ellis J (2013) Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolates identified in a Sydney population and pathogenic potential of Blastocystis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32:335–343
Scicluna SM, Tawari B, Clark CG (2006) DNA barcoding of Blastocystis. Protist 157:77–85
Stensvold CR (2013) Blastocystis: genetic diversity and molecular methods for diagnosis and epidemiology. Trop Parasitol 3:26–34
Stensvold R, Brillowska-Dabrowska A, Nielsen HV, Arendrup MC (2006) Detection of Blastocystis hominis in unpreserved stool specimens by using polymerase chain reaction. J Parasitol 92:1081–1087
Stensvold CR, Traub RJ, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Jespersgaard C, Nielsen HV, Thompson RC (2007a) Blastocystis: subtyping isolates using pyrosequencing technology. Exp Parasitol 116:111–119
Stensvold CR, Arendrup MC, Jespersgaard C, Mølbak K, Nielsen HV (2007b) Detecting Blastocystis using parasitologic and DNA-based methods: a comparative study. Diagn Microbiol Dis 59:303–307
Stensvold CR, Suresh GK, Tan KS, Thompson RC, Traub RJ, Viscogliosi E, Yoshikawa H, Clark CG (2007c) Terminology for Blastocystis subtypes—a consensus. Trends Parasitol 23:93–96
Stensvold CR, Nielsen HV, Mølbak K, Smith HV (2008) Pursuing the clinical significance of Blastocystis—diagnostic limitations. Trends Parasitol 25:23–29
Stenzel DJ, Boreham PF (1996) Blastocystis hominis revisited. Clin Microbiol Rev 9:563–584
Tan KS (2004) Blastocystis in humans and animals: new insights using modern methodologies. Vet Parasitol 126:121–144
Tan KS (2008) New insights on classification, identification, and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:639–665
Vennila GD, Suresh Kumar G, Khairul Anuar A, Rajah S, Saminathan R, Sivanandan S, Ramakrishnan K (1999) Irregular shedding of Blastocystis hominis. Parasitol Res 85:162–164
Verweij JJ, Blange RA, Tempeton K, Schinkel J, Brienen EA, van Rooyen MA, van Lieshout L, Polderman AM (2004) Simultaneous detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium parvum in fecal samples using multiplex real-time PCR. J Clin Microbiol 42:1220–1223
Yoshikawa H, Abe N, Wu Z (2003) Genomic polymorphism among Blastocystis isolates and development of PCR based identification of zoonotic isolates. J Eukaryot Microbiol 50:710–711
Yoshikawa H, Wu Z, Kimata I, Iseki M, Ali IK, Hossain MB, Zaman V, Haque R, Takahashi Y (2004) Polymerase chain reaction-based genotype classification among human Blastocystis hominis populations isolated from different countries. Parasitol Res 92:22–29
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Mira Barak, Shifra Ken-Dror, and Elsa Pavlotzky from Central Laboratories Haifa and Western Galilee, Clalit Health Services (Israel), for their contribution in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dogruman-Al, F., Turk, S., Adiyaman-Korkmaz, G. et al. A novel ELISA test for laboratory diagnosis of Blastocystis spp. in human stool specimens. Parasitol Res 114, 495–500 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4208-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4208-y