Abstract
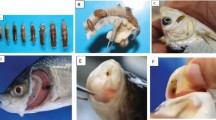
This study aimed to demonstrate the ability of Argulus japonicus to infect a wide range of freshwater fishes, as well as to understand the effects of fish origin and host body size on the incidence of A. japonicus. Samples of cultured and wild fish were collected randomly from July 2010 to March 2013, using angling, long-lining, gill-netting, and trapping from rivers and fish farms in Guangdong province, South China. Eight fish species were found to be heavily infected including the common carp, the goldfish, the black carp, the silver carp, the brown trout, the rainbow trout, the mandarin fish, and the perch. Furthermore, the black carp, the brown trout, and the mandarin fish were recorded as new hosts for the first time. During the present study, a total of 2,271 fishes were examined, out of which 712 fishes were found to be infected by a total of 1,443 A. japonicus. Abundance and intensity of A. japonicus infection were significantly influenced by origin of fishes (cultured and wild) and total length (class I, <250 mm; class II, 250–350 mm; and class III, >350 mm) of fish species, whereas varied impacts on prevalence of infection were observed. The correlation between total length of fishes and prevalence of A. japonicus infection was variable, where no significant correlation was observed in the black carp, the silver carp, the mandarin fish, and the perch. In spite of the weak negative correlation between body size of the silver carp and prevalence of infection, A. japonicus was the most abundant and intensive in the silver carp. Thus, aquaculturists should pay particular attention to the control of these fish lice due to its host biodiversity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsarakibi M, Wadeh H, Li GQ (2012) Freshwater abiotic components’ impact on the viability of fish lice, Argulus sp., in Guangdong province, China. Parasitol Res 111(1):331–339
Alvarez–Pellitero P (2008) Fish immunity and parasite infections: from innate immunity to immunoprophylactic prospects. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 126:171–198
Arme C, Owen RW (1967) Infections of the three spined stickleback, Gasterosteous aculeatus L. with the plerocercoid larvae of Schistocephalus solidus (Muller, 1776), with special reference to pathological effects. Parasitology 57:301–314
Bakke TA, Harris PD, Cable J (2002) Host specificity dynamics: observations on Gyrodactylids monogeneans. Int J Parasitol 32:281–308
Bandilla M, Valtonen ET, Suomalainen LR, Aphalo PJ, Hakalahti T (2006) A link between ectoparasite infection and susceptibility to bacterial disease in rainbow trout. Int J Parasitol 36:987–991
Bush AO, Lafferty KD, Lotz JM, Shostak AW (1997) Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J Parasitol 83:575–583
Bush AO, Fernandez J, Esch GW, Seed J (2003) Parasitism: the diversity and ecology of animal parasites. Cambridge University, Cambridge, England
Carpenter JW, Mashima TY, Rupiper DJ (2001) Exotic animal formulary. W.B. Saunders Company, St. Louis
Cowx IG (1992) Aquaculture development in Africa: training and reference manual for aquaculture extensionists. Food production and rural development Division, London
Crowden AE, Broom DM (1980) Effects of the eyefluke, Diplostomum spathaceum, on the behaviour of dace (Leuciscus leuciscus). Anim Behav 28:287–294
Forlenza M, Walker PD, de Vries BJ, Bonga SEW, Wiegertjes GF (2008) Transcriptional analysis of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) immune response to the fish louse Argulus japonicus Thiele (Crustacea: Branchiura). Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:76–83
Grutter AS (1994) Spatial and temporal variations of the ectoparasites of seven reef fish species from Lizard Island and Heron Island, Australia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 115:21–30
Ibrahim MM (2012) Variation in parasite infracommunies of Tilapia zillii in relation to some biotic and abiotic factors. Int J Zool Res 8:59–70
Kabata Z (1981) Copepoda (Crustacea) parasitic on fishes: problems and perspectives. Adv Parasitol 19:1–71
Kearn GC (2004) Leeches, lice and lampreys: a natural history of skin and gill parasites of fishes. Springer, Dordrecht, the Netherlands
Khan RA (2009) Parasites causing disease in wild and cultured fish in Newfoundland. Icel Agric Sci 22:29–35
Khan RA (2012) Host–parasite interactions in some fish species. J Parasitol Res, article ID 237280, 7 pages. doi:10.1155/2012/237280
Kimura S (1970) Notes on the reproduction of water lice (Argulus japonicus Thiele). Bull Freshw Fish Res Lab 20:109–126
Lewis RM, Hettler WF (1968) Effects of temperature and salinity on the survival of young Atlantic menhaden, Brevoortia tyrannus. Trans Am Fish Soc 97:344–349
Lo CM, Morand S, Galzin R (1998) Parasite diversity/host age and size relationship in three coral–reef fishes from French Polynesia. Int J Parasitol 28:1695–1708
McPherson NJ, Norman RA, Hoyle AS, Bron JE, Taylor NGH (2012) Stocking methods and parasite–induced reductions in capture: modelling Argulus foliaceus in trout fisheries. J Theor Biol 312:22–33
Mikheev VN, Pasternak AF, Valtonen ET (2007) Host specificity of Argulus coregoni (Crustacea: Branchiura) increases at maturation. Parasitology 134(Pt 12):1767–1774
Milinski M (1984) Parasites determine a predator’s optimal feeding strategy. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 15:35–37
Nagasawa K (2009) Synopsis of branchiurans of the genus Argulus (Crustacea, Argulidae), ectoparasites of freshwater and marine fishes, in Japan (1900–2009). Bull Biogeogr Soc Jpn 64:135–148
Omeji S, Solomon SG, Idoga ES (2011) A comparative study of the common protozoan parasites of clarias gariepinus from the wild and cultured environments in Benue State, Nigeria. J Parasitol Res, Article ID 916489, 8 pages. doi:10.1155/2011/916489
Poulin R (2006) Variation in infection parameters among populations within parasite species: intrinsic properties versus local factors. Int J Parasitol 36:877–885
Poulin R, Krasnov BR, Mouillot D (2011) Host specificity in phylogenetic and geographic space. Trends Parasitol 27:355–361
Qizhong Z, Chenglin M (1994) The parasitic crustaceans of fishes from Sichuan Province. J Southeast China Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 19(1):58–61
Tavares–Dias M, Martins ML, Moraes FL (2000) Condition factor, hepatosomatic and splenosomatic relation of freshwater fishes naturally parasitized. Acta Sci Biol Sci 22:533–537
Taylor NGH, Sommerville C, Wootten R (2006) The epidemiology of Argulus spp. (Crustacea: Branchiura) infections in stillwater trout sheries. J Fish Dis 29:193–200
Taylor NGH, Wootten R, Sommerville C (2009) Using length–frequency data to elucidate the population dynamics of Argulus foliaceus (Crustacea: Branchiura). Parasitol 1023–1032
Tucker CS, Sommerville C, Wooten R (2002) Does size really matter? Effects of fish surface area on the settlement and initial survival of Lepeophtheirus salmonis, an ectoparasite of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Dis Aquat Org 49:145–152
Violante–Gonzalez J, Garcia–Varela M, Rojas–Herrera A, Guerrero S (2009) Diplostomiasis in cultured and wild tilapia Oreochromis niloticus in Guerrero State, Mexico. Parasitol Res 105:803–807
Wadeh H, Yang JW, Li GQ (2008) Ultrastructure of Argulus japonicus Thiele, 1900 (Crustacea: Branchiura) collected from Guangdong, China. Parasitol Res 102(4):765–770
Walker PD, Flik G, Bonga SEW (2004) The biology of parasites from the genus Argulus and a review of the interactions with its host. Symp Soc Exp Biol 55:107–129
Walker PD, Harris J, Van der Velde G, Bonga SEW (2007) Size matters: stickleback size and infection with Argulus foliaceus (L., 1758) (Branchiura, Arguloida). Crustaceana 80(11):1397–1401
Walker PD, Harris JE, Van der Velde G, Bonga SEW (2008) Differential host utilisation by different life history stages of the fish ectoparasite Argulus foliaceus (Crustacea: Branchiura). Folia Parasitol 55:141–149
Walker PD, Russon IJ, Duijf R, Van der Velde G, Bonga SEW (2011a) The off–host survival and viability of a native and non–native fish louse (Argulus, Crustacea: Branchiura). Curr Zool 57(6):828–835
Walker PD, Russon IJ, Haond C, Van der Velde G, Bonga SEW (2011b) Feeding in adult Argulus japonicus Thiele, 1900 (Maxillopoda, Branchiura), an ectoparasite on fish. Crustaceana 84(3):307–318
Zander CD (2004) Four-year monitoring of parasite communities in gobiid fishes of the south–western Baltic. II: infracommunity. Parasitol Res 93:17–29
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30972179, 31272551) and the PhD Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (200805640004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsarakibi, M., Wadeh, H. & Li, G. Parasitism of Argulus japonicus in cultured and wild fish of Guangdong, China with new record of three hosts. Parasitol Res 113, 769–775 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3708-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3708-5