Abstract
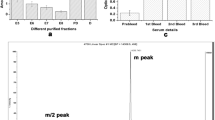
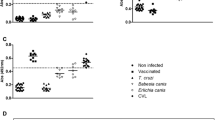
An antigenic conserved B domain was previously identified within nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolases (NTPDases) of plants and parasites. Now, the r-potDomain B, a 6× His-tag polypeptide belonging to the conserved B domain from the potato apyrase, and synthetic peptides LbB1LJ and LbB2LJ derived from the B domain from Leishmania NTPDase 1 were used as molecular tools for studies of the Leishmania amazonensis NTPDase 1. Widespread subcellular location of the specific NTPDase 1 was detected by Western blots of promastigote fractions and ultrastructural immunocytochemical microscopy using immune sera raised against these biomolecules. In addition, the L. amazonensis-infected BALB/c mice were evaluated at 12 to 120 days after infection, which progresses showing typical nodular lesion. High antibody reactivity with either r-potDomain B, LbB1LJ, or LbB2LJ was found in L. amazonensis-infected BALB/c mice indicating the antigenicity of the B domain from NTPDase 1 isoform. The IgG1 antibody reactivity significantly increased at 90–120 days postinfection, 18- to 24-fold when compared to the 12th day, and remained elevated even at 120th after infection, coinciding with the most active stage of the disease. In contrast, significantly higher IgG2a antibody reactivity with each biomolecule was observed at 40th day, about two- to fourfold higher than those found at 12th or 20th day, and decreased along 120-day period. Apparently, the conserved B domain is capable to induce IgG2a production in early disease stages. All together, these results suggest that r-potDomain B or synthetic peptides could be molecular starting points in experimental protocols of immunotherapy and/or vaccination for leishmaniasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu-Silva AL, Calabrese KS, Cupolilo SMN, Cardoso FO, Souza CSF, Gonçalves da Costa SC (2004) Histopathological studies of visceralized Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis in mice experimentally infected. Vet Parasitol 121:179–187
Almeida RP, Barral-Neto M, Jesus AMR, Freitas LAR, Carvalho EM, Barral A (1996) Biological behavior of Leishmania amazonensis isolated from human with cutaneous, mucosal, or visceral leishmaniasis in BALB/c mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg 54:178–184
Asai T, Mizuno F, Kojima S, Takeuchi T, Kobayashi A, Suzuki Y (1992) High correlation in antibody titers between the Sabin-Feldman dye test and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detecting immunoglobulin G antibodies to the nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase of Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol 30:1291–1293
Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A (2009) Evolutionary origins of the purinergic signaling system. Acta Physiol 195:415–447
Cardoso FO, Souza CSF, Mendes VG, Abreu-Silva AL, Gonçalves da Costa SC, Calabrese KS (2010) Immunopathological studies of Leishmania amazonensis infection in resistant and in susceptible mice. J Infect Dis 201:1933–1940
Chu N, Thomas BN, Patel SR, Buxbaum LU (2010) IgG1 is pathogenic in Leishmania mexicana infection. J Immunol 185:6939–6946
Coimbra ES, Gonçalves-Da-Costa SC, Corte-Real S, Freitas FGR, Durão A, Souza CSF, Silva Santos MI, Vasconcelos EG (2002) Characterization and cytochemical localization of an ATP diphosphohydrolase from Leishmania amazonensis promastigote. Parasitology 124:137–143
Coimbra ES, Gonçalves-Da-Costa SC, Costa BLS, Giarola NLL, Rezende-Soares FA, Fessel MR, Ferreira AP, Souza CSF, Abreu-Silva AL, Vasconcelos EG (2008) A Leishmania (L.) amazonensis ATP diphosphohydrolase isoform and potato apyrase share epitopes: antigenicity and correlation with disease progression. Parasitology 135:327–335
Cupolilo SMN, Souza CSF, Abreu-Silva AL, Calabrese KS, Gonçalves da Costa SC (2003) Biological behavior of Leishmania (L.) amazonensis isolated from a human diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis in inbred strains of mice. Histol Histopathol 18:1059–1065
Faria-Pinto P, Meirelles MNL, Lenzi HL, Mota EM, Penido MLO, Coelho PMZ, Vasconcelos EG (2004) ATP diphosphohydrolase from Schistosoma mansoni egg: characterization of a new antigen. Parasitology 129:51–57
Faria-Pinto P, Rezende-Soares FA, Molica AM, Montesano MA, Marques MJ, Rocha MOC, Gomes JAS, Enk MJ, Correa-Oliveira R, Coelho PMZ, Neto SM, Franco OL, Vasconcelos EG (2008) Mapping of the conserved antigenic domains shared between potato apyrase and parasites ATP diphosphohydrolases: potential application in human parasitic diseases. Parasitology 135:943–953
Faria-Pinto P, Mendes RGPR, Carvalho-Campos C, Maia ACRG, Oliveira AA, Coelho PMZ, Vasconcelos EG (2010a) Detection of IgG1 and IgG4 subtypes reactive against potato apyrase in schistosomiasis patients. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 105:370–373
Faria-Pinto P, Montesano MA, Jacinto AA, Santos RS, Bordin FHS, Ferreira AP, Penido MLO, Coelho PMZ, Vasconcelos EG (2010b) Antibody reactivity against potato apyrase, a protein that shares epitopes with Schistosoma mansoni ATP diphosphohydrolase isoforms, in acute and chronically infected mice, after chemotherapy and reinfection. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 105:374–379
Iborra S, Parody N, Abánades DR, Bonay P, Prates D, Novais FO, Barral-Neto M, Alonso C, Soto M (2008) Vaccination with the Leishmania major ribosomal proteins plus CpG oligodeoxynucleotides induces protection against experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis in mice. Microbes Infect 10:1133–1341
Kamath KS, Vasavada MS, Srivastava S (2011) Proteomic databases and tools to decipher post-translation modifications. J Proteomics 75:127–144
Kikuchi T, Furuta T, Kojima S (2001) Membrane localization and demonstration of isoforms of nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase from Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 122:15–23
Kikuchi T, Furuta T, Kojima S (2002) Kinetics of the nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase of Toxoplasma gondii in mice with acute and chronic toxoplasmosis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 96:35–41
Knowles AF (2011) The GDA1_CD39 superfamily: NTPDases with diverse functions. Purinergic Signal 7:21–45
Korkmaz B, Attucci S, Juliano MA, Kalupov T, Jourdan ML, Juliano L, Gauthier F (2008) Measuring elastase, proteinase 3 and cathepsin G activities at the surface of human neutrophils with fluorescence resonance energy transfer substrates. Nat Protoc 3:991–1000
Maia ACRG, Detoni ML, Porcino GN, Soares TV, Gusmão MAN, Fessel MR, Marques MJ, Souza MA, Coelho PMZ, Estanislau JASG, Rocha MOC, Santos MO, Faria-Pinto P, Vasconcelos EG (2011) Occurrence of a conserved domain in ATP diphosphohydrolases from pathogenic organisms associated to antigenicity in human parasitic diseases. Dev Comp Immunol 35:1057–1065
Maia ACRG, Porcino GN, Detoni MD, Emidio NB, Marconato DG, Faria-Pinto P, Fessel MR, Reis AB, Juliano LJ, Juliano MA, Marques MJ, Vasconcelos EG (2013) An antigenic domain within a catalytically active Leishmania infantum nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase (NTPDase 1) is a target of inhibitory antibodies. Parasitol Int 62:44–52
Mendes RGPR, Gusmão MANG, Maia ACRG, Detoni ML, Porcino GN, Soares TV, Juliano MA, Juliano LJ, Coelho PM, Lenzi HL, Faria-Pinto P, Vasconcelos EG (2011) Immunostimulatory property of a synthetic peptide belonging to the soluble ATP diphosphohydrolase isoform (SmATPDase 2) and immunolocalization of this protein in the Schistosoma mansoni egg. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 106:808–813
Peacock CS, Seeger K, Harris D, Murphy L, Ruiz JC, Quail MA, Peters N, Adlem E, Tivey A, Aslett M, Kerhornou A, Ivens A, Fraser A, Rajandream M-A, Carver T, Norbertczak H, Chillingworth T, Hance Z, Jagels K, Moule S, Ormond D, Rutter S, Squares R, Whitehead S, Rabbinowitsch E, Arrowsmith C, White B, Thurston S, Bringaud F, Baldauf SL, Faulconbridge A, Jeffares D, Depledge DP, Oyola SO, Hilley JD, Brito LO, Tosi LRO, Barrell B, Cruz AK, Mottram JC, Smith DF, Berriman M (2007) Comparative genomic analysis of three Leishmania species that cause diverse human disease. Nat Genet 39:839–847
Pereira BAS, Alves CR (2008) Immunological characteristics of experimental murine infection with Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis. Vet Parasitol 158:239–255
Pinheiro CM, Martins-Duarte ES, Ferraro RB, Fonseca de Souza AL, Gomes MT, Lopes AH, Vannier-Santos MA, Santo AL, Meyer-Fernandes JR (2006) Leishmania amazonensis: biological and biochemical characterization of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase activities. Exp Parasitol 114:16–25
Porcino GN, Carvalho-Campos C, Maia ACRG, Detoni ML, Faria-Pinto P, Coimbra ES, Marques MJ, Juliano MA, Juliano L, Diniz VA, Corte-Real S, Vasconcelos EG (2012) Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase (NTPDase 1): Localization and in vitro inhibition of promastigotes growth by polyclonal antibodies. Exp Parasitol 132:293–299
Ramírez L, Iborra S, Cortés J, Bonay P, Alonso C, Barral-Netto M, Soto M (2010) BALB/c mice vaccinated with Leishmania major ribosomal proteins extracts combined with CpG Oligodeoxynucleotides become resistant to disease caused by a secondary parasite challenge. J Biomed Biotechnol. Volume 2010, Article ID 181690, 9 pages, doi: 10.1155/2010/181690
Requena JM, Alonso C, Soto M (2000) Evolutionarily conserved proteins as prominent immunogens during Leishmania infections. Parasitol Today 16:246–250
Requena JM, Iborra S, Carrión J, Alonso C, Soto M (2004) Recent advances in vaccines for leishmaniasis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 4:1505–1517
Rezende-Soares FA, Carvalho-Campos C, Marques MJ, Porcino GN, Giarola NL, Costa BL, Taunay-Rodrigues A, Faria-Pinto P, Souza MA, Diniz VA, Corte-Real S, Juliano MA, Juliano L, Vasconcelos EG (2010) Cytochemical localization of ATP diphosphohydrolase from Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis promastigotes and identification of an antigenic and catalytically active isoform. Parasitology 137:773–783
Souza VL, Veras PST, Welby-Borges M, Silva TMC, Leite BR, Ferraro RB, Meyer-Fernandes JR, Barral A, Costa JML, Freitas LAR (2011) Immune and inflammatory responses to Leishmania amazonensis isolated from different clinical forms of human leishmaniasis in CBA mice. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 106:23–31
Tan F, Hu S, Luo F-J, Pan C-W, Chen X-G (2011) Induction of protective Th1 immune responses in mice by vaccination with recombinant Toxoplasma gondii nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase-II. Vaccine 29:2742–2748
Tan F, Xin H, Pan C-W, Ding J-Q, Chen X-G (2010) Monoclonal antibodies against nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase-II can reduce the replication of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol Int 59:141–146
Vasconcelos EG, Faria-Pinto P, Rezende-Soares FA, Penido ML, Gonçalves-da-Costa SC, Coelho PMZ (2009) Potato apyrase: a new tool for parasitic disease research. In: Tennant P, Benkeblia N (eds) Fruit, vegetable and cereal science and biotechnology 3. Global Science Books, Ikenobe, pp 80–88
Zaverucha do Valle T, Gaspar EB, Souza-Lemos C, Souza CS, Marquez FB, Baetas-da-Cruz W, d’Escofier LN, Corte-Real S, Calabrese KS, Gonçalves da Costa SC (2007) Experimental Leishmania (L.) amazonensis leishmaniasis: characterization and immunogenicity of subcellular fractions. Immunol Invest 36:473–492
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (FAPES), and Instituto Oswaldo Cruz. M.A. Juliano, L. Juliano, and S.C. Gonçalves-da-Costa are recipients of senior fellowships from CNPq. M.L. Detoni, A.C.R.G. Maia, G.N. Porcino, and L.R. Quellis were recipients of Master’s and Doctoral fellowships from FAPEMIG, PROQUALIS/UFJF, CAPES/REUNI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Detoni, M.L., Fessel, M.R., Maia, A.C.R.G. et al. An antigenic domain of the Leishmania amazonensis nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase (NTPDase 1) is associated with disease progression in susceptible infected mice. Parasitol Res 112, 2773–2782 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3445-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3445-9