Abstract
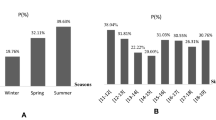
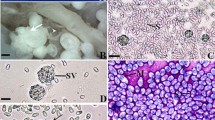
One hundred three out of 225 (45.8%) of the Red Sea fish Saurida tumbil were infected with microsporidian parasites. The infection was recorded as tumor-like masses (whitish macroscopic cysts) or xenomas often up to 2 cm in diameter and embedded in the peritoneal cavity. Generally, the infection was increased during winter 63.8% (86 out of 135) and fall to 18.9% (17 out of 90) in summer. Light microscopic study revealed that xenomas were encapsulated by a fibrous layer encircling numerous sporophorous vesicles filled with mature spores measuring 1.7 ± 0.6 (1.5–2.7 μm) × 1.5 ± 0.3 μm (1.2–1.8 μm) in size. Ultrastructural microscopic study showed the presence of smooth membranes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum forming a thick, amorphous coat surrounding various developmental stages of the parasite. The various recognizable stages of the parasite were uninuclear, binucleated, and multinucleated meronts followed by detachment of the plasmalemma of the sporont from the sporophorous vesicle producing sporoblasts. Mature spores consist of a spore coat and spore contents. The spore contents consist of the uninucleated sporoplasm and a posterior vacuole located at the posterior end. The polar tube consists of a straight shaft and a coiled region (26–32 coils) arranged in many rows along the inside periphery of the spore. The polaroplast consisted of an anterior region of closely and loosely packed membranes. Molecular analysis based on the small subunit rDNA gene was performed to determine the phylogenetic position of the present species. The percentage identity between this species and a range of other microsporidia predominantly from aquatic hosts demonstrated a high degree of similarity (>92%) with eight Pleistophora species. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences and divergence showed that the sequence of the present microsporidium was most similar to that of Pleistophora anguillarum (99.8% identity) differing in 13 nucleotide positions. So, the present species was recorded and phylogenetically positioned as a new species of Pleistophora.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Bashtar AR, Mehlhorn H, Al-Rasheid K, Al-Olayan E, Koura E, Morsy K (2009) Ultrastructure, development, and host-parasite relationship of a new species of the genus Pleistophora–a microsporidian parasite of the marine fish Epinephelus chlorostignei. Parasitol Res 106(1):39–46
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Bashtar AR, Mehlhorn H, Al-Rasheid K, Morsy K (2011) Microsporidian parasites: a danger facing marine fishes of the Red Sea. Parasitol Res 108(1):219–225
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman D (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Andreadis TG, Vossbrinck CR (2002) Life cycle, ultrastructure and molecular phylogeny of Hyalinocysta chapmani (Microsporidia: Thelohaniidae), a parasite of Culiseta melanura (Diptera: Culicidae) and Orthocyclops modestus (Copepoda: Cyclopidae). J Eukaryot Microbiol 49:350–364
Baker ND, Vossbrink CR, Maddox JV, Undeen AH (1994) Phylogenetic relationships among Vairimorpha and Nosema species (Microspora) based on ribosomal RNA sequence data. J Invertebr Pathol 64:100–106
Baker MD, Vossbrinck CR, Didier ES, Maddox JV, Shadduck JA (1995) Small subunit ribosomal DNA phylogeny of various microsporidia with emphasis on AIDS related forms. J Eukaryot Microbiol 42:564–570
Basch PF (1971) Transmission of microsporidian infection in the snail Indoplanorbis exustus in West Malaysia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2:380–383
Bayne CJ, Owczarzak A, Noonan WE (1975) In vitro cultivation of cells and a microsporidian parasite of Biomphalaria glabrata (Pulmonata: Basommatophora). Ann N Y Acad Sci 266:513–527
Bossanquet WC (1910) Brief notes on two myxosporidian organisms (Pleistophora hippoglossoideos n. sp. and Myxidiun mackiei n. sp.). Zool Anz 35:434–438
Canning EU (1976) Microsporidia in vertebrates: host-parasite relations at the organismal level. In: Bulla LA, Cheng TC (eds) Comparative pathobiology. Biology of the microsporidia, vol 1. Plenum, New York, pp 137–202
Canning EU, Hazard EI (1982) Genus Pleistophora Gurley, 1893: an assemblage of at least three genera. J Protozool 29:39–49
Canning EU, Nicholas JP (1980) Genus Pleistophora (Phylum Microspora): redescription of the type species, Pleistophora typicalis Gurley, 1893 and ultrastructural characterization of the genus. J Fish Dis 3:317–338
Canning EU, Refardt D, Vossbrinck CR, Okamura B, Curry A (2002) New diplokaryotic microsporidia (phylum Microsporidia) from freshwater bryozoans (Bryozoa, Phylactolaemata). Eur J Protistol 38:247–265
Casal G, Matos E, Teles-Grilo ML, Azevedo C (2008) A new microsporidian parasite, Potaspora morhaphis n. gen., n. sp. (Microsporidia) infecting the teleostean fish, Potamorhaphis guianensis from the River Amazon. Morphological, ultrastructural and molecular characterization. Parasitol 135(9):1053–1064
Cavalier-Smith T, Chao EE (1996) Molecular phylogeny of the free-living archezoan Trepomonas agi1is and the nature of the first eukaryote. J Mol Evol 43:551–562
Cheney SA, Lafranchi-Tristem NJ, Canning EU (2000) Phylogenetic relationships of Pleistophora-like microsporidia based on small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences and implications for the source of Trachipleistophora hominis infections. J Eukaryot Microbiol 47:280–287
Dugourd D, Jacques M, Bigras-Poulin M, Harel J (1996) Characterization of Serpulina hyodysenteriae isolates of serotypes 8 and 9 by random amplification of polymorphic DNA analysis. Vet Microbiol 48:305–314
Dykova I (1995) Phylum microspora. In: Woo PTK (ed) Fish diseases and disorders. Vol. 1, protozoan and metazoan infections. CAB International, Cambridge, pp 149–179
Fries I, Paxton RJ, Tengo J, Slemenda SB, da Silva AJ, Pieniazek NJ (1999) Morphological and molecular characterization of Antonospora scoticae n. ben., n. sp. (Protozoa, Microsporidia) a parasite of the communal bee, Andrena scotica Perkins, 1916 (Hymenoptera, Andrenidae). Eur J Protistol 35:183–193
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hartskeerl RA, van Gool T, Schuitema AR, Didier ES, Terpstra WJ (1995) Genetic and immunological characterization of the microsporidian Septata intestinalis Cali, Kotter and Orenstein, 1993: reclassification to Encephalitozoon intestinalis. Parasitology 110:277–285
Hatakeyama Y, Bansal AK, Iwano H, Kawakami Y, Ishihara R (2000) Characterization of SSU-rRNA sequence of a new microsporidium Nosema sp. (Nosematidae: Microsporidia), isolated from Antheraea mylitta Drury (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) in India. Indian J Seric 39:131–134
Hung HW, Lo CF, Tseyg CC, Peng SE, Chou CM, Kou' GH (1998) The small subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequence of Pleistophora anguillarum and the use of PCR primers for diagnostic detection of the parasite. J Euk Microbiol 45(5):556–560
Joh SJ, Kwon YK, Kim MC, Kim MJ, Kwon HM, Park JW, Kwon JH, Kim JH (2007) Heterosporis anguillarum infections in farm cultured eels (Anguilla japonica) in Korea. J Vet Sci 8:147–149
Kabata Z (1959) On two little-known microsporidia of marine fishes. Parasitol 49:309–315
Kawakami Y, Inoue T, Kikuchi M, Takayanagi M, Sunairi M, Ando T, Ishihar R (1992) Primary and secondary structures of 5S ribosomal RNA of Nosema bombycis (Nosematidae: Microsporidia). J Seric Sci Jpn 61:321–327
Kent ML, Speare DJ (2005) Review of the sequential development of Loma salmonae (Microsporidia) based on experimental infections of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Chinook salmon (O. Tshwytscha). Folia parasitol Praha 52(1–2):63–68
Kudo RR, Daniels EW (1963) An electron microscope study of the spore of a microsporidian, Thelohania calefornia. J Protozool 10:112–120
Leipe DD, Gunderson JH, Nerad TA, Sogin ML (1993) Small subunit ribosomal RNA of Hexamitu inflata and the quest for the first branch in the eukaryotic tree. Mol Biochem Parasit 59:41–48
Lom J (2002) A catalogue of described genera and species of microsporidians parasitic in fish. Syst Parasitol 53:81–99
Lom J, Corliss JO (1997) Ultrastructural observations on the development of the microsporidian protozoan Pleistophora hyphessobryconis Schäperclaus. J Protozool 14:141–152
Lom J, Dyková I (2005) Microsporidian xenomas in fish seen in wider perspective. Folia Parasitol 52:69–81
Lom J, Nilsen F (2003) Fish microsporidia: fine structural diversity and phylogeny. Int J Parasitol 33:107–127
Lom J, Dykova I, Koerting W, Klinger H (1989) Heterosporis schuberti new species of microsporidian parasite of aquarium fish. Eur J Protistol 25:129–135
Lom J, Dykova I, Tonguthai K, Chinabut S (1993) Muscle infection due to Heterosporis sp. in the Siamese fighting fish, Betta splendens Regan. J Fish Diseases 16:513–516
Lom J, Dyková I, Tonguthai K (2000a) Kabatana gen.n., new name for the microsporidian genus Kabataia Lom, Dykova' and Tonguthai, 1999. Folia Parasitol 47:78
Lom J, Dykova I, Wang CH, Lo CF, Kou GH (2000b) Ultrastructural justification for the transfer of Pleistophora anguillarum Hoshina, 1959 to the genus Heterosporis Schubert, 1969. Dis Aquat Org 43:225–231
Lom J, Dyková I, Wang CH, Lo CF, Kou GH (2000c) Ultrastructural justification for transfer of Pleistophora anguillarum Hoshina, 1959 to the genus Heterosporis Schubert, 1969. Dis Aquat Org 43:225–231
Lom J, Nilsen F, Dyková I (2001) Thelohania contejeani Henneguy, 1892: dimorphic life cycle and taxonomic affinities, as indicated by ultrastructural and molecular study. Parasitol Res 87:860–872
Lorn J, Dykova I (1992) Protozoan parasites of fishes. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Lovy J, Wright GM, Speare DJ (2007) Ultrastructural examination of the host inflammatory response within gills of netpen reared chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytsha) with microsporidial gill disease. Fish shell fish immunol 22(1–2):131–149
Maddox JV, Baker MD, Jeffords MR, Kuras M, Linde A, Solter LF, McManus ML, Vávra J, Vossbrinck CR (1999) Nosema portugal, n. sp., isolated from gypsy moths (Lymantria dispar L.) collected in Portugal. J Invertebr Pathol 73:1–14
Mathis A, Michel M, Kuster H, Muller C, Weber R, Deplazes P (1997) Two Encephalitozoon cuniculi strains of human origin are infectious to rabbits. Parasitology 114:29–35
Matos E, Corral L, Azevedo C (2005) Ultrastructural details of the xenoma of Loma myrophis (phylum Microsporidia) and extrusion of the polar tube during autoinfection. Dis Aquat Org 54:203–207
Matthews JL, Brown AMV, Larison K, Bishop-Stewart JK, Rogers P, Kent ML (2001) Pseudoloma neurophilia n. g., n. sp., a new microsporidium from the central nervous system of the zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Eukaryot Microbiol 48:227–233
Maurand J, Loubes C, Gasc C, Pelletier J, Barral J (1988) Pleistophora miradendellae Vaney and Conte, 1901, a microsporidian histopathology. J Fish diseases 11:251–258
McGourty KR, Kinziger AP, Hendrickson GL, Goldsmith GH, Casal G, Azevedo C (2007) A new microporidian infecting the musculature of the endangered tide water goby (Gobiidae). J Parasitol 93(3):655–660
Mercer CF, Wigley PJ (1987) A microsporidian pathogen of the Poroporo stem borer, Sceliodes cordalis (Dbld) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Invertbr Pathol 49:93–101
Moodie EG, Le Jambre LF, Katz M (2003) Ultrastructural characteristics and small subunit ribosomal DNA sequence of Vairimorpha cheracis sp. nov., (Microspora: Burenellidae), a parasite of the Australian yabby, Cherax destructor (Decapoda: Parastacidae). J Invertebr Pathol 84:198–213
Nilsen F, Endresen C, Hordvik I (1998) Molecular phylogeny of microsporidians with particular reference to muscle infecting species of fishes. J Eukaryot Microbiol 45:535–543
Rao SN, Muthulakshmi M, Kanginakudru S, Nagarajua J (2004) Phylogenetic relationships of three new microsporidian isolates from the silkworm. Bombyx mori J Invertebr Pathol 86:87–95
Rao SN, Nath BS, Saratchandra B (2005) Characterization and phylogenetic relationships among microsporidia infecting silkworm, Bombyx mori, using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and small subunit rRNA (SSU-rRNA) sequence analysis. Genome 48:355–366
Raynaud L, Delbac F, Broussolle V, Rabodonirina M, Girault V, Wallon M, Cozon G, Vivares CP, Peyron F (1998) Identification of Encephalitozoon intestinalis in travellers with chronic diarrhea by specific PCR amplification. J Clin Microbiol 36:37–40
Rodriguez-Tovar LE, Wright GM, Wadowska DW, Speare DJ, Markham RJF (2003) Ultrastructural study of the late stages of Loma salmonae development in the gills of experimentally infected rainbow trout. J Parasitol 89:464–474
Sokolova YY, Dolgikh VV, Morzhina EV, Nassonova ES, Issi IV, Terry RS, Ironside JE, Smith JE, Vossbrinck CR (2003) Establishment of the new genus Paranosema based on the ultrastructure and molecular phylogeny of the type species Paranosema grylli gen. nov., comb. nov. (Sokolova, Selezniov, Dolgikh, Issi 1994), from the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus Deg. J Invertebr Pathol 84:159–172
Sprague V (1966) Two new species of Plistophora (Microsporida, Nosematidae) in decapods with particular reference to one in the blue crab. J Protozool 13:196–199
Stephens FJ (2009) Unidentified microsporidian in western pygmy perch Edelia vittata (Nannopercidae) from Australia. Aust Vet J 87(1):61–62
Sutherland DR (2002) Heterosporis update, March 12, 2002. State of Michigan Document
Sutherland D, Marcquenski S, Marcino J, Lom J, Dykova I, Hsu HM, Jahns W, and Nilsen F (2000) Heterosporis sp. (Microspora: Glugeidae): a new parasite from Perca flavescens in Wisconsin and Minnesota. Proceedings of the 62nd Midwest Fish and Wildlife Conference, December 3–6, Minneapolis, Minnesota
Sutherland D, Cooper S, Stelzig P, Marcquenski S, Marcino J, Lom J, Dykova I, Nilsen F, Hsu HM, Jahns W, Hoyle J, Penney R (2004) Heterosporis sp. (Microspora): a new parasite from yellow perch (Perca flavescens) and walleye (Stizostedion vitreum) in Minnesota, Wisconsin and Lake Ontario, North America. 13th International Conference on Aquatic Invasive Species, September 20–24, Ennis, County Clare, Ireland
Terry RS, Smith JE, Bouchon D, Rigaud R, Duncanson P, Sharpe RG, Dunn AM (1999) Ultrastructural characterisation and molecular taxonomy of Nosema granulosis sp.n., a transovarially transmitted, feminising (TTF) microsporidium. J Eukaryot Microbiol 46:492–499
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
USEPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2008) Predicting future introductions of nonindigenous species to the Great Lakes. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Washington, DC; EPA/600/R-08/066F. Available from the National Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA, and http://www.epa.gov/ncea. Accessed 26 May 2011
Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1997) Evolutionary relationships among the eukaryotic crown taxa taking into account site-to-site rate variation in 18S rRNA. J Mol Evol 45:619–630
Vavra J, Hylis M, Vossbrinck CR, Pilarska DK, Linde A, Weiser J, McManus ML, Hoch G, Solter LF (2006) Vairimorpha disparis n. comb. (Microsporidia: Burenellidae): a redescription and taxonomic revision of Thelohania disparis Timofejeva 1956, a microsporidian parasite of the gypsy moth Lymantria dispar (L.) (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). J Euk Microbiol 53:292–304
Vossbrinck C, Andreadis TG (2007) The phylogenetic position of Ovavesicula popilliae (Microsporidia) and its relationship to Antonospora and Paranosema based on small subunit rDNA analysis. J Inv Path 96:270–273
Vossbrink CR, Baker MD, Didier ES, Debrunner-Vossbrink BA, Shadduck JA (1993) Ribosomal DNA sequences of Encephalitozoon hellem and Encephalitozoon cuniculi: species identification and phylogenetic construction. J Eukaryot Microbiol 40:354–362
Weiss LM (2001) Microsporidia 2001: Cincinnati. J Euk Microbiol Suppl:47S–49S
Weiss LM, Vossbrinck CR (1999) Molecular biology, molecular phylogeny, and molecular diagnostic approaches to the Microsporidia. In: Wittner M, Weiss LM (eds) The microsporidia and microsporidiosis. ASM Press, Washington, D.C, pp 129–171
Weissenberg R (1976) Microsporidian interactions with host cells. In: Bulla LA, Cheng TC (eds) Comparative pathobiology. Biology of the microsporidia, vol 1. Plenum, New York, pp 203–237
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Center of Excellence, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Ghaffar, F., Bashtar, AR., Morsy, K. et al. Morphological and molecular biological characterization of Pleistophora aegyptiaca sp. nov. infecting the Red Sea fish Saurida tumbil . Parasitol Res 110, 741–752 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2597-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2597-8