Abstract
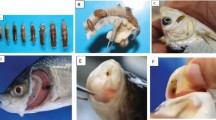
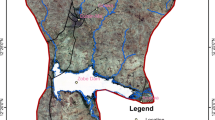
Various studies have shown that the Asian fish tapeworm, Bothriocephalus acheilognathi causes great economic loss in hatcheries, fish farms as well as in lakes. In order to understand the seasonal variation of infection in a nutrient-enriched lake, parasitological investigation was carried out in the indigenous cyprinid fish, Schizothorax niger Heckel 1838 from September, 2008 to August, 2009. Overall, this study revealed definite seasonality of infection (p < 0.05), with greater infection in summer (prevalence = 39.5%) and lesser in winter (prevalence = 8.1%). The prevalence among different seasons revealed significant differences (p < 0.05). Sex was not an important factor influencing the prevalence of the Asian tapeworm. A strong positive correlation (Pearson’s correlation, r = 0.7; p = 0.02) between total length of S. niger and number of Asian fish tapeworms was observed. Similarly, a strong positive correlation existed between weight of fish and number of tapeworms (Pearson’s correlation, r = 0.7; p = 0.005). Prevalence and mean abundance were positively and significantly correlated with water temperature (r = 0.8, p < 0.01 and r = 0.8, p < 0.01, respectively). Thus seasonal dynamics, total length and weight of the host significantly influenced the tapeworm infection. The above findings will be useful in devising the appropriate control strategies for the Asian tapeworm in wild fish in Kashmir valley as well as in similar climatic zones of other parts of the world. Also, information from this study will be used to assess the spread and extent of B. acheilognathi which is a potential threat to the indigenous fish fauna of Anchar Lake.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, the American Water Works Association and the Water Environment Federation, Washington, p 1220
Andrews C, Chub JC, Coles T, Dearsley A (1981) The occurrence of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934 (B. gowkongensis) (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) in the British Isles. J Fish Dis 4:89–93
Bean MG, Škeříková A, Bonner TH, Scholz T, Huffman DG (2007) First record of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) in the Rio Grande with comparative ITS2 and V4-18S rDNA sequencing. J Aquat Anim Health 19:71–76
Beer SA, German SM (1993) Ecological prerequisites of worsening of the cercariosis situation in cities of Russia (Moscow Region as an example). Parazitologiya 27:441–449
Bertasso A, Avevant-Oldewage A (2005) Aspects of the ecology of the Asian tapeworm, Bothriocephalus acheilognathi, 1934 in the Yellowfish in Vaal Dam, South Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 72:207–217
Brouder MJ (1999) Relationship between length of roundtail chub and infection intensity of Asian fish tapeworm Bothriocephalus acheilognathi. J Aquat Anim Health 11:302–304
Brouder MJ, Hoffnagle TL (1997) Distribution and prevalence of the Asian fish tapeworm, Bothriocephalus acheilognathi, in the Colorado River and tributaries, Grand Canyon, Arizona, including two new host records. J Helminthol Soc Wash 64:219–226
Bush AO, Lafferty KD, Lotz JM, Shostak AW (1997) Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J Parasitol 83:575–583
Choudhury AE, Charipar P, Nelson JR, Hodgson S, Bonar CRA (2006) Update on the distribution of the invasive Asian fish tapeworm, Bothriocephalus acheilognathi, in the U.S. and Canada. Comparative Parasitology 73:269–273
Chubb JC (1977) Seasonal occurrence of helminths in freshwater fishes. I. Monogenea. Adv Parasitol 15:133–199
Chubb JC (1980) Seasonal occurrence of helminthes in freshwater fishes. Part III. Larval Cestoda and Nematoda. Adv Parasitol 17:141–313
Deacon, JE (1988) The endangered woundfin and water management in the Virgin River, Utah, Arizona, Nevada. Fisheries 13:18–24
Dechtiar AO (1972) New parasite records for Lake Erie fish. Great Lakes Fish Comm Technical Rep 17:1–20
Díaz-Castaneda V, Carabez-Trejo A, Lamothe-Argumendo R (1995) Ultrastructure of the pseudophyllidean cestode Bothriocephalus acheilognathi, parasite of freshwater fish of commercial importance. Anales del Instituto de Biología, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Ser Zoología 66:1–16
Dogiel VA, Pertrushevski GK, Polyanski YI (1961) Parasitology of fishes. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh and London, p 384
Dogiel. VA, Pettruschevski GK, Yu (1970) Parasitology of fishes. 3rd ed. (Oliver and Boyd ltd.) (English translation by Z. Kabata)
Dove ADM, Fletcher AS (2000) The distribution of the introduced tapeworm Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in Australian freshwater fishes. J Helminthol 74:121–127
Ergens R, Lom J (1970) Causative agents of fish diseases. Academia, Prague, p.384
Granath WO Jr, Esch GW (1983) Survivorship and parasite-induced host mortality among mosquitofish in a predator-free, North Carolina cooling reservoir. Am Midl Naturalist 110:314–323
Hansen SP, Choudhury A, Heisey DM, Ahumada JA, Hoffnagle TL, Cole RA (2006) Experimental infection of the endangered bonytail chub (Gila elegans)with the Asian fish tapeworm (Bothriocephalus acheilognathi): impacts on survival, growth, and condition. Can J Zool 84:1383–1394
Hoffman GL (1976) The Asian tapeworm, Bothriocephalus gowkongensis, in the United States and research needs in fish parasitology. Proc. 1976 Fish Farming Conference and Annual Convention of the Catfish Farmers of Texas. 2 84–91
Hoffman GL (1980) Asian tapeworm Bothriocephalus acheilognathi, Yamaguti, 1934 in North America. Fisch und Umwelt 8:69–75
Hoole D, Nisan H (1994) Ultrastructural studies on intestinal responses of carp, Cyprinus carpio L., to the pseudophyllidean tapeworm, Bothriocephalus acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934. J Fish Dis 17:623–629
Hubbs CRJ, Edwards GGP (1991) An annotated checklist of the freshwater fishes of Texas, with keys to identification of species. Tex J of Sci 43:1–56
Khan RA, Thulin J (1991) Influence of pollution on parasites of aquatic animals. Adv Parasitol 30:201–238
Klenov AP (1972) Seasonal and age dynamics of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi infection in Ctenopharyngodon idella. Byulleten Vsesoyuznogo Instituta Gelmintologii 8:25–27
Korting W (1975) Larval development of Bothriocephalus sp. (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) from carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) in Germany. J Fish Biol 7:727–733
Koskivaara M (1992) Environmental factors affecting monogeneans parasitic on freshwater fishes. Parasitol Today 8:339–342
Lafferty KD (1997) Environmental parasitology: what can parasites tell us about human impacts on the environment? Parasitol Today 13:251–255
Lafferty KD, Kuris AM (2005) Parasitism and environmental disturbances. In Thomas, F., Guégan, J.F. & Renaud, F. (Eds) Parasitism and ecosystems pp. 113–23.
Le Cren ED (1951) The length-weight relationship and seasonal cycle in gonadal weight and condition in the perch, Perca fluviatilus. J Anim Ecol 20:201–219
Liao H, Shih L (1956) Contribution to the biology and control of Bothriocephalus gowkongensis Yeh, a tapeworm parasitic in the young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus C. & V.). Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica 2:129–185
Mackereth FJH, Heron J, Talling JF (1978) Water analysis: some revised methods for limnologists. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication 120 pp
Mackie GL, Morton WB, Ferguson MS (1983) Fish parasites in a new impoundment and differences upstream and downstream. Hydrobiologia 99:197–205
Malhotra YR (1970) Studies on the seasonal changes in the ovary of Schizothorax niger Heckel from Dal Lake in Kashmir. Japanese J of Ichthology 17:3
Marcogliese DJ (2001) Implications of climate change for parasitism of animals in the aquatic environment. Can J Zool 79(8):1331–1352
Marcogliese DJ, Esch GW (1989) Alterations in seasonal dynamics of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in a North Carolina cooling reservoir in seven year period. J Parasitol 75:378–382
Margolis L, Esch GW, Holmes JC, Kuris AM, Schad GA (1982) The use of ecological terms in parasitology (report Bush et al.—Parasite Ecology and Terminnology 583 of an adhoc committee of the American Society of Parasitologists). J Parasitol 68:131–133
Megan G, Bean BS (2008) Occurrence and impact of the asian fish tapeworm Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in the Rio Grande (Rio Bravo Del Norte). Dissertation, Texas State University
Mitchell AJ, Hoffman GL (1980) Important tapeworms of North American freshwater fishes. United States Fish and Wildl Service Fish Dis Leaflet 59:1–18
Morley NJ, Irwin SWB, Lewis JW (2003) Pollution toxicity to the transmission of larval digeneans through their molluscan hosts. Parasitology 126:s5–s26
Nie P, Kennedy CR (1991) Occurrence and seasonal dynamics of Pseudodactylogyrus anguillae (Yin and Sproston) (Monogenes) in eel, Anguilla anguilla (L.), in England. J F Biology, 39:897–900
Ondrackova M, Davidova M, Blazek R, Gelnar M, Jurajda P (2009) The interaction between an introduced fish host and local parasite fauna: Neogobius kessleri in the middle Danube River. Par Res 105:201–208
Organisation for Economic Co-operation & Development (1982) Eutrophication of waters. Monitoring, assessment and control. Organisation for Economic Co-operation & Development, Paris, p 154
Pandit AK, Yousuf AR (2002) Trophic status of Kashmir Himalayan lakes as depicted by water chemistry. J of Res & Development 2:0972–5407
Paperna I (1996) Parasites, infections and diseases of fishes in Africa—an update. Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, Rome. CIFA Technical Paper, No. 31. 220 pp
Polacik M, Janac M, Jurajda P, Adamek Z, Ondrackova M, Trichkova T, Vassilev M (2009) Invasive gobies in the Danube: invasion success facilitated by availability and selection of superior food resources. Ecol Fresh Fish 8:640–649
Pool DW (1987) A note on the synonomy of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934, B. aegyptiacus Ryšavý and Moravec, 1975 and B. kivuensis Baer and Fain, 1958. Parasitol Res 73:146–150
Pool W, Chubb JC (1985) A critical scanning electron microscope study of the scolex of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934, with a review of the taxonomic history of the genus Bothriocephalus parasitizing cyprinid fishes. Syst Parasitol 7:199–211
Poulin R (1992) Toxic pollution and parasitism in freshwater fish. Parasitol Today 8:58–60
Retief N-R, Avenant-Oldewage A, DU Preez HH (2007) Ecological aspects of the occurrence of Asian tapeworm, Bothriocephalus acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934 infection in the Largemouth yellowfish, Labeobarbus kimberleyensis Gilchrist and Thompson, 1913 in the Vaal Dam, South Africa. J Phys Chem Earth 32 (15-18) 1384–1390
Riggs MR, Esch GW (1987a) The growth, biomass, and fecundity of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in a North Carolina cooling reservoir. J Parasitol 73:893–900
Riggs MR, Esch GW (1987b) The suprapopulation dynamics of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in a North Carolina reservoir: abundance, dispersion, and prevalence. J Parasitol 73:877–892
Rumyantsev, EA (1988) Some aspects in the studies of fish parasite fauna in the lakes of different type. In Nauer, O.N. & Drozdov S. N. (Eds) Parasites of fresh water fishes of north-west Europe. Materials of the international Symposium within the programme of the Soviet-Finnish Cooperative, Petrozavodsk, U.S.S.R. pp. 130–136
Salgado-Maldonado G, Pineda-López R (2003) The Asian fish tapeworm Bothriocephalus acheilognathi: a potential threat to native freshwater fish species in Mexico. Biological Invasions 5:261–268
Sandland GJ, Goater CP (2000) Development and intensity dependence of Ornithodiplostomum ptychocheilus metacercariae in fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). J Parasitol 86:1056–1060
Scholz T (1997) A revision of the species of Bothriocephalus Rudolphi, 1808 (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) parasitic in American freshwater fishes. Syst Parasitol 36:85–107
Scott AL, Grizzle JM (1979) Pathology of cyprinid fishes caused by Bothriocephalus gowkongensis Yeh, 1955 (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea). J Fish Dis 2:69–73
Snieszko SF (1974) The effects of environmental stress on outbreaks of infectious diseases of fishes. J Fish Biol 6:197–208
Sunder S, Bhagat MJ, Joshi CB, Ramakrishna KV (1979) Fishing methods and fish catch composition of Dal lake, Kashmir (J&K) during 1969–72. J Inland Fish Soc India 10:9–18
Tekin-Ozan S, Kir I, Barlas M (2008) Helminth parasites of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) in Beyşehir Lake and population dynamics related to month and host size. Turkish J of Fish and Aquatic Sci 8:201–205
The Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (1974) An analytical guide, Part I. National Institute for Water Research, Pretoria South Africa
Valtonen ET, Holmes JC, Koskivaara M (1997) Eutrophication, pollution and fragmentation: effects on the parasite communities in roach and perch in four lakes in Central Finland. Parassitologia 39:233–236
Williams, H. & Jones, A. Parasitic worms of fish. Taylor & Francis; 1994. 593 pp.
Acknowledgement
Financial grants by the University Grants Commission (UGC) to 1st author (Ummer Rashid Zargar) in the form of a fellowship is acknowledged. We also acknowledge fishermen for their help during the catching of fish.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zargar, U.R., Chishti, M.Z., Yousuf, A.R. et al. Infection level of the Asian tapeworm (Bothriocephalus acheilognathi) in the cyprinid fish, Schizothorax niger, from Anchar Lake, relative to season, sex, length and condition factor. Parasitol Res 110, 427–435 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2508-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2508-z