Abstract
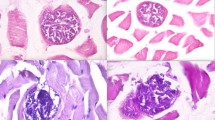
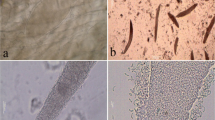
Four Sarcocystis species, i.e., Sarcocystis fusiformis and Sarcocystis buffalonis with cats as definitive hosts, Sarcocystis levinei with dogs as definitive host, and Sarcocystis dubeyi with unknown definitive host, have previously been described from water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). The aim of the present study was genetic characterization of the causative agent(s) of water buffalo sarcocystosis in Khuzestan Province, western Iran. RFLP-PCR and partial sequence analysis of 18S rDNA gene were used for the genetic characterization of the specimens directly obtained from water buffalo. In RFLP-PCR, four restriction enzymes (Dra1, Ssp1, Fok1 and Bsl1) were used for species discrimination of Sarcocystis spp. in this host. Comparison of the molecular sequencing results and RFLP-PCR pattern of the samples obtained in the present study with those previously reported for different Sarcocystis spp. revealed that all positive Sarcocystis samples represented S. fusiformis. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of the existence of S. fusiformis in the Iranian water buffalo population by a genetic approach. In addition, comparison between the alignments between the Iranian 18S rDNA sequences (HQ703791), made in this study, and those previously reported for S. fusiformis in different geographical location (accession nos. AF176927, AF176926, and U03071) showed the occurrence of local genetic polymorphisms and heterogeneity in this ribosomal locus. Despite the occurrence of some genetic variations in the hypervariable regions of the 18S rDNA in S. fusiformis, Dra I restriction site was conserved among all sequences available. According to the present study, it seems that cats have a more significant epidemiological role than dogs in transmission of sarcocystosis agent to water buffalo in Iran.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Al-Johany AM (2002) A light and electron microscope study of Sarcocystis mitrani (sp. Nov.) infecting the skink Scincus mitranus in the central region of Saudi Arabia. Parasitol Res 88:102–106
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Hilali M, Scholtyseck E (1978) Ultrastructure study of Sarcocystis fusiformis (Railliet 1897) infecting the Indian water buffalo Bubalus bubalis of Egypt. Tropenmed Parasitol 29:289–294
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Bashtar AR, Ashour MB, Sakran TH (1990) Life cycle of Sarcocystis gongyli Trinci 1911 in the shink Chalcides ocellatus and the snake Spalerosophis diadema. Parasitol Res 76:444–450
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Mehlhorn H, Bashtar AR, Al-Rasheid K, Sakran T, El-Fayoumi H (2009) Life cycle of Sarcocystis camelicanis infecting the camel (Camelus dromedarius) and the dog (Canis familiaris), light and electron microscopic study. Parasitol Res 106:189–195
Chen XW, Zuo YX, Hu JJ (2003) Experimental Sarcocystis hominis infection in a water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). J Parasitol 89:393–394
Claveria FG, Cruz MJ (2000) Sarcocystis levinei infection in Philippine water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). Parasitol Int 48:243–247
Dahlgren S, Gjerde B (2007) Genetic characterization of six Sarcocystis species from reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway based on the small subunit rRNA gene. Vet Parasitol 146:204–213
Dalimi A, Paykari A, Esmaeilzadeh M, Valizadeh M, Karimi G, Motamedi G, Abdi Goodarzi M (2008) Identification of Sarcocystis species of infected sheep in Ziaran abattoir, Qazvin, using PCR-RFLP (In Persian). Modares Med Sci 11:65–72
Dubey JP (1976) A review of Sarcocystis of domestic animals and of other coccidia of cats and dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 169:1061–1078
Dubey JP, Speer CA, Fayer R (1989a) Sarcocystosis in animals and man, 1st edn. CRC, Boca Raton, FL, pp 1–145
Dubey JP, Speer CA, Shah HL (1989b) Ultrastructure of sarcocysts from water buffalo in India. Vet Parasitol 34:149–152
Entzeroth R, Chobotar B, Scholtyseck E, Nemeseri L (1985) Light and electron microscope study of Sarcocystis sp from the fallow deer (Cervius lama). Z Parasitenkd Parasitol Res 71:33–39
FAO (2007) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available from: http://faostat.fao.org/site/573/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=573#ancor
Fayer R (2004) Sarcocystis spp. in human infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:894–902
Fischer S, Odening K (1998) Characterization of bovine Sarcocystis species by analysis of their 18S ribosomal DNA sequences. J Parasitol 84:50–54
Holmdahl OJM, Mattsson JG, Uggla A, Johansson KE (1994) The phylogeny of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii based on ribosomal RNA sequences. FEMS Microbiol Lett 119:187–192
Holmdahl OJM, Morrison DA, Ellis JT, Huong LTT (1999) Evolution of ruminant Sarcocystis (Sporozoa) parasites based on small subunit rDNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 11:27–37
Huong LTT (1999) Prevalence of Sarcocystis spp. in water buffaloes in Vietnam. Vet Parasitol 86:33–39
Huong LTT, Uggla A (1999) Sarcocystis dubeyi n. sp. (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) in the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). J Parasitol 85:102–104
Huong LTT, Dubey JP, Nikkilä T, Uggla A (1997) Sarcocystis buffalonis n. sp. (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) from the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in Vietnam. J Parasitol 83:471–474
Jeffries AC, Schnitzler B, Heydorn AO, Johnson AM, Tenter AM (1997) Identification of synapomorphic characters in the genus Sarcocystis based on 18S rDNA sequence comparison. J Eukaryot Microbiol 44:388–392
Jehle C, Dinkel A, Sander A, Morent M, Romig T, Luc PV, De TV, Thai VV, Mackenstedt U (2009) Diagnosis of Sarcocystis spp. in cattle (Bos Taurus) and water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in northern Vietnam. Vet Parasitol 166:314–320
Kia EB, Mirhendi H, Rezaeian M, Zahabiun F, Sharbatkhori M (2011) First molecular identification of Sarcocystis meischeriana (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) from wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Iran. Exp Parasitol 127:724–726
Levine ND (1986) The taxonomy of Sarcocystis (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) species. J Parasitol 72:372–382
Li QQ, Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Attwood SW, Chen XW, Zhang YP (2002) A PCR-based RFLP analysis of Sarcocystis cruzi (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) in Yunnan province, PR China, reveals the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) as a natural intermediate host. J Parasitol 88:1259–1261
Mehlhorn H, Heydorn AO (1979) Electron microscopical study on gamogony of Sarcocystis suihominis in human tissue cultures. Z Parasitenkd Parasitol Res 58:97–113
Motamedi GR, Dalimi A, Nouri A, Aghaeipour K (2011) Ultrastructural and molecular characterization of Sarcocystis isolated from camel (Camelus dromedarius) in Iran. Parasitol Res 108:949–954
Mugridge NB, Morrison DA, Heckeroth AR, Johnson AM, Tenter AM (1999) Phylogenetic analysis based on full-length large subunit ribosomal RNAgene sequence comparison reveals that Neospora caninum is more closely related to Hammondia hedorni than to Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol 29:1545–1556
Mugridge NB, Morrison DA, Jekel T, Heckeroth AR, Tenter AM, Johnson AM (2000) Effect of sequence alignment for the Protozona family Sarcocystidae. Soc Mol Biol Evol 17:1842–1853
Naghibi A, Razmi G, Ghasemifard M (2002) Identification of Sarcocystis cruzi in cattle by using of experimentally infection in final and intermediate hosts (In Persian). J Fac Vet Med Univ Tehran 57:67–69
Nourollahi Fard SR, Asghari M, Nouri F (2009) Survey of Sarcocystis infection in slaughtered cattle in Kerman, Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 41:1633–1636
Oryan A, Moghaddar N, Gaur SNS (1996) The distribution pattern of Sarcocystis species, their transmission and pathogenesis in sheep in Fars Province of Iran. Vet Res Commun 20:243–253
Oryan A, Ahmadi N, Modarres Mousavi SM (2010) Prevalence, biology and distribution pattern of Sarcocystis infection in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 42:1513–1518
Shekarforoush SS, Razavi SM, Dehghan SA, Sarihi K (2005) Prevalence of Sarcocystis species in slaughtered goats in Shiraz, Iran. Vet Rec 156:418–420
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Bio Evol 24:1596–1599
Valinezhad A, Oryan A, Ahmadi N (2008) Sarcocystis and its complications in camels (Camelus dromedarius) of eastern provinces of Iran. Korean J Parasitol 46:229–234
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX (2000) The new views of the researchers on cyst forming coccidia species including Sarcocystis by using the molecular biological techniques. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis 18:120–126
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Ding B, Chen XW, Luo J, Zhang YP (2000) 18S rRNA gene of Sarcocystis hominis cyst from water buffalo and cattle. Zool Res 21:133–138
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Ding B, Chen XW, Luo J, Zhang YP (2001a) Identification of Sarcocystis hominis-like (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) cyst in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) based on 18S rRNA gene sequences. J Parasitol 87:934–937
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Yao YG, Chen XW, Yang GC, Zhang YP (2001b) Analysis of the 18S rRNA genes of Sarcocystis species suggests that the morphologically similar organisms from cattle and water buffalo should be considered the same species. Mol Biochem Parasitol 115:283–288
Yang ZQ, Li QQ, Zuo YX, Chen XW, Chen YJ, Nie L, Wei CG, Zen JS, Attwood SW, Zhang XZ, Zhang YP (2002) Characterization of Sarcocystis species in domestic animals using a PCR-RFLP analysis of variation in the 18S rRNA gene: a cost-effective and simple technique for routine species identification. Exp Parasitol 102:212–217
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Ms. M. Masoudiyan from the Department of Pathobiology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran for her technical assistance. The authors would like to thank the abattoir officials of Ahvaz Slaughterhouse for their cooperation. This study was partly supported by a grant from the School of Veterinary Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oryan, A., Sharifiyazdi, H., Khordadmehr, M. et al. Characterization of Sarcocystis fusiformis based on sequencing and PCR-RFLP in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in Iran. Parasitol Res 109, 1563–1570 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2412-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2412-6