Abstract
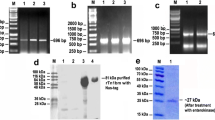
DEAD box proteins are putative RNA unwinding proteins found in organisms ranging from mammals to bacteria. We have identified a novel immunodominant cDNA clone, BmL3-helicase, encoding DEAD box RNA helicase by immunoscreening of a larval stage cDNA library of Brugia malayi. The cDNA sequence exhibited strong sequence homology to Caenorhabditis elegans and C. briggsae RNA helicase, a prototypic member of the DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box protein family. The clone also showed similarity with RNA helicase of Wolbachia, an endosymbiotic bacterium of filarial parasite. It was overexpressed as ∼50 kDa His-tag fusion protein, and ATP hydrolysis assay of recombinant enzyme showed that either ATP or dATP was required for the unwinding activity, indicating BmL3-helicase as an ATP/dATP-dependent RNA helicase. The recombinant protein also demonstrated cross-seroreactivity with human bancroftian sera. The presence of BmL3-helicase in various life stages of B. malayi was confirmed by immunoblotting of parasite-life-cycle extracts with polyclonal sera against the BmL3-helicase, which showed high levels of expression in microfilaria, L3, and adult (both male and female) stages. In the absence of an effective macrofilaricidal agent and validated anti-filarial drug targets, RNA helicases could be utilized as a rational drug target for developing agents against the human filarial parasite.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasdair JN, Pauline C, Robin BG (2004) Molecular biology of reproduction and development in parasitic nematodes: progress and opportunities. Int J Parasitol 34:125–138
Andersen CB, Ballut L, Johansen JS, Chamieh H, Nielsen KH, Oliveira CL, Pedersen JS, Seraphin B, Le Hir H, Andersen GR (2006) Structure of the Exon junction core complex with a trapped DEAD-box ATPase bound to RNA. Science 313:1968–1972
Bradford MA (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chan KM, Delfert D, Junger KD (1986) A direct colorimetric assay for Ca+2-stimulated ATPase Activity. Anal. Biochem 157:375–380
Cheng Z, Coller J, Parker R, Song H (2005) Crystal structure and functional analysis of DEAD-box protein Dhh1p. RNA 1258–1270
Christine SR, Eugene S, James HM-Tt, Garson KL, Philip JR, Irwin DK, Fred EC (1993) Structure-based inhibitor design by using protein models for the development of antiparasitic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:3583–3587
David NF (2003) Helicases as antiviral drug targets. Drug News Perspect 16:355
Deborah LR, Karen LB (1993) glh-1, a germ-line putative RNA helicase from Caenorhabditis, has four zinc fingers. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:9300–9304
Elodie G et al (2007) Draft genome of the filarial nematode parasite Brugia malayi. Science 317:1756
Feng J, Zhan B, Liu Y, Liu S, Williamson A, Goud G, Loukas A, Hotez P (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of Ac-MTP-2, an astacin-like metalloprotease release. Mol Biochem Parasitol 152(2):132–138
Frank GR, Tripp CA, Grieve RB (1996) Molecular cloning of a developmentally regulated protein isolated from excretory–secretory products of larval Dirofilaria immitis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 75:231–240
Geldhof P, Visser A, Clark D, Saunders G, Britton C, Gilleard J, Berriman M, Knox D (2006) RNA interference in parasitic helminths: current situation, potential pitfalls and future prospects.1–11
Gnanasekar M, Rao KVN, He Y-X, Mishra PK, Nutman TB, Kaliraj P, Ramaswamy K (2004) Novel phage display-based subtractive screening to identify vaccine candidates of Brugia malayi. Infect Immun 72(8):4707–4715
Gorbaleny AE, Koonin EV (1993) Helicases: amino acid sequence comparisons and structure–function relationships. Curr Opin Struct Biol 3:419–429
Helmy H, Weil GJ, Faris R, Gad AM, Chandrashekar R, Ashour A, Ramzy RM (2000) Human antibody responses to Wuchereria bancrofti infective larvae. Parasite Immunol 22:89–96
Hogbom M, Collins R, van den Berg S, Jenvert RM, Karlberg T, Kotenyova T, Flores A, Karlsson HGB, Holmberg SLH (2007) Crystal structure of conserved domains 1 and 2 of the human DEAD-box Helicase DDX3X in complex with the mononucleotide AMP. Mol Biol 372:150–159
Ibrahim MS, Richie TL, Scott AL (1992) Surface-associated antigens of Brugia malayi L2 and L3 parasites during vector-stage development. Mol Biochem Parasitol 52:97–110
Ismail MM (1998) Efficacy of single dose combinations of albendazole, ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine for the treatment of bancroftian filariasis. Trans of the Royal Soc of Trop Med and Hyg 92:94–97
Jankowsky E, Bowers H (2006) Remodeling of ribonucleoprotein complexes with DExH/D RNA helicases. Nucleic Acids Res 34:4181–4188
Kamath R S, Fraser A G, Dong Y, Poulin G, Durbin R, Gotta M, Kanapink A, Bot N L, Kamath RS, Fraser AG, Dong Y, Poulin G, Durbin R et al (2003) Systematic functional analysisof the Caenorhabditis elegans genome using RNAi. Nature 421
Kobayashi Y, Ishizaki S, Shimakura K, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2007) Molecular cloning and expression of two new allergens from Anisakis simplex. Parasitol Res 100(6):1233–1241
Laemmli UK, Molbert E, Showe M, Kelenberger E (1970) Form-determining function of genes required for the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol 49:99–113
Merriweathera A, Guenzlerb V, Brennerb M, Unnasch TR (2001) Characterization and expression of enzymatically active recombinant filarial prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Mol Biochem Parasitol 116(2):185–197
Michael E (2000). The population dynamics and epidemiology of lymphatic Filariasis. Imperial College Press, London. 1: 41–82
Nisbet AJ, Halliday AM, Parker L, David SW, Kenyon F, Knox DP, Huntley JF (2008) Psoroptes ovis: identification of vaccine candidates by immunoscreening. Exp Parasitol 120(2):194–199
Ottesen EA, Duke BO, Karam M, Behbehani K (1997) Strategies and tools for the control/ elimination of lymphatic filariasis. Bulletin of WHO 75:491–503
Pugh GE, Nicol SM, Fuller-Pace FV (1999) Interaction of the Escherichia coli DEAD box protein DbpA with 23S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol 292:771–778
Rao UR, Salinas G, Mehta K, Klei TR (2000) Identification and localization of glutathione-S-transferase as a potential target enzyme in Brugia species. Parasitol Res 86:908–915
Rosa EN, Eun YS, Yuji K, Andrew S, Blackwell TK (2001) cgh-1, a conserved predicted RNA helicase required for gametogenesis and protection from physiological germline apoptosis in C. elegans. Development 128:3221–3232
Sharma DC (2002) New goals set for filariasis elimination in India: news. The Lan Infec Dis 2:389
Shibuia A, Takamotob M, Shib Y, Komiyamaa A, Suganeb K (2001) Cloning and characterization of a novel gene encoding keratin-like protein from nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—Gene Structure and Expression 1522(1):59–61
Singh U, Misra S, Murthy PK, Katiyar JC, Agarwal A, Sircar AR (1997) Immunoreactive molecules of Brugia malayi and their diagnostic potential. Serodiag Immunotherap Infect Dis 8:207–212
Story RM, Li H, Abelson JN (2001) Crystal structure of a DEAD box protein from the hyperthermophile Methanococcus jannaschii. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:1465–1470
Taylor MJ, Bandi C, Hoerauf AM, Lazdins J (2000) Wolbachia bacteria of filarial nematodes: a target for control? Science S0169-4758(00)01661-6
Tuteja R (2007) Helicases-feasible antimalarial drug target for Plasmodium falciparum. FEBS J 274:4699–4704
Verma SK, Bansal I, Vedi S, Saxena JK, Katoch VM, Bhattacharya SM (2007) Molecular cloning, purification and characterization of myosin of human lymphatic filarial parasite Brugia malayi. Parasitol Res 102:481–489
Walker JE, Saraste M, Runswick MJ, Gay NJ (1982) Distantly related sequences in the alpha-and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J 1:945–951
Weil GJ, Li BW, Liftis F, Chandrashekar R (1992) Brugia malayi: antibody responses to larval antigens in infected and immunized jirds. Exp Parasitol 74:315–323
WHO (1997) Lymphatic filariasis: Reasons for hope. Document No.WHO/CTD/FIL/97.4, Geneva
Youliang H, Zhi-Ren L (2002) The ATPase, RNA unwinding, and RNA binding activities of recombinant p68 RNA helicase. J Biol Chem 277:12810–12815
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India, for financial assistance in the form of Senior Research Fellowships to M.S. We are grateful to Mr. A. K. Roy and R. N. Lal for their excellent technical assistance in maintenance of B. malayi infection in laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nucleotide sequence reported in this paper is available in the GenBank™, EMBL, and DDBJ databases under the accession number EF409381.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Srivastava, K.K. & Bhattacharya, S.M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel immunoreactive ATPase/RNA helicase in human filarial parasite Brugia malayi . Parasitol Res 104, 753–761 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1251-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1251-6