Abstract
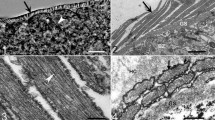
Having studied 67 birds of six species of the family Corvidae, Sarcocystis cysts were found in 16 (23.9%) individuals belonging to three species. The highest prevalence of infection (35.9%) was determined in the hooded crow (Corvus cornix). Two types of sarcocysts, which were temporarily called cysts type I and type V, were determined in the corvids examined. By light microscope, type I cyst wall seemed to be thin (< 1.0 μm) and smooth. Banana shaped cystozoites measured 6.0–8.0 μm in length. By light microscope, type V cyst wall seemed striated and reached up to 2.5 μm. Banana shaped cystozoites measured 6.1–7.9 × 1.4–1.8 μm. Ultrastructurally, the cyst wall amounted to 2.1 μm and had stump-like protrusions that differed greatly in size and shape. The parasitophorous vacuolar membrane had indentations and clearly visible (up to 0.2 μm in length) microprojections, which also differed considerably in size and shape. The ultrastructure of type V cyst wall differed from all those Sarcocystis spp. described thus far. On the basis of this—Sarcocystis cornixi sp. nov.—is proposed for this type of sarcocysts. Partial sequences of 18S rRNA and 28S rRNA genes were determined for this species and a phylogenetic analysis of the Sarcocystidae family was performed. In the phylogenetic tree, S. cornixi is grouped together with Frenkelia microti, F. glareoli, S. muris, S. neurona and the unnamed Sarcocystis species whose intermediate hosts are birds. S. cornixi is the most closely related to Sarcocystis sp. (cyst type I) from the white-fronted geese.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljanabi SM, Martinez I (1997) Universal and rapid salt-extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR-based techniques. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4692–4693
Černá Ž (1984) The role of birds as definitive hosts and intermediate hosts of heteroxenous coccidians. J Protozool 31:579–581
Dahlgren SS, Gjerde B (2007) Genetic characterisation of six Sarcocystis species from reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway based on the small subunit rRNA gene. Vet Parasitol 146:204–213
Dahlgren SS, Gjerde B (2008) Sarcocystis in moose (Alces alces): molecular identification and phylogeny of six Sarcocystis species in moose, and a morphological description of three new species. Parasitol Res 103:93–110
Dahlgren SS, Gjerde B, Skirnisson K, Gudmundsdottir B (2007) Morphological and molecular identification of three species of Sarcocystis in reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Iceland. Vet Parasitol 149:191–198
Doležel D, Koudela B, Jirků M, Hypša V, Oborník M, Votýpka J, Modrý D, Šlapeta JR, Lukeš J (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of Sarcocystis spp. of mammals and reptiles supports the coevolution of Sarcocystis spp. with their final hosts. Int J Parasitol 29:795–798
Drouin TE, Mahrt JL (1979) The prevalence of Sarcocystis Lankester, 1882, in some bird species in western Canada, with notes on its life cycle. Can J Zool 57:1915–1921
Dubey JP, Speer CA, Fayer R (1989) Sarcocystosis of animals and man. CRC, Boca Raton, FL
Dylko NI (1962) Distribution of Sarcosporidia among wild vertebrates in Belorussia. Dokl Akad Nauk 6:399–400
Elsheikha HM, Lacher DW, Mansfield LS (2005) Phylogenetic relationships of Sarcocystis neurona of horses and opossums to other cyst-forming coccidia deduced from SSU rRNA gene sequences. Parasitol Res 97:345–357
Jeffries AC, Schnitzler B, Heydorn AO, Johnson AM, Tenter AM (1997) Identification of synapomorphic characters in the genus Sarcocystis based on 18S rDNA sequences comparison. J Eukaryot Microbiol 44:388–392
Krone O, Rudolph M, Jakob W (2000) Protozoa in the breast muscle of raptors in Germany. Acta Protozool 39:35–42
Kutkienė L, Sruoga A (2004) Sarcocystis spp. in birds of the order Anseriformes. Parasitol Res 92:171–172
Kutkienė L, Sruoga A, Butkauskas D (2006) Sarcocystis sp. from white-fronted goose (Anser albiforns): cyst morphology and life cycle studies. Parasitol Res 99:562–565
Lindsay DS, Blagburn BL (1999) Prevalence of encysted apicomplexans in muscles of raptors. Vet Parasitol 80:341–344
Logminas V (comp.) (1990) Fauna of Lithuania. Aves 1. Mokslas, Vilnius
Mehlhorn H, Heydorn AO (1978) The Sarcosporidia (Protozoa, Sporozoa): life cycle and fine structure. Adv Parasitol 16:43–91
Mugridge NB, Morrison DA, Johnson AM, Luton K, Dubey JP, Votýpka J, Tenter AM (1999) Phylogenetic relationships of the genus Frenkelia: a review of its history and new knowledge gained from comparison of large subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene sequences. Int J Parasitol 29:957–972
Mugridge NB, Morrison DA, Jäkel T, Heckeroth AR, Tenter AM, Johnson AM (2000) Effects of sequence alignment and structural domains of ribosomal DNA on phylogeny reconstruction for the protozoan family Sarcocystidae. Mol Biol Evol 17:1842–1853
Munday BL, Hartley WJ, Harrigan KE, Presidente PJA, Obendorf DL (1979) Sarcocystis and related organisms in Australian wildlife: II. Survey findings in birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish. J Wildl Dis 15:57–73
Odening K, Stolte M, Walter G, Bockhardt I (1994) The European badger (Carnivora: Mustelidae) as intermediate host of further three Sarcocystis species (Sporozoa). Parasite 1:23–30
Pak SM, Eshtokina NV (1984) Sarcosporidians of birds. In: Panin VJ (ed) Sarcosporidians of animals in Kazakhstan. Nauka, Alma-Ata, pp 150–168
Šlapeta JR, Modrý D, Votýpka J, Jirků M, Koudela B, Lukeš J (2001) Multiple origin of the dihomoxenous life cycle in Sarcosporidia. Int J Parasitol 31:413–417
Šlapeta JR, Modrý D, Votýpka J, Jirků M, Lukeš J, Koudela B (2003) Evolutionary relationships among cyst-forming coccidia Sarcocystis spp. (Alveolata: Apicomplexa: Coccidea) in endemic African tree vipers and perspective for evolution of heteroxenous life cycle. Mol Phylogenet Evol 27:464–475
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tenter AM, Baverstock PR, Johnson AM (1992) Phylogenetic relationships of Sarcocystis species from sheep, goats, cattle and mice based on ribosomal RNA sequences. Int J Parasitol 22:503–513
Valkiūnas G, Križanauskienė A, Iezhova TA, Hellgren O, Bensch S (2007) Molecular phylogenetic analysis of circumnuclear haemoproteids (Haemosporida, Haemoproteidae) of sylviid birds, with description of Haemoproteus parabelopolskyi sp. nov. J Parasitol 93:680–687
Votýpka J, Hypša V, Jirků M, Flegr J, Vávra J, Lukeš J (1998) Molecular pyhlogenetic relatedness of Frenkelia spp. (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) to Sarcocystis falcatula Stiles 1893: is the genus Sarcocystis paraphyletic. J Eukaryot Microbiol 45(1):137–141
Wesemeier H-H, Sedlaczek J (1995) One known Sarcocystis species and two found for the first time in red deer and wapiti (Cervus elaphus) in Europe. Appl Parasitol 36:245–251
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Ding B, Chen XW, Luo J, Zhang YP (2001) Identification of Sarcocystis hominis-like (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) cyst in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) based on 18S rRNA gene sequences. J Parasitol 87:934–937
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr. Jitender P. Dubey from Animal Parasitic Diseases Laboratory, United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Animal and Natural Resources Institute for evaluation of sarcocyst wall ultra-structure. We express our sincere gratitude to Professor Ilan Paperna from Hebrew University of Jerusalem for the valuable comments on the draft of the paper. We are grateful to Mrs. I. Žalakevičienė from the Institute of Experimental and Clinical Medicine for her help in carrying out investigations of electron microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutkienė, L., Prakas, P., Sruoga, A. et al. Sarcocystis in the birds family Corvidae with description of Sarcocystis cornixi sp. nov. from the hooded crow (Corvus cornix). Parasitol Res 104, 329–336 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1196-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1196-9