Abstract
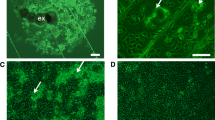
Cloned populations were generated from Indian isolates of Toxoplasma gondii by transferring single tissue cysts from the brains of chronically infected mice to confluent murine macrophage (J774A.1) monolayers. The clones were then maintained continuously as tachyzoites in culture. Physical rupture of the tissue cysts and release of bradyzoites prior to seeding was found to be necessary for establishment of the parasite in culture. Although intact tissue cysts seeded over monolayers released bradyzoites spontaneously, they did not succeed in setting up an infection in the monolayers. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD)-PCR, which revealed distinct patterns for a clone and its progenitor, further confirmed the efficiency of the technique. The cloning technique was found to be simple and rapid compared to those involving limiting dilutions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basagoudanavar SH, Rao JR, Singh RK, Butchaiah G (1999) Random amplification of polymorphic DNA fingerprinting of Trypanosoma evansi. Vet Res Commun 23:249–255
Darde ML, Bouteille B, Pestre-Alexandre M (1988) Analyse isoenzymatique do souches clonees de Toxoplasma gondii. Bull Soc Fr Parasitol 6:41–46
Dubey JP, Beattie CP (1988) Toxoplasmosis of animals and man. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Edgar SA, Seibold CT (1964) A new coccidium of chickens, Eimeria mivati sp. n. (Protozoa: Eimeriidae) with details of its life history. J Parasitol 50:193–204
Guo ZG, Johnson AM (1995) Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains by random amplified polymorphic DNA polymerase chain reaction. Parasitology 111:127–132
Guo ZG, Johnson AM (1996) DNA polymorphisms associated with murine virulence of Toxoplasma gondii identified by RAPD-PCR. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 219:17–26
Howe DK, Sibley LD (1995) Toxoplasma gondii comprises of three clonal lineages: correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. J Infect Dis 172:5561–5566
Pfefferkorn ER, Pfefferkorn LC (1976) Toxoplasma gondii: isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature sensitive mutants. Exp Parasitol 39:365–376
Rosen NL, Onodera M, Hotez PJ, Bogucki MS, Elce BM, Patton C, Konigsberg WH, Cross GAM, Richards FF (1981) Trypanosoma congolense: surface glycoproteins of two early blood stream variants. 1. Production of relapsing infection in rodents. Exp Parasitol 52:210–218
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989). Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd edn , vol 2. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sibley LD, Boothroyd JC (1992) Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature 39:82–85
Sreekumar C, Rao JR, Mishra AK, Ray D, Singh RK, Joshi P (2001) First isolation of Toxoplasma gondii from chicken in India. J Vet Parasitol 15:103–106
Teale AJ, Wambugu J, Gwakasa PS, Stranzinger G, Bradley D, Kemp SJ (1995) A polymorphism in randomly amplified DNA that differentiates the Y chromosomes of Bos indicus and Bos taurus. Anim Genet 26:243–248
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Director and Joint Director (Academic), Indian Veterinary Research Institute, for providing the facilities to conduct the research. Thanks are also due to ICAR and IVRI for the fellowship awarded to the senior author. The authors are grateful to Dr. J.P. Dubey, USDA, for his constructive criticism on the manuscript and to Valsin Fournet, USDA, for assisting with the figures. The experiments comply with the current laws applicable to animal experimentation in India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sreekumar, C., Rao, J.R., Mishra, A.K. et al. In vitro generation of cloned populations of Toxoplasma gondii . Parasitol Res 90, 489–492 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0898-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0898-2