Abstract
Purpose
To construct a nomogram for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients base on HCC-GRIm score.
Methods
Clinical cases of HCC patients diagnosed at Hunan Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital were included, and these were randomly divided into the training cohort (n = 219) and the validation cohort (n = 94), and those patients were divided into low GRIm-Score group (scores 0, 1, and 2) and high GRIm-Score group (scores 3, 4, and 5). In the training cohort, independent risk factors were determined by Cox regression analysis, and a nomogram was constructed by independent risk factors. The efficiency and the clinical applicability of nomograms were evaluated using ROC curves, calibration plot, and the decision curve (DCA), and the patients were divided into high-risk, middle-risk, and low-risk groups according to total score of nomogram.
Results
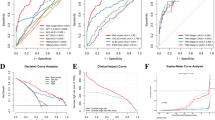
Compared to low HCC-GRIm score group, high HCC-GRIm score group with BCLC stage is more advanced (P < 0.001), and fewer patients received TACE (P = 0.005) and surgical treatment (P = 0.001). There was higher rate of the presence of vascular invasion (P < 0.001) and distant metastasis (P < 0.001). Multivariate Cox regression analysis screened 4 independent risk factors to construct a nomogram of HCC patients, including HCC-GRIm score, BCLC stage, albumin-to-globulin ratio (AGR), and glutamyl trans-peptidase (GGT). The consistency index (C-index) of the nomogram of the training was 0.843 (0.832–0.854) and the validation was 0.870 (0.856–0.885). The time-dependent parameter showed the AUC values of the training cohort at 1, 3, and 5 years were 0.954 (95% CI 0.929–0.980), 0.952 (95% CI 0.919–0.985), and 925 (95% CI 0.871–0.979), while the AUC values of validation cohort at 1, 3, and 5 years were 0.974 (95% CI 0.950–0.998), 0.965 (95% CI 0.931–0.999), and 0.959 (95% CI 0.898–1.021). The calibration plot showed the nomogram fits well onto perfect curves, and the DCA curve showed the net benefit of the nomogram at a certain probability threshold is significantly higher than the net benefit of the BCLC stage at the same threshold probability. Finally, all patients were divided into high-risk, middle-risk, and low-risk groups based on the total score of nomogram, and it showed effectively to identify high-risk patients.
Conclusion
The nomogram constructed by the independent risk factors can predict the prognosis of HCC patients, providing an effective tool with clinical workers to evaluate the prognosis and survival time of HCC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Azab B, Kedia S, Shah N et al (2013) The value of the pretreatment albumin/globulin ratio in predicting the long-term survival in colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 28(12):1629–36
Bai L, Lin ZY, Lu YX et al (2021) The prognostic value of preoperative serum lactate dehydrogenase levels in patients underwent curative-intent hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases: a two-center cohort study. Cancer Med. 10(22):8005–8019
Bigot F, Castanon E, Baldini C et al (2017) Prospective validation of a prognostic score for patients in immunotherapy phase I trials: the Gustave Roussy immune score (GRIm-score). Eur J Cancer 84:212–218
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL (2004) X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res. 10(21):7252–9
Chan AW, Kumada T, Toyoda H et al (2016) Integration of albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score into Barcelona clinic liver cancer (BCLC) system for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31(7):1300–6
Chen W, Wang W, Zhou L et al (2022) Elevated AST/ALT ratio is associated with all-cause mortality and cancer incident. J Clin Lab Anal. 36(5):e24356
Du XJ, Tang LL, Mao YP et al (2014) The pretreatment albumin to globulin ratio has predictive value for long-term mortality in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 9(4):e94473
Feng JF, Wang L, Yang X, Chen S (2020) Gustave Roussy immune score (GRIm-Score) is a prognostic marker in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer. 11(6):1334–1340
Gomez D, Farid S, Malik HZ et al (2008) Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 32(8):1757–62
Greten FR, Grivennikov SI (2019) Inflammation and cancer: triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity 51(1):27–41
Hatanaka T, Naganuma A, Kakizaki S (2021) Lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma: a literature review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 36
Hatanaka T, Naganuma A, Hiraoka A et al (2023) The hepatocellular carcinoma modified Gustave Roussy immune score (HCC-GRIm score) as a novel prognostic score for patients treated with atezolizumab and bevacizumab: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Cancer Med. 12(4):4259–4269
Hofbauer SL, Stangl KI, de Martino M et al (2014) Pretherapeutic gamma-glutamyltransferase is an independent prognostic factor for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 111(8):1526–1531
Hu J, Wang Y, Deng L et al (2022) Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting the cancer-specific survival of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Updates Surg. 74(5):1589–1599
Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C et al (2015) Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J Clin Oncol. 33(6):550–8
Kanda T, Goto T, Hirotsu Y, Moriyama M, Omata M (2019) Molecular mechanisms driving progression of liver cirrhosis towards hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B and C infections: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 20(6):1358
Kelley RK, Miksad R, Cicin I et al (2022) Efficacy and safety of cabozantinib for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma based on albumin-bilirubin grade. Br J Cancer 126(4):569–575
Kong W, Zuo X, Liang H et al (2018) Prognostic value of lactate dehydrogenase in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 201:1723184
Kusumanto YH, Dam WA, Hospers GA, Meijer C, Mulder NH (2003) Platelets and granulocytes, in particular the neutrophils, form important compartments for circulating vascular endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis 6(4):283–287
Li L, Mo F, Hui EP et al (2019) The association of liver function and quality of life of patients with liver cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 19(1):66
Li SJ, Zhao L, Wang HY et al (2020) Gustave Roussy immune score based on a three-category risk assessment scale serves as a novel and effective prognostic indicator for surgically resectable early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: a propensity score matching retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 84:25–40
Li Y, Pan Y, Lin X et al (2021) Development and validation of a prognostic score for hepatocellular carcinoma patients in immune checkpoint inhibitors therapies: the hepatocellular carcinoma modified gustave roussy immune score. Front Pharmacol 12:819985
Limaye AR, Clark V, Soldevila-Pico C et al (2013) Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts overall and recurrence-free survival after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 43(7):757–64
Liu K, Huang G, Chang P et al (2020) Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Sci Rep. 10(1):21376
Minami S, Ihara S, Komuta K (2019a) Gustave Roussy immune score is a prognostic factor for chemotherapy-naive pulmonary adenocarcinoma with wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor. World J Oncol 10(1):55–61
Minami S, Ihara S, Ikuta S, Komuta K (2019b) Gustave Roussy immune score and royal marsden hospital prognostic score are biomarkers of immune-checkpoint inhibitor for non-small cell lung cancer. World J Oncol 10(2):90–100
Nicolini D, Agostini A, Montalti R et al (2017) Radiological response and inflammation scores predict tumour recurrence in patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization before liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 23(20):3690–3701
Ozyar E, Caglar HB, Atalar B (2012) In regard to Zhou et al “Baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase levels for patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a predictor of poor prognosis and subsequent liver metastasis.” Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83(2):482–483 (Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012;82:e359–e365)
Singh N, Baby D, Rajguru JP, Patil PB, Thakkannavar SS, Pujari VB (2019) Inflammation and cancer. Ann Afr Med. 18(3):121–126
Suh B, Park S, Shin DW et al (2014) Low albumin-to-globulin ratio associated with cancer incidence and mortality in generally healthy adults. Ann Oncol. 25(11):2260–2266
Sullivan KM, Groeschl RT, Turaga KK et al (2014) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a Western perspective. J Surg Oncol. 109(2):95–7
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71(3):209–249
Tian S, Cao Y, Duan Y, Liu Q, Peng P (2021) Gustave Roussy immune score as a novel prognostic scoring system for colorectal cancer patients: a propensity score matching analysis. Front Oncol 11:737283
Ueshima K, Nishida N, Hagiwara S et al (2019) Impact of baseline ALBI grade on the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with lenvatinib: a multicenter study. Cancers (Basel). 11(7):952
Vickers AJ, Elkin EB (2006) Decision curve analysis: a novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med Decis Making. 26(6):565–74
Wan G, Gao F, Chen J et al (2017) Nomogram prediction of individual prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 17(1):91
Wu J, Zhang H, Li L et al (2020) A nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma: a population-based analysis. Cancer Commun (Lond). 40(7):301–312
Xie D, Allen MS, Marks R et al (2018) Nomogram prediction of overall survival for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer incorporating pretreatment peripheral blood markers. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 53(6):1214–1222
Yang F, Zhang S, Yang H et al (2015) Prognostic significance of gamma-glutamyltransferase in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 28(5):496–504
Yang JG, He XF, Huang B, Zhang HA, He YK (2018) Rule of changes in serum GGT levels and GGT/ALT and AST/ALT ratios in primary hepatic carcinoma patients with different AFP levels. Cancer Biomark. 21(4):743–746
Yang D, Zhu M, Xiong X et al (2022) Clinical features and prognostic factors in patients with microvascular infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma: Development and validation of a nomogram and risk stratification based on the SEER database. Front Oncol 12:987603
Zhang B, Yu W, Zhou LQ et al (2015) Prognostic significance of preoperative albumin-globulin ratio in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. PLoS One. 10(12):e0144961
Zhang Z, Li Y, Yan X et al (2019a) Pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase may predict outcome of advanced non small-cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 8(4):1467–1473
Zhang LX, Lv Y, Xu AM, Wang HZ (2019b) The prognostic significance of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase levels and AST/ALT in primary hepatic carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 19(1):841
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82074425, 82205227); Hunan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Program Project (D2022010); Natural Foundation of Hunan Provincial (2021JJ30417); Young Qihuang Scholars Talent Project of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Hunan Provincial Health Commission Traditional Chinese Medicine Shennong Leading Talent Project; Hunan Province Science and Technology Top Leading Talent Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have access to the data and all drafts of the manuscript. Specific contributions are as follows: The data collection, data management, data analysis, and manuscript drafting: XY. The study design: XY, RY, and KL. The manuscript review: all. Funding sources: PZ, ZH and KL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Our Institutional Review Board (Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine) approved this study and waived the need for informed consent from patients.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Yang, R., He, Z. et al. Construction and validation of a nomogram for hepatocellular carcinoma patients based on HCC-GRIm score. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 12013–12024 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05037-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05037-x