Abstract
Purpose
To assess the feasibility and prognostic value of minimal residual disease (MRD) evaluated by multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC) in newly diagnosed amyloid light chain (AL) amyloidosis.
Methods
Clinical data from 25 consecutive newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis patients with MRD data tested at 3 months after first-line therapy completion were retrospectively analysed in a single centre from 2012 to 2019. First-line therapy included 8 courses of VD or 4 courses of VD plus sequential autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), both without maintenance therapy.
Results
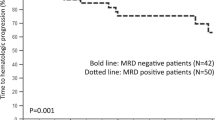
Of 25 patients with very good partial response (VGPR) or better, 19 (76%) achieved MRD negativity. Baseline characteristics were not different between MRD-negative and MRD-positive patients. More ASCT patients than non-ASCT patients (90.0% vs 53.3%, p = 0.043) achieved MRD negativity. In the MRD-negative and MRD-positive groups, cardiac response was observed in 93% and 25% (p = 0.019) and any organ response in 94% and 50%, respectively (p = 0.023). At a median follow-up of 25.1 months, MRD-negative patients showed significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) from diagnosis than MRD-positive patients (24.52 vs 76.39 months, p = 0.004).
Conclusions
MRD negativity measured by MFC at 3 months after first-line therapy completion in patients with AL amyloidosis is measurable and associated with improved organ response rates and PFS over a long follow-up.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Attal M, Lauwers-Cances V, Hulin C et al (2017) Lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone with transplantation for myeloma. N Engl J Med 376:1311–1320. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1611750
Dittrich T, Bochtler T, Kimmich C, Becker N, Jauch A, Goldschmidt H, Ho AD, Hegenbart U, Schonland SO (2017) AL amyloidosis patients with low amyloidogenic free light chain levels at first diagnosis have an excellent prognosis. Blood 130:632–642. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-02-767475
Gu J, Liu J, Chen M, Huang B, Li J (2018) Longitudinal flow cytometry identified “minimal residual disease” (MRD) evolution patterns for predicting the prognosis of patients with transplant-eligible multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 24:2568–2574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.07.040
Jelinek T, Bezdekova R, Zatopkova M, Burgos L, Simicek M, Sevcikova T, Paiva B, Hajek R (2018) Current applications of multiparameter flow cytometry in plasma cell disorders. Blood Cancer J 8:e621. https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2017.101
Kastritis E, Kostopoulos IV, Terpos E et al (2018) Evaluation of minimal residual disease using next-generation flow cytometry in patients with AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J 8:46. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-018-0086-3
Kastritis E, Kostopoulos IV, Theodorakakou F et al (2020) Next generation flow cytometry for MRD detection in patients with AL amyloidosis. Amyloid 28:19–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2020.1802713
Kaufman GP, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA et al (2015) Kinetics of organ response and survival following normalization of the serum free light chain ratio in AL amyloidosis. Am J Hematol 90:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.23898
Lee H, Duggan P, Neri P, Tay J, Bahlis NJ, Jimenez-Zepeda VH (2017) Minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment by flow cytometry after ASCT for AL amyloidosis: are we there yet? Bone Marrow Transplant 52:915–917. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2017.28
Merlini G, Stone MJ (2006) Dangerous small B-cell clones. Blood 108:2520–2530. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-03-001164
Merlini G, Dispenzieri A, Sanchorawala V, Schönland SO, Palladini G, Hawkins PN, Gertz MA (2018) Systemic immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:38. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0034-3
Muchtar E, Gertz MA, Kumar SK et al (2017a) Improved outcomes for newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis between 2000 and 2014: cracking the glass ceiling of early death. Blood 129:2111–2119. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-11-751628
Muchtar E, Jevremovic D, Dispenzieri A et al (2017b) The prognostic value of multiparametric flow cytometry in AL amyloidosis at diagnosis and at the end of first-line treatment. Blood 129:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-06-721878
Muchtar E, Dispenzieri A, Jevremovic D et al (2020) Survival impact of achieving minimal residual negativity by multi-parametric flow cytometry in AL amyloidosis. Amyloid 27:13–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2019.1666709
Munshi NC, Avet-Loiseau H, Rawstron AC, Owen RG, Child JA, Thakurta A, Sherrington P, Samur MK, Georgieva A, Anderson KC, Gregory WM (2017) Association of minimal residual disease with superior survival outcomes in patients with multiple myeloma: a meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 3:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.3160
Paiva B, Garcia-Sanz R, San Miguel JF (2016) Multiple myeloma minimal residual disease. Cancer Treat Res 169:103–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40320-5_7
Palladini G, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA et al (2012) New criteria for response to treatment in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis based on free light chain measurement and cardiac biomarkers: impact on survival outcomes. J Clin Oncol 30:4541–4549. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.37.7614
Rawstron AC, Child JA, de Tute RM et al (2013) Minimal residual disease assessed by multiparameter flow cytometry in multiple myeloma: impact on outcome in the Medical Research Council Myeloma IX Study. J Clin Oncol 31:2540–2547. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.46.2119
Sidana S, Tandon N, Dispenzieri A et al (2018) Clinical presentation and outcomes in light chain amyloidosis patients with non-evaluable serum free light chains. Leukemia 32:729–735. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.286
Sidana S, Muchtar E, Sidiqi MH et al (2020) Impact of minimal residual negativity using next generation flow cytometry on outcomes in light chain amyloidosis. Am J Hematol 95:497–502. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25746
Staron A, Burks EJ, Lee JC, Sarosiek S, Sloan JM, Sanchorawala V (2020) Assessment of minimal residual disease using multiparametric flow cytometry in patients with AL amyloidosis. Blood Adv 4:880–884. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001331
Szalat R, Sarosiek S, Havasi A, Brauneis D, Sloan JM, Sanchorawala V (2020) Organ responses after highdose melphalan and stem cell transplantation in AL amyloidosis. Leukemia 35:916–919. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-1006-7
Acknowledgements
We thank the research staff for recruiting patients to the study and for their involvement in patient recruitment, data collection, and data management.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by BH, JL, MC and JG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JL and XL and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Huang, B., Liu, J. et al. Clinical value of minimal residual disease assessed by multiparameter flow cytometry in amyloid light chain amyloidosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 913–919 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03653-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03653-z