Abstract
Purpose
F-box proteins, as components of the Skp1-Cullin 1-F-box protein (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligase, can specifically bind to substrates and regulate multiple tumor behaviors. However, the role of F-box proteins in squamous-cell lung carcinoma (SqCLC) has not been established.
Methods
We identified the differentially expressed F-box protein-encoding genes in SqCLC by analyzing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases. Prognosis data were evaluated using the Kaplan–Meier (KM) plotter website. The FBXO5 and FBXO45 mRNA levels were analyzed by real time RT-PCR. The impact of the inhibition of these genes with si-RNA on apoptosis and migration was also investigated.
Results
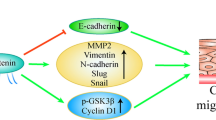
The FBXO45 and FBXO5 genes were significantly up-regulated in SqCLC compared with normal lung (p values = 0.002 and 0.025, respectively). FBXO45 was significantly elevated in each tumorigenic step, including dysplasia, in situ and SqCLC. The RT-PCR analysis results showed that FBXO5 and FBXO45 were elevated in cancer tissues (p values = 0.024 and 0.004, respectively). Overexpression of FBXO5 and FBXO45 was associated with shorter overall survival (OS) in the SqCLC patients from the K–M plotter database [FBXO5 HR: 1.53 (1.03–2.28), p = 0.036]; [FBXO45 HR: 1.47 (1.03–2.08), p = 0.030]. The GO and KEGG pathway analysis showed that FBXO5 and FBXO45 were associated with cell cycle and adhesion, respectively. Knockdown of FBXO5 leads to increased apoptosis, while knockdown of FBXO45 facilitates the process of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Conclusions
Our results provide evidence that FBXO45 and FBXO5 may play a key role in tumorigenesis and prognosis of SqCLC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abshire CF, Carroll JL, Dragoi AM (2016) FLASH protects ZEB1 from degradation and supports cancer cells’ epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogenesis 5:e254. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2016.55
Amm I, Sommer T, Wolf DH (2014) Protein quality control and elimination of protein waste: the role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1843:182–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.031
Barbash O, Diehl JA (2008) SCF (Fbx4/alphaB-crystallin) E3 ligase: when one is not enough. Cell Cycle 7:2983–2986. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.7.19.6775
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N (2012) Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 489:519–525 https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11404
Cerami E et al (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2:401–404. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
Cheng Y, Li G (2012) Role of the ubiquitin ligase Fbw7 in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-011-9330-z
Choi M et al (2017) Mutation profiles in early-stage lung squamous cell carcinoma with clinical follow-up and correlation with markers of immune function. Ann Oncol 28:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw437
Chung FZ, Sahasrabuddhe AA, Ma K, Chen X, Basrur V, Lim MS, Elenitoba-Johnson KS (2014) Fbxo45 inhibits calcium-sensitive proteolysis of N-cadherin and promotes neuronal differentiation. J Biol Chem 289:28448–28459. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.561241
Davis RJ, Welcker M, Clurman BE (2014) Tumor suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: mechanisms and opportunities. Cancer Cell 26:455–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.013
Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H, Xue Y (2014) HemI: a toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PloS One 9:e111988. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111988
Di Fiore B, Pines J (2008) Defining the role of Emi1 in the DNA replication-segregation cycle. Chromosoma 117:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-008-0152-x
Diaz VM, de Herreros AG (2016) F-box proteins: keeping the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in check. Semin Cancer Biol 36:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.10.003
Duan S et al (2012) FBXO11 targets BCL6 for degradation and is inactivated in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Nature 481:90–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10688
Edelmann MJ, Nicholson B, Kessler BM (2011) Pharmacological targets in the ubiquitin system offer new ways of treating cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and infectious diseases. Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e35. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1462399411002031
Ettinger DS et al (2017) Non-small cell lung cancer, version 5.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 15:504–535
Frescas D, Pagano M (2008) Deregulated proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and beta-TrCP: tipping the scales of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8:438–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2396
Gao M, Karin M (2005) Regulating the regulators: control of protein ubiquitination and ubiquitin-like modifications by extracellular stimuli. Mol Cell 19:581–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.08.017
Gao J et al (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 6:pl1. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2004088
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J, Lanczky A (2013) Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PloS One 8:e82241. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082241
Hebbar N, Burikhanov R, Shukla N, Qiu S, Zhao Y, Elenitoba-Johnson KSJ, Rangnekar VM (2017) A naturally generated decoy of the prostate apoptosis response-4 protein overcomes therapy resistance in tumors. Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1970
Heo J, Eki R, Abbas T (2016) Deregulation of F-box proteins and its consequence on cancer development, progression and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 36:33–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.015
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn923
Langer CJ et al (2016) Incremental innovation and progress in advanced squamous cell lung cancer: current status and future impact of treatment. J Thorac Oncol 11:2066–2081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.08.138
Lee J, Kim JA, Barbier V, Fotedar A, Fotedar R (2009) DNA damage triggers p21WAF1-dependent Emi1 down-regulation that maintains G2 arrest. Mol Biol Cell 20:1891–1902. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E08-08-0818
Liao SY et al (2017) CK1δ/GSK3β/FBXW7α axis promotes degradation of the ZNF322A oncoprotein to suppress lung cancer progression. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.168
Lu Y et al (2012) The F-box protein FBXO44 mediates BRCA1 ubiquitination and degradation. J Biol Chem 287:41014–41022. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.407106
Lu Y, Lee BH, King RW, Finley D, Kirschner MW (2015) Substrate degradation by the proteasome: a single-molecule kinetic analysis. Science 348:1250834. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1250834
Peschiaroli A, Scialpi F, Bernassola F, Pagano M, Melino G (2009) The F-box protein FBXO45 promotes the proteasome-dependent degradation of p73. Oncogene 28:3157–3166. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.177
Randle SJ, Laman H (2016) F-box protein interactions with the hallmark pathways in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 36:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.013
Reimann JD, Freed E, Hsu JY, Kramer ER, Peters JM, Jackson PK (2001) Emi1 is a mitotic regulator that interacts with Cdc20 and inhibits the anaphase promoting complex. Cell 105:645–655
Schwaederle M, Elkin SK, Tomson BN, Carter JL, Kurzrock R (2015) Squamousness: next-generation sequencing reveals shared molecular features across squamous tumor types. Cell Cycle 14:2355–2361. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2015.1053669
Shibue T, Weinberg RA (2017) EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.44
Shimizu N et al (2013) Selective enhancing effect of early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) depletion on the sensitivity of doxorubicin or X-ray treatment in human cancer cells. J Biol Chem 288:17238–17252. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.446351
Socinski MA et al (2016) Clinicopathologic features of advanced squamous NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 11:1411–1422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.05.024
Subramanian A et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Szklarczyk D et al (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D447–D452 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
Uddin S, Bhat AA, Krishnankutty R, Mir F, Kulinski M, Mohammad RM (2016) Involvement of F-BOX proteins in progression and development of human malignancies. Semin Cancer Biol 36:18–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.008
Uhlen M et al (2017) A pathology atlas of the human cancer ranscriptome. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan2507
Vaidyanathan S, Cato K, Tang L, Pavey S, Haass NK, Gabrielli BG, Duijf PH (2016) In vivo overexpression of Emi1 promotes chromosome instability and tumorigenesis. Oncogene 35:5446–5455. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.94
Wang Z, Liu P, Inuzuka H, Wei W (2014) Roles of F-box proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 14:233–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3700
Wang K et al (2016) The impact of ramucirumab on survival in patients with advanced solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized II/III controlled trials. Clin Drug Investig 36:27–39
Xu M et al (2015) Atypical ubiquitin E3 ligase complex Skp1-Pam-Fbxo45 controls the core epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors. Oncotarget 6:979–994. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2825
Xu W, Taranets L, Popov N (2016) Regulating Fbw7 on the road to cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 36:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.005
Yokobori T et al (2014) FBXW7 mediates chemotherapeutic sensitivity and prognosis in NSCLCs Molecular cancer research. MCR 12:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0341
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (8160101782), and Key Research and Development Plan of Shandong Province (2015GSF118063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jiajun Du declares that he has no conflict of interest. Kai Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xiao Qu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shaorui Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xudong Yang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Fenglong Bie declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yu Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Cuicui Huang declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the ethic community of Shandong Provincial Hospital and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2018_2653_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Mutation alterations of F-box proteins in all TCGA LUSC samples from cBioportal (S1A). Detailed mutations of FBXW7 were shown in S1B. Kaplan Meier curve from K–M plotter showed that over-expression of FBXW7 indicated a favorable prognosis (S1C) (TIF 2332 KB)
432_2018_2653_MOESM2_ESM.tif
The impact of differentially expressed F-box proteins on overall survival in I-IIIA resected SqCLC patients from TCGA database (FBXL6: A; FBXL19: B; FBXO5: C; FBXO17: D; FBXO27: E; FBXO32: F; FBXO41: G; FBXO43: H; FBXO45: I) (TIF 596 KB)
432_2018_2653_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of FBXO45 (S3A) and FBXO5 (S3B) in TCGA SqCLC database. GSEA analysis showed pathways enriched in high FBXO5 group (S3C), low FBXO45 group (S3D) and high FBXO45 group (S3E) (TIF 1194 KB)
432_2018_2653_MOESM4_ESM.tif
The expression of FBXO5 and FBXO45 was elevated in squamous lung cancer cell lines than lung adenocarcinoma cell lines (GSE57083, S4A). Protein expression of FBXO5 and FBXO45 in cell lines was shown in S4B. Immunohistochemical (IHC) images showed FBXO5 staining of pneumonocytes in normal lung tissues (Upper line) and FBXO5 staining in squamous lung cancer tissues (Bottom line, from left to right: not detected, weak staining, moderate/strong staining, S4E). Immunohistochemical (IHC) images showed FBXO45 staining of pneumonocytes in normal lung tissues (Upper line) and FBXO45 staining in squamous lung cancer tissues (Bottom line, from left to right: not detected, weak staining, moderate/strong staining, S4F). The quantitive scores were shown in S4C. Wound healing assay results showed the increased migration of FBXO5 knockdown group (bottom line) compared to negative group (upper line) at 0, 24, 48 hours (from left to right, S4D) (TIF 14462 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Qu, X., Liu, S. et al. Identification of aberrantly expressed F-box proteins in squamous-cell lung carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 1509–1521 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2653-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2653-1