Abstract
Purpose
We performed deep sequencing of target genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumors to identify somatic mutations that are associated with induction chemotherapy (IC) response.
Methods
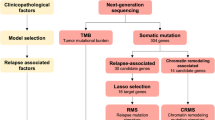
Patients who were diagnosed with HNSCC were retrospectively identified. Patients who were treated with IC were divided into two groups: good responders and poor responders by tumor response and progression-free survival. Targeted gene sequencing for 2404 somatic mutations of 44 genes was performed on HNSCC tissues. Mutations with total coverage of <500 were excluded, and the cutoff for altered allele frequency was >10 %.
Results
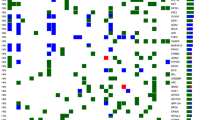
Of the 71 patients, 45 were treated upfront with IC. Mean total coverage was 1941 per locus, and 42.2 % of tumors had TP53 mutations. Thirty-three mutations in TP53, NOTCH3, FGFR2, FGFR3, ATM, EGFR, MET, PTEN, FBXW7, SYNE1, and SUFU were frequently altered in poor responders. Among the patients who were treated with IC, those with unfavorable genomic profiles had significantly poorer overall survival than those without unfavorable genomic profiles (hazard ratio 6.45, 95 % confidence interval 2.07–20.10, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Comprehensive analysis of mutation frequencies identified unfavorable genomic profiles, and the patients without unfavorable genomic profiles can obtain clinical benefits from IC in patients with HNSCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal N et al (2011) Exome sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma reveals inactivating mutations in NOTCH1. Science 333:1154–1157. doi:10.1126/science.1206923
Azuma K et al (2014) Association of PD-L1 overexpression with activating EGFR mutations in surgically resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 25:1935–1940. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu242
Byers LA et al (2013) An epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene signature predicts resistance to EGFR and PI3 K inhibitors and identifies Axl as a therapeutic target for overcoming EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin Cancer Res 19:279–290. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1558
Chung CH et al (2014) p16 Protein expression and human papillomavirus status as prognostic biomarkers of nonoropharyngeal head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 32:3930–3938. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.5228
Cohen EE et al (2014) Phase III randomized trial of induction chemotherapy in patients with N2 or N3 locally advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 32:2735–2743. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.6309
Eisenhauer EA et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Ghi MG et al (2014) Concomitant chemoradiation (CRT) or cetuximab/RT (CET/RT) versus induction Docetaxel/Cisplatin/5-Fluorouracil (TPF) followed by CRT or CET/RT in patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck (LASCCHN). A randomized phase III factorial study (NCT01086826). J Clin Oncol 32:(suppl; abstr 6004)
Gronhoj Larsen C et al (2014) Correlation between human papillomavirus and p16 overexpression in oropharyngeal tumours: a systematic review. Br J Cancer 110:1587–1594. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.42
Haddad R et al (2013) Induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy (sequential chemoradiotherapy) versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in locally advanced head and neck cancer (PARADIGM): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:257–264. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70011-1
Han JY et al (2014) Comparison of targeted next-generation sequencing with conventional sequencing for predicting the responsiveness to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy in never-smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 85:161–167. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.04.009
Hitt R et al (2014) A randomized phase III trial comparing induction chemotherapy followed by chemoradiotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy alone as treatment of unresectable head and neck cancer. Ann Oncol 25:216–225. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt461
Hoadley KA et al (2014) Multiplatform analysis of 12 cancer types reveals molecular classification within and across tissues of origin. Cell 158:929–944. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.049
Hudson AM et al (2014) Discrepancies in cancer genomic sequencing highlight opportunities for driver mutation discovery. Cancer Res 74:6390–6396. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1020
India Project Team of the International Cancer Genome C (2013) Mutational landscape of gingivo-buccal oral squamous cell carcinoma reveals new recurrently-mutated genes and molecular subgroups. Nat Commun 4:2873. doi:10.1038/ncomms3873
Keck MK et al (2015) Integrative analysis of head and neck cancer identifies two biologically distinct HPV and three non-HPV subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 21:870–881. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2481
Lechner M et al (2013) Targeted next-generation sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma identifies novel genetic alterations in HPV+ and HPV− tumors. Genome Med 5:49. doi:10.1186/gm453
Lefebvre JL, Chevalier D, Luboinski B, Kirkpatrick A, Collette L, Sahmoud T (1996) Larynx preservation in pyriform sinus cancer: preliminary results of a European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial. EORTC Head and Neck Cancer Cooperative Group. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:890–899
Lim Y et al (2013) Clinical outcomes of radiation-based locoregional therapy in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients not responding to induction chemotherapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 116:55–60. doi:10.1016/j.oooo.2013.02.007
Ock CY et al (2014) Effect of induction chemotherapy on survival in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy: single center experience. Head Neck. doi:10.1002/hed.23891
Pickering CR et al (2013) Integrative genomic characterization of oral squamous cell carcinoma identifies frequent somatic drivers. Cancer Discov 3:770–781. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0537
Riaz N, Morris LG, Lee W, Chan TA (2014) Unraveling the molecular genetics of head and neck cancer through genome-wide approaches. Genes Dis 1:75–86. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2014.07.002
Rischin D et al (2010) Prognostic significance of p16INK4A and human papillomavirus in patients with oropharyngeal cancer treated on TROG 02.02 phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 28:4142–4148. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.29.2904
Seiwert TY et al (2015) Integrative and comparative genomic analysis of HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 21:632–641. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3310
Singh RR et al (2013) Clinical validation of a next-generation sequencing screen for mutational hotspots in 46 cancer-related genes. J Mol Diagn JMD 15:607–622. doi:10.1016/j.jmoldx.2013.05.003
Stransky N et al (2011) The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science 333:1157–1160. doi:10.1126/science.1208130
Vrieling H, Thijssen JC, Rossi AM, van Dam FJ, Natarajan AT, Tates AD, van Zeeland AA (1992) Enhanced hprt mutant frequency but no significant difference in mutation spectrum between a smoking and a non-smoking human population. Carcinogenesis 13:1625–1631
Wittekindt C, Wagner S, Mayer CS, Klussmann JP (2012) Basics of tumor development and importance of human papilloma virus (HPV) for head and neck cancer. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. doi:10.3205/cto000091
Wolf GT, Hong WK, Fisher SG (1991) Induction chemotherapy plus radiation compared with surgery plus radiation in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer. The Department of Veterans Affairs Laryngeal Cancer Study Group. N Engl J Med 324:1685–1690. doi:10.1056/NEJM199106133242402
Zhang W et al (2014) Whole genome sequencing of 35 individuals provides insights into the genetic architecture of Korean population. BMC Bioinform 15(Suppl 11):S6. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-15-S11-S6
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and their families who generously donated valuable tissue samples.
Funding
This study was supported by SNUH Research Fund (Grant Nos. 04-2013-0760 and 30-2013-0070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (approval number: H-1307-051-504) and was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
For the patients diagnosed before January 31, 2013, the institutional review board approved the waiver of informed consent for this retrospective analysis according to Bioethics and Safety Act of Korea. For the patients diagnosed after February 1, 2013, we obtained informed consents from the patients.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ock, CY., Son, B., Keam, B. et al. Identification of genomic mutations associated with clinical outcomes of induction chemotherapy in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 873–883 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2083-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2083-2