Abstract
Purpose
Musculoskeletal pain is a common side effect of aromatase inhibitors (AIs), the adjuvant hormonal treatment of choice for postmenopausal estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Although the pain is usually attributed to the estrogen depletion associated with AIs, not all women on AIs experience these symptoms. Thus, the goal of this study was to examine whether changes in the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis were associated with pain among women initiating AI therapy or a comparison group of women without a history of cancer.
Methods
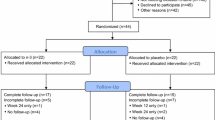
Data were analyzed from a cohort study of 52 breast cancer patients for whom AI therapy was planned and 88 women without a history of cancer. Questionnaire data on pain symptoms were collected, and blood was drawn at baseline (prior to AI therapy for patients) and 6 months after baseline. The blood samples were assayed for IGF-1 and IGF-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3).
Results
While results showed no statistically significant changes in any of the measures across time for either the breast cancer or the comparison group, increases in both IGF-1 concentrations and the IGF-1/IGFBP-3 ratio over the first 6 months of AI treatment were significantly associated with the onset or increase in musculoskeletal pain among the breast cancer patients. Associations between IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and the IGF-1/IGFBP-3 ratio and pain were not observed in the comparison group.
Conclusions
Although preliminary, findings from this study implicate the IGF axis in the development of AI-associated musculoskeletal pain and represent a first step in developing effective interventions to alleviate this side effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajetta E, Ferrari L, Celio L, Mariani L, Miceli R, Di Leo A et al (1997) The aromatase inhibitor letrozole in advanced breast cancer: effects on serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3 levels. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 63:261–267
Bellantoni MF, Vittone J, Campfield AT, Bass KM, Harman SM, Blackman MR (1996) Effects of oral versus transdermal estrogen on the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis in younger and older postmenopausal women: a clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:2848–2853
Blackman MR, Sorkin JD, Munzer T, Bellantoni MF, Busby-Whitehead J, Stevens TE et al (2002) Growth hormone and sex steroid administration in healthy aged women and men: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288:2282–2292
Cigler T, Tu D, Yaffe MJ, Findlay B, Verma S, Johnston D, Richardson H, Hu H, Qi S, Goss PE (2010) A randomized, placebo-controlled trial (NCIC CTG MAP1) examining the effects of letrozole on mammographic breast density and other end organs in postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120:427–435
Coates AS, Keshaviah A, Thurlimann B, Mouridsen H, Mauriac L, Forbes JF et al (2007) Five years of letrozole compared with tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: update of study BIG 1–98. J Clin Oncol 25:486–492
Coombes RC, Hall E, Gibson LJ, Paridaens R, Jassem J, Delozier T et al (2004) A randomized trial of exemestane after 2–3 years of tamoxifen therapy in postmenopausal women with primary breast cancer. N Engl J Med 350:1081–1092
Coombes RC, Kilburn LS, Snowdon CF, Paridaens R, Coleman RE, Jones SE et al (2007) Survival and safety of exemestane versus tamoxifen after 2–3 years’ tamoxifen treatment (Intergroup exemestane study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 369:559–570
Corpas E, Harman SM, Blackman MR (1993) Human growth hormone and human aging. Endocr Rev 14:20–39
Decensi A, Robertson C, Viale G, Pigatto F, Johansson H, Kisanga ER et al (2003) A randomized trial of low-dose tamoxifen on breast cancer proliferation and blood estrogenic biomarkers. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:779–790
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 365:1687–1717
Ferrari L, Martinetti A, Zilembo N, Pozzi P, Buzzoni R, La Torre I et al (2002) Short-term effects of anastrozole treatment on insulin-like growth factor system in postmenopausal advanced breast cancer patients. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 80:411–418
Frost VJ, Helle SI, Lonning PE, van der Stappen JW, Holly JM (1996) Effects of treatment with megestrol acetate, aminoglutethimide, or formestane on insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I and II, IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs), and IGFBP-3 protease status in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:2216–2221
Goss PE (2007) Letrozole in the extended adjuvant setting: MA.17. Breast Cancer Res Treat 105:45–53
Goss PE, Ingle JN, Ales-Martinez JE, Cheung AM, Chlebowski RT, Wactawski-Wende J et al (2011) Exemestane for breast-cancer prevention in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med 364:2381–2391
Hadji P, Kieback DG, Tams J, Hasenburg A, Ziller M (2012) Correlation of treatment-emergent adverse events and clinical response to endocrine therapy in early breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of the German cohort of TEAM. Ann Oncol 23:2566–2572
Helle SI, Omsjo IH, Hughes SC, Botta L, Huls G, Holly JM, Lonning PE (1996) Effects of oral and transdermal oestrogen replacement therapy on plasma levels of insulin-like growth factors and IGF binding proteins 1 and 3: a cross-over study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 45:727–732
Helzlsouer KJ, Gallicchio L, MacDonald R, Wood B, Rushovich E (2012) A prospective study of aromatase inhibitor therapy, vitamin D, C-reactive protein and musculoskeletal symptoms. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131:277–285
Henry NL, Giles JT, Stearns V (2008) Aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal symptoms: etiology and strategies for management. Oncology (Williston Park) 22:1401–1408
Holmes MD, Pollak MN, Hankinson SE (2002) Lifestyle correlates of plasma insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 concentrations. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:862–867
Hou X, Huang F, Macedo LF, Harrington SC, Reeves KA, Greer A, Finckenstein FG, Brodie A, Gottardis MM, Carboni JM, Haluska P (2011) Dual IGF-1R/InsR inhibitor BMS-754807 synergizes with hormonal agents in treatment of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Cancer Res 71:7597–7607
Howell A, Cuzick J, Baum M, Buzdar A, Dowsett M, Forbes JF et al (2005) Results of the ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination) trial after completion of 5 years’ adjuvant treatment for breast cancer. Lancet 365:60–62
Janssen YJ, Helmerhorst F, Frolich M, Roelfsema F (2000) A switch from oral (2 mg/day) to transdermal (50 μg/day) 17beta-estradiol therapy increases serum insulin-like growth factor-I levels in recombinant human growth hormone (GH)-substituted women with GH deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:464–467
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16:3–34
Laroche M, Borg S, Lassoued S, De Lafontan B, Roche H (2007) Joint pain with aromatase inhibitors: abnormal frequency of Sjogren’s syndrome. J Rheumatol 34:2259–2263
Lien EA, Johannessen DC, Aakvaag A, Lonning PE (1992) Influence of tamoxifen, aminoglutethimide and goserelin on human plasma IGF-I levels in breast cancer patients. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 41:541–543
Lintermans A, Neven P (2011) Pharmacology of arthralgia with estrogen deprivation. Steroids 76:781–785
Lintermans A, Van CB, Van HM, Pans S, Verhaeghe J, Westhovens R et al (2011) Aromatase inhibitor-induced loss of grip strength is body mass index dependent: hypothesis-generating findings for its pathogenesis. Ann Oncol 22:1763–1769
Litton JK, Arun BK, Brown PH, Hortobagyi GN (2012) Aromatase inhibitors and breast cancer prevention. Expert Opin Pharmacother 13:325–331
Presant CA, Bosserman L, Young T, Vakil M, Horns R, Upadhyaya G, Ebrahimi B, Yeon C, Howard F (2007) Aromatase inhibitor-associated arthralgia and/or bone pain: frequency and characterization in non-clinical trial patients. Clin Breast Cancer 7:775–778
Raudaskoski T, Knip M, Laatikainen T (1998) Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding proteins 1 and 3 during continuous nonoral and oral combined hormone replacement therapy. Menopause 5:217–222
Shanmugam VK, McCloskey J, Elston B, Allison SJ, Eng-Wong J (2012) The CIRAS study: a case control study to define the clinical, immunologic, and radiographic features of aromatase inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal symptoms. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131:699–708
Thurlimann B, Keshaviah A, Coates AS, Mouridsen H, Mauriac L, Forbes JF et al (2005) A comparison of letrozole and tamoxifen in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353:2747–2757
Weroha SJ, Haluska P (2008) IGF-1 receptor inhibitors in clinical trials–early lessons. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13:471–483
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (R03 CA132147), AstraZeneca (IRUSANAS0073), and the Susan G. Komen for the Cure Foundation (POP0601174). Dr. Gallicchio is supported, in part, by a Career Catalyst Research Grant from Susan G. Komen for the Cure Foundation (KG110356).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallicchio, L., MacDonald, R. & Helzlsouer, K.J. Insulin-like growth factor 1 and musculoskeletal pain among breast cancer patients on aromatase inhibitor therapy and women without a history of cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 837–843 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1391-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1391-7