Abstract
Purpose
Lung is a common site for the occurrence of melanoma metastasis, the mechanism by which primary melanoma affects the lungs before tumor cells arrival is poorly understood. The aim of this study was to explore lung microenvironment response to primary melanoma in the premetastatic phase.
Methods
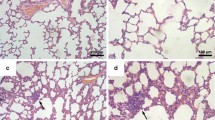
Melanoma cells (B16) were implanted into the Balb/c mice back, pulmonary inflammation response was analyzed by wet/dry ratios and H&E staining, the relationship between inflammation cells and metastatic foci was analyzed by bone marrow transplant mouse model, pulmonary vasculature was further analyzed by whole mount staining, and the circulating levels of proinflammatory cytokines in sera were evaluated by mouse cytokine array.
Results
In the premetastatic stage, significant inflammation response in lungs was induced by a distant primary melanoma, inflammation cells colonize in premetastatic sites before tumor cells arrived, and the sites of inflammation cells clusters are tumor metastasis sites. VEGF, M-CSF and TNF-α may be the underlying factors responsible for the increased metastasis in the B16-bearing mice. Treatment with celecoxib had effects on inflammation response and reduced cancer metastasis.
Conclusions
In the premetastatic phase, the melanoma induces pulmonary inflammation response, changes the lung environment and then facilitates lung metastasis. Thus, inhibition of lung inflammation may provide potential targets for the prevention of metastasis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkan D, Green JE, Chambers AF (2010) Extracellular matrix: a gatekeeper in the transition from dormancy to metastatic growth. Eur J Cancer 46:1181–1188
Dawson MR, Duda DG, Chae SS, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2009a) VEGFR1 activity modulates myeloid cell infiltration in growing lung metastases but is not required for spontaneous metastasis formation. PLoS ONE 4:e6525
Dawson MR, Duda DG, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2009b) VEGFR1 activity independent metastasis formation. Nature 461:E4–E5
DeNardo DG, Coussens LM (2007) Inflammation and breast cancer. Balancing immune response: crosstalk between adaptive and innate immune cells during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res 9:212
Du R, Lu KV, Petritsch C, Liu P, Ganss R, Passegué E, Song H, Vandenberg S, Johnson RS, Werb Z, Bergers G (2008) HIF1α induces the recruitment of bone marrow-derived vascular modulatory cells to regulate tumor angiogenesis and invasion. Cancer Cell 13:206–220
Duda DG, Cohen KS, Kozin SV, Perentes JY, Fukumura D, Scadden DT, Jain RK (2006) Evidence for incorporation of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells into perfused blood vessels in tumors. Blood 107:2774–2776
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Cox TR, Lang G, Bird D, Koong A, Le QT, Giaccia AJ (2009) Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell 15:35–44
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Fidler IJ (2003) The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3:453–458
Fridlender ZG, Sun J, Kim S, Kapoor V, Cheng G, Ling L (2009) Polarization of tumor associated neutrophil (TAN) phenotype by TGF-beta: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell 16:183–194
Gassmann P, Haier J, Schlüter K, Domikowsky B, Wendel C, Wiesner U, Kubitza R, Engers R, Schneider SW, Homey B, Müller A (2009) CXCR4 regulates the early extravasation of metastatic tumor cells in vivo. Neoplasia 11:651–661
Gerber PA, Hippe A, Buhren BA, Müller A, Homey B (2009) Chemokines in tumor-associated angiogenesis. Biol Chem 390:1213–1223
Gupta GP, Massague J (2006) Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell 127:679–695
Gupta GP, Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Bos PD, Kim JY, Nadal C, Gomis RR, Manova-Todorova K, Massagué J (2007) Mediators of vascular remodeling co-opted for sequential steps in lung metastasis. Nature 446:765–770
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H, Maru Y (2006) Tumor-mediated up-regulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 8:1369–1375
Hiratsuka S, Goel S, Kamoun WS, Maru Y, Fukumura D, Duda DG, Jain RK (2011) Endothelial focal adhesion kinase mediates cancer cell homing to discrete regions of the lungs via E-selectin up-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:3725–3830
Huang Y, Song N, Ding Y, Yuan S, Li X, Cai H, Shi H, Luo Y (2009) Pulmonary vascular destabilization in the premetastatic phase facilitates lung metastasis. Cancer Res 69:7529–7537
Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S, Bramley AH, Vincent L, Costa C, MacDonald DD, Jin DK, Shido K, Kerns SA, Zhu Z, Hicklin D, Wu Y, Port JL, Altorki N, Port ER, Ruggero D, Shmelkov SV, Jensen KK, Rafii S, Lyden D (2005) VEGFR1 positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 438:820–827
Kim S, Takahashi H, Lin WW, Descargues P, Grivennikov S, Kim Y, Luo JL, Karin M (2009) Carcinoma-produced factors activate myeloid cells through TLR2 to stimulate metastasis. Nature 457:102–106
Kitamura T, Kometani K, Hashida H, Matsunaga A, Miyoshi H, Hosogi H, Aoki M, Osima M, Hattori M, Takabayashi A, Minato N, Taketo MM (2007) SMAD4- deficient intestinal tumors recruit CCR1+ myeloid cells that promote invasion. Nat Genet 39:467–475
Langley RR, Fidler IJ (2010) The seed and soil hypothesis revisited-the role of tumor-stroma interactions in metastasis to different organs. Int J Cancer 128:2527–2535
Lee CG, Link H, Baluk P, Homer RJ, Chapoval S, Bhandari V, Kang MJ, Cohn L, Kim YK, McDonald DM, Elias JA (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces remodeling and enhances TH2-mediated sensitization and inflammation in the lung. Nat Med 10:1095–1103
Lichtenberger BM, Tan PK, Niederleithner H, Ferrara N, Petzelbauer P, Sibilia M (2010) Autocrine VEGF signaling synergizes with EGFR in tumor cells to promote epithelial cancer development. Cell 140:268–279
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454:436–444
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL, Massagué J (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436:518–524
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB, Lewis CE (2008) The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 8:618–631
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9:274–284
Nozawa H, Chiu C, Hanahan D (2006) Infiltrating neutrophils mediate the initial angiogenic switch in a mouse model of multistage carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12493–12498
Olkhanud PB, Baatar D, Bodogai M, Hakim F, Gress R, Anderson RL, Deng J, Xu M, Briest S, Biragyn A (2009) Breast cancer lung metastasis requires expression of chemokine receptor CCR4 and regulatory T cells. Cancer Res 69:5996–6004
Padua D, Zhang XH, Wang Q, Nadal C, Gerald WL, Gomis RR, Massaque J (2008) TGFβ primes breast tumors for lung metastasis seeding through angiopoietin-like 4. Cell 133:66–77
Pollard JW (2003) Tumour educated macrophages promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 4:71–78
Serafini P, Borrello I, Bronte V (2006) Myeloid suppressor cells in cancer: recruitment, phenotype, properties, and mechanisms of immune suppression. Semin Cancer Biol 16:53–65
Shojaei F, Wu X, Malik AK, Zhong C, Baldwin ME, Schanz S, Fuh G, Gerber HP, Ferrara N (2007) Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b+ Gr1+ myeloid cells. Nat Biotechnol 25:911–920
Solinas G, Marchesi F, Garlanda C, Mantovani A, Allavena P (2010) Inflammation- mediated promotion of invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29:243–248
Steeg PS (2006) Tumor metastasis mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med 12:895–904
Stockmann C, Doedens A, Weidemann A, Zhang N, Takeda N, Greenberg JI, Cheresh DA, Johnson RS (2008) Deletion of vascular endothelial growth factor in myeloid cells accelerates tumorigenesis. Nature 456:814–818
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil A, Aakre M, Carbone DP, Matrisian LM, Richmond A, Lin PC, Moses HL (2008) Abrogation of TGFβ signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1+ CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 13:23–35
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by General programs of Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. BS2009SW050) and Key Development Program for Basic Research of Shandong Province (2007GG20002007).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, M., Xu, J., Bi, Y. et al. Primary tumor regulates the pulmonary microenvironment in melanoma carcinoma model and facilitates lung metastasis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 57–65 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1299-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1299-7