Abstract
Objective
Abrogation of the function of TP53 gene is supposed to lead to a more aggressive breast cancer phenotype that produces a less favorable clinical outcome. The p21 gene on chromosome 6p21.2 can be stimulated by an activated TP53 gene. A product of transcription, the p21 protein, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases, has its function in gene repair and angiogenesis during cell division, and can regulate apoptosis. The purpose of this analysis was to examine for an association between the genotypes measured on two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located within the TP53 and p21 genes.
Methods
In a clinical epidemiological case–control study, 814 individuals were recruited. 550 samples (275 cases/275 control) of peripheral blood obtained from women (aged 22–87 years) with breast cancer and from healthy women (aged 23–87 years) were genotyped for frequencies of the following gene variances: R72P/rs1042522 (gene TP53) and S31R/ss4388499 (gene p21).
Results
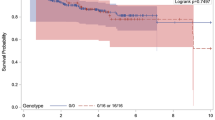
For the variance in gene TP53 no significant differences between the control group and women with breast cancer could be estimated. For the variance in gene p21 a statistically significant association between the SNP measured within p21 and breast cancer status was observed. The odds ratio for the increased risk for those carrying the CA genotype as opposed to the CC genotype is 1.74 (95% confidence ratio = 1.00–3.05).
Conclusion
Despite this finding p21 does not appear to act as an exclusive prognostic marker for breast cancer disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asada M, Yamada T, Ichijo H, Delia D, Miyazono K, Fukumuro K, Mizutani S (1999) Apoptosis inhibitory activity of cytoplasmic p21(Cip1/WAF1) in monocytic differentiation 2. EMBO J 18:1223–1234
Bahl R, Arora S, Nath N, Mathur M, Shukla NK, Ralhan R (2000) Novel polymorphism in p21(waf1/cip1) cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor gene: association with human esophageal cancer. Oncogene 19:323–328
Baker SJ, Fearon ER, Nigro JM, Hamilton SR, Preisinger AC, Jessup JM, van Tuinen P, Ledbetter DH, Baker DF, Nakamura Y, White R, Vogelstein B (1989) Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science 244:217–221
Bansal A, van den Boom D, Kammerer S, Honisch C, Adam G, Cantor CR, Kleyn P, Braun A (2002) Association testing by DNA pooling: an effective initial screen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16871–16874
Buetow KH, Edmonson M, MacDonald R, Clifford R, Yip P, Kelley J, Little DP, Strausberg R, Koester H, Cantor CR, Braun A (2001) High-throughput development and characterization of a genome wide collection of gene-based single nucleotide polymorphism markers by chip-based matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:581–584
Calabretta B, Kaczmarek L, Selleri L, Torelli G, Ming PM, Ming SC, Mercer WE (1986) Growth-dependent expression of human Mr 53,000 tumor antigen messenger RNA in normal and neoplastic cells. Cancer Res 46:5738–5742
Castells A, Puig P, Móra J, Boadas J, Boix L, Urgell E, Solé M, Capellà G, Lluis F, Fernández-Cruz L, Navarro S, Farré A (1999) K-ras mutations in DNA extracted from the plasma of patients with pancreatic carcinoma: diagnostic utility and prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol 17:578–584
Chedid M, Michieli P, Lengel C, Huppi K, Givol D (1994) A single nucleotide substitution at codon 31 (Ser/Arg) defines a polymorphism in a highly conserved region of the p53-inducible gene WAF1/CIP1. Oncogene 9:3021–3024
Crook T, Crossland S, Crompton MR, Osin P, Gusterson BA (1997) P53 mutations in BRCA1-associated familial breast cancer. Lancet 350:638–639
Deppert W, Buschhausen-Denker G, Patschinsky T, Steinmeyer K (1990) Cell cycle control of p53 in normal (3T3) and chemically transformed (Meth A) mouse cells II. Requirement for cell cycle progression. Oncogene 5:1701–1706
Doll R, Peto R (1981) The causes of cancer: quantitative estimates of avoidable risks of cancer in the United States today. J Natl Cancer Inst 66:1191–1308
Dunning AM, Healey CS, Pharoah PD, Teare MD, Ponder BA, Easton DF (1999) A systematic review of genetic polymorphisms and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 8:843–854
el Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1993) WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75:817–825
Field JK, Spandidos DA (1990) The role of ras and myc oncogenes in human solid tumours and their relevance in diagnosis and prognosis (review) 1. Anticancer Res 10:1–22
Gulbis B, Galand P (1993) Immunodetection of the p21-ras products in human normal and preneoplastic tissues and solid tumors: a review. Hum Pathol 24:1271–1285
Hachiya T, Kuriaki Y, Ueoka Y, Nishida J, Kato K, Wake N (1999) WAF1 genotype and endometrial cancer susceptibility. Gynecol Oncol 72:187–192
Hoyal CR, Kammerer S, Roth RB, Reneland R, Marnellos G, Kiechle M, Schwarz-Boeger U, Griffiths LR, Ebner F, Rehbock J, Nelson MR, Braun A (2005) Genetic polymorphisms in DPF3 associated with risk of breast cancer and lymph node metastases. J Carcinog 4:13
Kammerer S, Roth RB, Reneland R, Marnellos G, Hoyal CR, Markward NJ, Ebner F, Kiechle M, Schwarz-Boeger U, Griffiths LR, Ulbrich C, Chrobok K, Forster G, Praetorius GM, Meyer P, Rehbock J, Cantor CR, Nelson MR, Braun A (2004) Large-scale association study identifies ICAM gene region as breast and prostate cancer susceptibility locus. Cancer Res 64:8906–8910
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Craig RW (1991) Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res 51:6304–6311
Kaul R, Mukherjee S, Ahmed F, Bhat MK, Chhipa R, Galande S, Chattopadhyay S (2003) Direct interaction with and activation of p53 by SMAR1 retards cell-cycle progression at G2/M phase and delays tumor growth in mice. Int J Cancer 103:606–615
Keshava C, Frye BL, Wolff MS, McCanlies EC, Weston A (2002) Waf-1 (p21) and p53 polymorphisms in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:127–130
Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB (1992) Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7491–7495
Lavigueur A, Maltby V, Mock D, Rossant J, Pawson T, Bernstein A (1989) High incidence of lung, bone, and lymphoid tumors in transgenic mice overexpressing mutant alleles of the p53 oncogene. Mol Cell Biol 9:3982–3991
Li Y, Dowbenko D, Lasky LA (2002) AKT/PKB phosphorylation of p21Cip/WAF1 enhances protein stability of p21Cip/WAF1 and promotes cell survival 1. J Biol Chem 277:11352–11361
Lukas J, Groshen S, Saffari B, Niu N, Reles A, Wen WH, Felix J, Jones LA, Hall FL, Press MF (1997) WAF1/Cip1 gene polymorphism and expression in carcinomas of the breast, ovary, and endometrium. Am J Pathol 150:167–175
Malkin D, Li FP, Strong LC, Fraumeni JF Jr, Nelson CE, Kim DH, Kassel J, Gryka MA, Bishoff FZ, Tainsky MA et al (1990) Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science 250:1233–1238
McCubrey JA, Abrams SL, Ligresti G, Misaghian N, Wong EW, Steelman LS, Bäsecke J, Troppmair J, Libra M, Nicoletti F, Molton S, McMahon M, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM (2008) Involvement of p53 and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in hematopoietic drug resistance. Leukemia 22:2080–2090
Mercer WE, Avignolo C, Baserga R (1984) Role of the p53 protein in cell proliferation as studied by microinjection of monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol 4:276–281
Milner J, McCormick F (1980) Lymphocyte stimulation: concanavalin A induces the expression of a 53 K protein. Cell Biol Int Rep 4:663–667
Osin PP, Lakhani SR (1999) The pathology of familial breast cancer: Immunohistochemistry and molecular analysis. Breast Cancer Res 1:36–40
Packer BR, Yeager M, Burdett L, Welch R, Beerman M, Qi L, Sicotte H, Staats B, Acharya M, Crenshaw A, Eckert A, Puri V, Gerhard DS, Chanock SJ (2006) SNP500Cancer: a public resource for sequence validation, assay development, and frequency analysis for genetic variation in candidate genes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:617–621
Powell BL, van Staveren IL, Roosken P, Grieu F, Berns EM, Iacopetta B (2002) Associations between common polymorphisms in TP53 and p21WAF1/Cip1 and phenotypic features of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 23:311–315
Reich NC, Levine AJ (1984) Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature 308:199–201
Sauer H (ed) Manual Mammakarzinom 2005, Tumorzentrum München, Zuckschwert Verlag München, Wien, New York
Shohat O, Greenberg M, Reisman D, Oren M, Rotter V (1987) Inhibition of cell growth mediated by plasmids encoding p53 anti-sense. Oncogene 1:277–283
Silva JM, Dominguez G, Garcia JM, Gonzalez R, Villanueva MJ, Navarro F, Provencio M, San Martin S, Espana P, Bonilla F (1999) Presence of tumor DNA in plasma of breast cancer patients: clinicopathological correlations. Cancer Res 59:3251–3256
Själander A, Birgander R, Hallmans G, Cajander S, Lenner P, Athlin L, Beckman G, Beckman L (1996) p53 polymorphisms and haplotypes in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 17:1313–1316
Soehnge H, Ouhtit A, Ananthaswamy HN (1997) Mechanisms of induction of skin cancer by UV radiation. Front Biosci 2:d538–d551
Steinmeyer K, Maacke H, Deppert W (1990) Cell cycle control by p53 in normal (3T3) and chemically transformed (Meth A) mouse cells. I. Regulation of p53 expression. Oncogene 5:1691–1699
Takahashi T, Nau MM, Chiba I, Birrer MJ, Rosenberg RK, Vinocour M, Levitt M, Pass H, Gazdar AF, Mima JD (1989) p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science 246:491–494
The Breast Cancer Association Consortium (2006) Commonly studies single-nucleotide polymorphisms and breast cancer: results from the breast cancer association consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1382–1396
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Kern SE, Preisinger AC, Leppert M, Nakamura Y, White R, Smits AM, Bos JL (1988) Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med 319:525–532
Weiss RH, Marshall D, Howard L, Corbacho AM, Cheung AT, Sawai ET (2003) Suppression of breast cancer growth and angiogenesis by an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide to p21(Waf1/Cip1). Cancer Lett 189:39–48
Yair D, Ben Baruch G, Chetrit A, Friedman T, Hirsh Yechezkel G, Gotlieb WH, Fishman A, Beller U, Bar-Am A, Fishman E (2000) p53 and WAF1 polymorphisms in Jewish-Israeli women with epithelial ovarian cancer and its association with BRCA mutations. BJOG 107:849–854
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the staff of the I Frauenklinik, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, for their excellent contributions and Dr.rer.nat. Dr.med. Andreas Braun and Dr.rer.nat. Stephan Kammerer, Sequenom Inc. San Diego, CA, USA, for all their outstanding help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebner, F., Schremmer-Danninger, E. & Rehbock, J. The role of TP53 and p21 gene polymorphisms in breast cancer biology in a well specified and characterized German cohort. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 1369–1375 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0788-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0788-9