Abstract
Purpose
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) is a transcription factor and a tumor suppressor. We aimed to assess its protein expression and prognostic value in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study on 50 HCC patients and performed immunohistochemistry against C/EBPα on tumors and adjacent nontumor specimens. Relationships of C/EBPα expression with clinical parameters and patient survival were analyzed.
Results
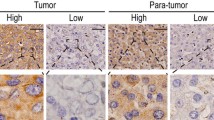
C/EBPα expression was not influenced by chronic alcohol exposure, viral hepatitis, or cirrhosis, but was reduced in 60% of HCC. Reduction of C/EBPα was associated with advanced tumor stage (P = 0.001). Patients with markedly reduced C/EBPα expression had a significantly shorter survival with a hazard ratio of 5.45 (95% confidence interval, 1.93–15.40; P = 0.001).
Conclusions
C/EBPα may be a potential prognostic marker or therapeutic target in HCC regardless of different etiology.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Joint Committee on Cancer (1997) AJCC cancer staging manual. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Bennett KL, Hackanson B, Smith LT, Morrison CD, Lang JC, Schuller DE et al (2007) Tumor suppressor activity of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha is epigenetically down-regulated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 67:4657–4664. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4793
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R (2004) Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 127:S5–S16. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.09.011
Bridle K, Cheung TK, Murphy T, Walters M, Anderson G, Crawford DG et al (2006) Hepcidin is down-regulated in alcoholic liver injury: implications for the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:106–112. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00002.x
Costa DB, Li S, Kocher O, Feins RH, Keller SM, Schiller JH et al (2007) Immunohistochemical analysis of C/EBPalpha in non-small cell lung cancer reveals frequent down-regulation in stage II and IIIA tumors: a correlative study of E3590. Lung Cancer 56:97–103. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.11.023
D’Alo F, Johansen LM, Nelson EA, Radomska HS, Evans EK, Zhang P et al (2003) The amino terminal and E2F interaction domains are critical for C/EBP alpha-mediated induction of granulopoietic development of hematopoietic cells. Blood 102:3163–3171. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-02-0479
Datta J, Majumder S, Kutay H, Motiwala T, Frankel W, Costa R et al (2007) Metallothionein expression is suppressed in primary human hepatocellular carcinomas and is mediated through inactivation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling cascade. Cancer Res 67:2736–2746. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4433
Diehl AM, Johns DC, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Yin M, Matelis LA et al (1996) Adenovirus-mediated transfer of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha identifies a dominant antiproliferative role for this isoform in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 271:7343–7350. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.13.7343
Farazi PA, DePinho RA (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer 6:674–687. doi:10.1038/nrc1934
Flodby P, Antonson P, Barlow C, Blanck A, Porsch-Hallstrom I, Xanthopoulos KG (1993) Differential patterns of expression of three C/EBP isoforms, HNF-1, and HNF-4 after partial hepatectomy in rats. Exp Cell Res 208:248–256. doi:10.1006/excr.1993.1244
Flodby P, Barlow C, Kylefjord H, AhrlundRichter L, Xanthopoulos KG (1996) Increased hepatic cell proliferation and lung abnormalities in mice deficient in CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha. J Biol Chem 271:24753–24760. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.40.24753
Frohling S, Schlenk RF, Stolze I, Bihlmayr J, Benner A, Kreitmeier S et al (2004) CEBPA mutations in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: prognostic relevance and analysis of cooperating mutations. J Clin Oncol 22:624–633. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.06.060
Gery S, Tanosaki S, Bose S, Bose N, Vadgama J, Koeffler HP (2005) Down-regulation and growth inhibitory role of C/EBPalpha in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:3184–3190. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2625
Halmos B, Huettner CS, Kocher O, Ferenczi K, Karp DD, Tenen DG (2002) Down-regulation and antiproliferative role of C/EBPalpha in lung cancer. Cancer Res 62:528–534
Haratake J, Takeda S, Kasai T, Nakano S, Tokui N (1993) Predictable factors for estimating prognosis of patients after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 72:1178–1183. doi :10.1002/1097-0142(19930815)72:4<1178::AID-CNCR2820720408>3.0.CO;2-Q
Hendricks-Taylor LR, Darlington GJ (1995) Inhibition of cell proliferation by C/EBP alpha occurs in many cell types, does not require the presence of p53 or Rb, and is not affected by large T-antigen. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4726–4733. doi:10.1093/nar/23.22.4726
Hirohashi S, Ishak KG, Kojiro M, Wanless IR, Theise ND, Tsukuma H et al (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA (eds) World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumors of the digestive system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 165–166
Lai CL, Wu PC, Lam KC, Todd D (1979) Histologic prognostic indicators in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 44:1677–1683. doi :10.1002/1097-0142(197911)44:5<1677::AID-CNCR2820440522>3.0.CO;2-D
Mann CD, Neal CP, Garcea G, Manson MM, Dennison AR, Berry DP (2007) Prognostic molecular markers in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer 43:979–992. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.01.004
Morrison C, Marsh W, Frankel WL (2002) A comparison of CD10 to pCEA, MOC-31, and hepatocyte for the distinction of malignant tumors in the liver. Mod Pathol 15:1279–1287. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000037312.69565.24
Muller C, Calkhoven CF, Sha X, Leutz A (2004) The CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) requires a SWI/SNF complex for proliferation arrest. J Biol Chem 279:7353–7358. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312709200
Nonami T, Harada A, Kurokawa T, Nakao A, Takagi H (1997) Hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg 173:288–291. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(96)00399-6
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Zhang P, Radomska HS, Narravula S, Schnittger S et al (2001) Dominant-negative mutations of CEBPA, encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha (C/EBP alpha), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 27:263–270. doi:10.1038/85820
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Preudhomme C, Sagot C, Boissel N, Cayuela J-M, Tigaud I, de Botton S et al (2002) Favorable prognostic significance of CEBPA mutations in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a study from the Acute Leukemia French Association (ALFA). Blood 100:2717–2723. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-03-0990
Ramji DP, Foka P (2002) CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 365:561–575
Schuster MB, Porse BT (2006) C/EBPalpha: a tumour suppressor in multiple tissues? Biochim Biophys Acta 1766:88–103
Shim M, Powers KL, Ewing SJ, Zhu S, Smart RC (2005) Diminished expression of C/EBPalpha in skin carcinomas is linked to oncogenic Ras and reexpression of C/EBPalpha in carcinoma cells inhibits proliferation. Cancer Res 65:861–867
Suriawinata A, Xu RL (2004) An update on the molecular genetics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 24:77–88. doi:10.1055/s-2004-860865
Tada Y, Brena RM, Hackanson B, Morrison C, Otterson GA, Plass C (2006) Epigenetic modulation of tumor suppressor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha activity in lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:396–406
Tan EH, Hooi SC, Laban M, Wong E, Ponniah S, Wee A et al (2005) CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha knock-in mice exhibit early liver glycogen storage and reduced susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 65:10330–10337. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4486
Timchenko NA, Harris TE, Wilde M, Bilyeu TA, BurgessBeusse BL, Finegold MJ, Darlington GJ (1997) CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha regulates p21 protein and hepatocyte proliferation in newborn mice. Mol Cell Biol 17:7353–7361
Tomizawa M, Watanabe K, Saisho H, Nakagawara A, Tagawa M (2003) Down-regulated expression of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha and beta genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a possible prognostic marker. Anticancer Res 23:351–354
Wang H, Iakova P, Wilde M, Welm A, Goode T, Roesler WJ et al (2001) C/EBPalpha arrests cell proliferation through direct inhibition of Cdk2 and Cdk4. Mol Cell 8:817–828. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00366-5
Xu LX, Sui YF, Wang WL, Liu YF, Gu JR (1994) Immunohistochemical demonstration of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) in human liver tissues of various origin. Chin Med J (Engl) 107:596–599
Xu L, Hui L, Wang S, Gong J, Jin Y, Wang Y et al (2001) Expression profiling suggested a regulatory role of liver-enriched transcription factors in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 61:3176–3181
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the National Science Council under the grant of NSC 94-2320-B-039-019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tseng, HH., Hwang, YH., Yeh, KT. et al. Reduced expression of C/EBPα protein in hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with advanced tumor stage and shortened patient survival. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135, 241–247 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0448-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0448-5