Abstract
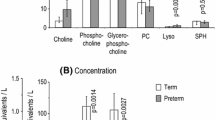
Choline is an essential constituent of membrane phospholipids in great demand in the developing brain and liver. We have previously demonstrated that human neonates excrete large amounts of betaine, a product of choline oxidation, in their urine. Estimates of perinatal choline intake using previously published data compared with our measurements of betaine excretion indicated that choline insufficiency might occur at certain periods after birth. In this study we measured the choline content of expressed human breast milk in colostrum (2–6 days after birth), mature milk (7–22 days after birth) and several infant formula foods, using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In colostrum choline was present in both the aqueous (free choline, phosphocholine and glycerophosphocholine) and lipid fractions (phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin). After 6–7 days there was a mean increase of 114% in the total choline content; 82% of the rise was accounted for by increases in phosphocholine and glycerophosphocholine, and 14% by (free) choline. The choline content of most formula feeds was comparable with the level in colostrum but below that of mature milk. Both the total choline content and ester composition of mature milk were comparable with more recent measurements using high-performance liquid chromatography.
Conclusion The choline content of human breast milk doubles 6–7 days after birth and, unlike that of many formula feeds, appears to be sufficient to account for betaine excretion in healthy full-term neonates. However, for premature babies who usually receive much lower quantities of milk, yet have a higher demand for choline, the intake may be inadequate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 February 1999 / Accepted: 15 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmes, H., I. Snodgrass, G. & Iles, R. Changes in the choline content of human breast milk in the first 3 weeks after birth. Eur J Pediatr 159, 198–204 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050050
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050050