Abstract
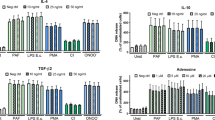
Bacterial lipopeptides represent a group of bacterial compounds able to trigger the functions of cells of the innate immune response. Whereas diacylated lipopeptides are recognized by TLR2/6 dimers, triacylated lipopeptides were shown to act via TLR2/1 dimers. Although several previous studies dealt with the effect of the TLR2/1 ligand Pam3CysSK4 on neutrophil granulocytes (PMN), it is still not clear whether TLR2/6 ligand lipopeptides can directly influence PMN functions. In the present study we used highly purified human neutrophils to investigate the direct effects of the diacylated mycoplasmal macrophage activating lipopeptide-2 (MALP-2) on the function of neutrophil granulocytes. After exposure to 10 ng/ml MALP-2 neutrophils acquired activated cell shape, secreted IL-8 and MIP-1β and their phagocytic capacity was enhanced. Analysis of cell surface activation markers confirmed the activating effect of MALP-2, the expression of CD62L was downregulated whereas CD11b was upregulated on PMN after exposure to MALP-2. The constitutive apoptosis of PMN was inhibited after exposure to MALP-2. However, MALP-2 exerted only a short-term effect on the apoptosis of resting neutrophils, a longer lasting effect was observed after transendothelial migration. MALP-2 did not directly induce the production of reactive oxygen intermediates but primed PMN for a fMLP-induced oxidative burst. The migration of neutrophils was enhanced after treatment with MALP-2. This was due, however, to a chemokinetic rather than to a chemotactic effect. Pam3CysSK4 also activated PMN, but in comparison to MALP-2, at higher concentrations. These findings suggest that diacylated lipopeptides are important microbial structures recognized by and acting on neutrophil granulocytes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanyan EA, Vallejo JG, Smith CW, Edwards MS (2000) Nonopsonic binding of type III Group B Streptococci to human neutrophils induces interleukin-8 release mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Infect Immun 68:2053–2060
Buwitt-Beckmann U, Heine H, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Brock R, Akira S, Ulmer AJ (2005) Toll-like receptor 6-independent signaling by diacylated lipopeptides. Eur J Immunol 35:282–289
Buwitt-Beckmann U, Heine H, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Brock R, Akira S, Ulmer AJ (2006) TLR1- and TLR6-independent recognition of bacterial lipopeptides. J Biol Chem 281:9049–9057
Cassatella MA (1999) Neutrophil-derived proteins: selling cytokines by the pound. Adv Immunol 73:369–509
Chiba K, Zhao W, Chen J, Wang J, Cui HY, Kawakami H, Miseki T, Satoshi H, Tanaka J, Asaka M, Kobayashi M (2004) Neutrophils secrete MIP-1 beta after adhesion to laminin contained in basement membrane of blood vessels. Br J Haematol 127:592–597
Colotta F, Re F, Polentarutti N, Sozzani S, Mantovani A (1992) Modulation of granulocyte survival and programmed cell death by cytokines and bacterial products. Blood 80:2012–2020
Francois S, El Benna J, Dang PM, Pedruzzi E, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Elbim C (2005) Inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis by TLR agonists in whole blood: involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and NF-kappaB signaling pathways, leading to increased levels of Mcl-1, A1, and phosphorylated Bad. J Immunol 174:3633–3642
Gainet J, Chollet-Martin S, Brion M, Hakim J, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Elbim C (1998) Interleukin-8 production by polymorphonuclear neutrophils in patients with rapidly progressive periodontitis: an amplifying loop of polymorphonuclear neutrophil activation. Lab Invest 78:755–762
Galanos C, Gumenscheimer M, Muhlradt P, Jirillo E, Freudenberg M (2000) MALP-2, a Mycoplasma lipopeptide with classical endotoxic properties: end of an era of LPS monopoly? J Endotoxin Res 6:471–476
Garcia J, Lemercier B, Roman-Roman S, Rawadi G (1998) A Mycoplasma fermentans-derived synthetic lipopeptide induces AP-1 and NF-kappaB activity and cytokine secretion in macrophages via the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Biol Chem 273:34391–34398
Guthrie LA, McPhail LC, Henson PM, Johnston RB Jr (1984) Priming of neutrophils for enhanced release of oxygen metabolites by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Evidence for increased activity of the superoxide-producing enzyme. J Exp Med 160:1656–1671
Hauschildt S, Hoffmann P, Beuscher HU, Dufhues G, Heinrich P, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Bessler WG (1990) Activation of bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by bacterial lipopeptide: cytokine production, phagocytosis and Ia expression. Eur J Immunol 20:63–68
Hayashi F, Means TK, Luster AD (2003) Toll-like receptors stimulate human neutrophil function. Blood 102:2660–2669
Hofman P, Piche M, Far DF, Le Negrate G, Selva E, Landraud L, Alliana-Schmid A, Boquet P, Rossi B (2000) Increased Escherichia coli phagocytosis in neutrophils that have transmigrated across a cultured intestinal epithelium. Infect Immun 68:449–455
Homburg CH, de Haas M, dem Borne AE, Verhoeven AJ, Reutelingsperger CP, Roos D (1995) Human neutrophils lose their surface Fc gamma RIII and acquire Annexin V binding sites during apoptosis in vitro. Blood 85:532–540
Kasama T, Streiter R, Lukacs NW, Burdick MD, Kunkel SL (1994) Regulation of neutrophil-derived chemokine expression by IL-10. J Immunol 152:3559–3569
Kaufmann A, Muhlradt PF, Gemsa D, Sprenger H (1999) Induction of cytokines and chemokines in human monocytes by Mycoplasma fermentans-derived lipoprotein MALP-2. Infect Immun 67:6303–6308
Kishimoto TK, Jutila MA, Berg EL, Butcher EC (1989) Neutrophil Mac-1 and MEL-14 adhesion proteins inversely regulated by chemotactic factors. Science 245:1238–1241
Klut ME, Whalen BA, Hogg JC (1997) Activation-associated changes in blood and bone marrow neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 62:186–194
Ko HJ, Lim SS (2002) Production of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 (MIP)-1alpha and MIP-1beta by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils stimulated with Porphyrommonas endodontalis lipopolysaccharide. J Endocrinol 28:754–757
Laufs H, Muller K, Fleischer J, Reiling N, Jahnke N, Jensenius JC, Solbach W, Laskay T (2002) Intracellular survival of Leishmania major in neutrophil granulocytes after uptake in the absence of heat-labile serum factors. Infect Immun 70:826–835
Lotz S, Aga E, Wilde I, van Zandbergen G, Hartung T, Solbach W, Laskay T (2004) Highly purified lipoteichoic acid activates neutrophil granulocytes and delays their spontaneous apoptosis via CD14 and TLR2. J Leukoc Biol 75:467–477
Ludwig A, Petersen F, Zahn S, Gotze O, Schroder JM, Flad HD, Brandt E (1997) The CXC-chemokine neutrophil-activating peptide-2 induces two distinct optima of neutrophil chemotaxis by differential interaction with interleukin-8 receptors CXCR-1 and CXCR-2. Blood 90:4588–4597
Luhrmann A, Deiters, Skokowa J, Hanke M, Gessner JE, Muhlradt PF, Pabst R, Tschernig T (2002) In vivo effects of a synthetic 2-kilodalton macrophage-activating lipopeptide of Mycoplasma fermentans after pulmonary application. Infect Immun 70:3785–3792
Maurer M, von Stebut E (2004) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1882–1886
McCurdy JD, Olynych TJ, Maher LH, Marshall JS (2003) Cutting edge: distinct Toll-like receptor 2 activators selectively induce different classes of mediator production from human mast cells. J Immunol 170:1625–1629
Muhlradt PF, Kiess M, Meyer H, Sussmuth R, Jung G (1997) Isolation, structure elucidation, and synthesis of a macrophage stimulatory lipopeptide from Mycoplasma fermentans acting at picomolar concentration. J Exp Med 185:1951–1958
Nadeau WJ, Pistole TG, McCormick BA (2002) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration across model intestinal epithelia enhances Salmonella typhimurium killing via the epithelial derived cytokine, IL-6. Microbes Infect 4:1379–1387
Nakao Y, Funami K, Kikkawa S, Taniguchi M, Nishiguchi M, Fukumori Y, Seya T, Matsumoto M (2005) Surface-expressed TLR6 participates in the recognition of diacylated lipopeptide and peptidoglycan in human cells. J Immunol 174:1566–1573
Neufert C, Pai RK, Noss EH, Berger M, Boom WH, Harding CV (2001) Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19-kDa lipoprotein promotes neutrophil activation. J Immunol 167:1542–1549
Nourshargh S, Marelli-Berg FM (2005) Transmigration through venular walls: a key regulator of leukocyte phenotype and function. Trends Immunol 26:157–165
Omueti KO, Beyer JM, Johnson CM, Lyle EA, Tapping RI (2005) Domain exchange between human toll-like receptors 1 and 6 reveals a region required for lipopeptide discrimination. J Biol Chem 280:36616–36625
Parker LC, Whyte MK, Dower SK, Sabroe I (2005) The expression and roles of Toll-like receptors in the biology of the human neutrophil. J Leukoc Biol 77:886–892
Power CP, Wang JH, Manning B, Kell MR, Aherne NF, Wu QD, Redmond HP (2004) Bacterial lipoprotein delays apoptosis in human neutrophils through inhibition of caspase-3 activity: regulatory roles for CD14 and TLR-2. J Immunol 173:5229–5237
Reinisch W, Lichtenberger C, Steger G, Tillinger W, Scheiner O, Gangl A, Maurer D, Willheim M (2003) Donor dependent, interferon-gamma induced HLA-DR expression on human neutrophils in vivo. Clin Exp Immunol 133:476–484
Sabroe I, Prince LR, Jones EC, Horsburgh MJ, Foster SJ, Vogel SN, Dower S, Whyte MK (2003) Selective roles for Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 in the regulation of neutrophil activation and life span. J Immunol 170:5268–5275
Savill JS, Wyllie AH, Henson JE, Walport MJ, Henson PM, Haslett C (1989) Macrophage phagocytosis of aging neutrophils in inflammation: programmed cell death in the neutrophil leads to its recognition by macrophages. J Clin Invest 83:865–875
Schroder NW, Heine H, Alexander C, Manukyan M, Eckert J, Hamann L, Gobel UB, Schumann RR (2004) Lipopolysaccharide binding protein binds to triacylated and diacylated lipopeptides and mediates innate immune responses. J Immunol 173:2683–2691
Seifert R, Schultz G, Richter-Freund M, Metzger J, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Bessler WG, Hauschildt S (1990) Activation of superoxide formation and lysozyme release in human neutrophils by the synthetic lipopeptide Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4 Involvement of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins and synergism with chemotactic peptides. Biochem J 267:795–802
Sengelov H, Kjeldsen L, Diamond MS, Springer TA, Borregaard N (1993) Subcellular localization and dynamics of Mac-1 (alpha m beta 2) in human neutrophils. J Clin Invest 92:1467–1476
Soler-Rodriguez AM, Zhang H, Lichenstein HS, Qureshi N, Niesel DW, Crowe SE, Peterson JW, Klimpel GR (2000) Neutrophil activation by bacterial lipoprotein versus lipopolysaccharide: differential requirements for serum and CD14. J Immunol 164:2674–2683
Swain SD, Rohn TT, Quinn MT (2002) Neutrophil priming in host defense: role of oxidants as priming agents. Antioxid Redox Signal 4:69–83
Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Muhlradt PF, Morr M, Radolf JD, Zychlinsky A, Takeda K, Akira S (2001) Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6. Int Immunol 13:933–940
Takeuchi O, Sato S, Horiuchi T, Hoshino K, Takeda K, Dong Z, Modlin RL, Akira S (2002) Cutting edge: role of Toll-like receptor 1 in mediating immune response to microbial lipoproteins. J Immunol 169:10–14
Taub DD, Conlon K, Lloyd AR, Oppenheim JJ, Kelvin DJ (1993) Preferential migration of activated CD4+ and CD8 + T cells in response to MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta. Science 60:355–358
van Eeden SF, Klut ME, Walker BA, Hogg JC (1999) The use of flow cytometry to measure neutrophil function. J Immunol Methods 232:23–43
Walmsley SR, Cowburn AS, Sobolewski A, Murray J, Farahi N, Sabroe I, Chilvers ER (2004) Characterization of the survival effect of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in human neutrophils. Biochem Soc Trans 32:456–460
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (La1267/1–2; SFB 367/B10) and from the Medical Faculty of the University of Luebeck (SP Infektabwehr/B1). The authors thank Dr. Ulrich Zähringer, Dr. Norbert Reiling and Ms. Uta Bussmeyer for fruitful discussions and Ms. Kirsten Broszat for expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilde, I., Lotz, S., Engelmann, D. et al. Direct stimulatory effects of the TLR2/6 ligand bacterial lipopeptide MALP-2 on neutrophil granulocytes. Med Microbiol Immunol 196, 61–71 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-006-0027-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-006-0027-9