Abstract
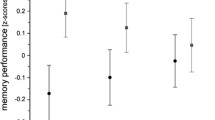
The hippocampus (Hc) consists of cytoarchitectonically and functionally distinct subfields: dentate gyrus (DG), cornu ammonis (CA1-3), and subiculum. In adults, a single nucleotide polymorphism (rs17070145, C→ T) in KIBRA, a gene encoding the eponymous (KIdney-BRAin) protein, is associated with variability in Hc subfield volumes and episodic memory. T-allele carriers have larger DG and CA volumes and better episodic memory compared to C-homozygotes. Little is known, however, about KIBRA’s role in the development of the brain and cognition. In a sample of children, adolescents, and young adults (N = 176, ages 5– 25 years), we replicated the adult association between KIBRA T-allele and larger DG and CA volumes but observed no relationship between KIBRA rs17070145 polymorphism and episodic memory. We noted, however, that a general cognitive performance index (IQ) differed across the allelic groups, with the lowest scores among T-homozygotes and the highest among C-homozygotes. Thus, in this developmental sample, KIBRA appears to have opposing effects on regional brain volume and cognition. These influences of KIBRA SNP may stem from associations between developmental reduction in brain volume and gains in cognitive performance—a hypothesis to be tested in longitudinal studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmetov II, Valeeva EV, Yerdenova MB, Datkhabayeva GK, Bouzid A, Bhamidimarri PM, Rees T (2023) KIBRA Gene variant is associated with ability in chess and science. Genes 14(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010204
Almeida OP, Schwab SG, Lautenschlager NT, Morar B, Greenop KR, Flicker L, Wildenauer D (2008) KIBRA genetic polymorphism influences episodic memory in later life, but does not increase the risk of mild cognitive impairment. J Cell Mol Med 12(5A):1672–1676. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00229.x
Bates TC, Price JF, Harris SE, Marioni RE, Fowkes FGR, Stewart MC, Deary IJ (2009) Association of KIBRA and memory. Neurosci Lett 458(3):140–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.04.050
Bender AR, Keresztes A, Bodammer NC, Shing YL, Werkle-Bergner M, Daugherty AM, Raz N (2018) Optimization and validation of automated hippocampal subfield segmentation across the lifespan. Hum Brain Map 39(2):916–931. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23891
Blanque A, Repetto D, Rohlmann A, Brockhaus J, Duning K, Pavenstädt H, Missler M (2015) Deletion of KIBRA, protein expressed in kidney and brain, increases filopodial-like long dendritic spines in neocortical and hippocampal neurons in vivo and in vitro. Front Neuroanatomy, 9(FEB), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00013
Boraxbekk CJ, Ames D, Kochan NA, Lee T, Thalamuthu A, Wen W, Mather KA (2015) Investigating the influence of KIBRA and CLSTN2 genetic polymorphisms on cross-sectional and longitudinal measures of memory performance and hippocampal volume in older individuals. Neuropsychologia 78:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.09.031
Daugherty AM, Bender AR, Raz N, Ofen N (2016) Age differences in hippocampal subfield volumes from childhood to late adulthood. Hippocampus 26(2):220–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22517
Daugherty AM, Flinn R, Ofen N (2017) Hippocampal CA3-dentate gyrus volume uniquely linked to improvement in associative memory from childhood to adulthood. Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.047
Delis DC, Kramer JH, Kaplan E, Ober BA (1994) California verbal learning test manual. San Antonio, TX: Pearson
Franks KH, Summers MJ, Vickers JC (2014) KIBRA gene polymorphism has no association with verbal or visual episodic memory performance. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 6(OCT), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00270
Han SD, Bondi MW (2008) Revision of the apolipoprotein E compensatory mechanism recruitment hypothesis. Alzheimer’s Dementia 4(4):251–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2008.02.006
Han SD, Tuminello ER (2011) The apolipoprotein e antagonistic pleiotropy hypothesis: review and recommendations. Int J Alzheimer’s Dis. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/726197
Heitz FD, Farinelli M, Mohanna S, Kahn M, Duning K, Frey MC, Mansuy IM (2016) The memory gene KIBRA is a bidirectional regulator of synaptic and structural plasticity in the adult brain. Neurobiol Learn Memory 135:100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2016.07.028
Jacobsen LK, Picciotto MR, Heath CJ, Mencl WE (2010) Allelic variation of calsyntenin 2 (CLSTN2) modulates the impact of developmental tobacco smoke exposure on mnemonic processing in adolescents. Psychiatry: Interpersonal and Biol Process 65(8):671–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.024
Jack CR Jr, Twomey CK, Zinsmeister AR, Sharbrough FW, Petersen RC, Cascino GD (1989) Anterior temporal lobes and hippocampal formations: normative volumetric measurements from MR images in young adults. Radiology 172(2):549–554. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.172.2.2748838
Johannsen S, Duning K, Pavenstädt H, Kremerskothen J, Boeckers TM (2008) Temporal-spatial expression and novel biochemical properties of the memory-related protein KIBRA. Neuroscience 155(4):1165–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.054
Jones MW, Mchugh TJ (2011) Updating hippocampal representations: CA2 joins the circuit. Trends Neurosci 34(10):526–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2011.07.007
Kauppi K, Nilsson LG, Adolfsson R, Eriksson E, Nyberg L (2011) Kibra polymorphism is related to enhanced memory and elevated hippocampal processing. J Neurosci 31(40):14218–14222. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3292-11.2011
Lindenberger U, von Oertzen T, Ghisletta P, Hertzog C (2011) Cross-sectional age variance extraction: What’s change got to do with it? Psychol Aging 26(1):34–47. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020525
Makuch L, Volk L, Anggono V, Johnson RC, Yu Y, Duning K, Huganir RL (2011) Regulation of AMPA receptor function by the human memory-associated gene KIBRA. Neuron 71(6):1022–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.017
Milnik A, Heck A, Vogler C, Heinze HJ, de Quervain DJF, Papassotiropoulos A (2012) Association of KIBRA with episodic and working memory: a meta-analysis. Am J Med Genet Part B 159 B(8), 958–969. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32101
Mollon J, Knowles EEM, Mathias SR, Gur R, Peralta JM, Weiner DJ, Glahn DC (2018) Genetic influence on cognitive development between childhood and adulthood. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0277-0
Muse J, Emery M, Sambataro F, Lemaitre H, Tan HY, Chen Q, Mattay VS (2014) WWC1 genotype modulates age-related decline in episodic memory function across the adult life Span. Biol Psychiatry 75(9):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.09.036
Need AC, Attix DK, McEvoy JM, Cirulli ET, Linney KN, Wagoner AP, Gumbs CE, Giegling I, Möller HJ, Francks C, Muglia P, Roses A, Gibson G, Weale ME, Rujescu D, Goldstein DB (2008) Failure to replicate effect of kibra on human memory in two large cohorts of European origin. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B(5):667–668
Palombo DJ, Amaral RSC, Olsen RK, Müller DJ, Todd RM, Anderson AK, Levine B (2013) KIBRA polymorphism is associated with individual differences in hippocampal subregions: evidence from anatomical segmentation using high-resolution MRI. J Neurosci 33(32):13088–13093. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1406-13.2013
Papassotiropoulos A, de Quervain DJF (2011) Genetics of human episodic memory: dealing with complexity. Trends Cogn Sci 15(9):381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.07.005
Papassotiropoulos A, Stephan DA, Huentelman MJ, Hoerndli FJ, Craig DW, Pearson JV, De Quervain DJF (2006) Common Kibra alleles are associated with human memory performance. Science 314(5798):475–478. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1129837
Piras IS, Krate J, Schrauwen I, Corneveaux JJ, Serrano GE, Sue L, Huentelman MJ (2017) Whole transcriptome profiling of the human hippocampus suggests an involvement of the KIBRA rs17070145 polymorphism in differential activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Hippocampus 27(7):784–793. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22731
Preuschhof C, Heekeren HR, Li SC, Sander T, Lindenberger U, Bäckman L (2010) KIBRA and CLSTN2 polymorphisms exert interactive effects on human episodic memory. Neuropsychologia 48(2):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.09.031
Rasch B, Papassotiropoulos A, de Quervain DF (2010) Imaging genetics of cognitive functions: focus on episodic memory. Neuroimage 53(3):870–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.001
Schaper K, Kolsch H, Popp J, Wagner M, Jessen F (2008) KIBRA gene variants are associated with episodic memory in healthy elderly. Neurobiol Aging 29(7):1123–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.02.001
Schuck NW, Doeller CF, Schjeide BMM, Schröder J, Frensch PA, Bertram L, Li SC (2013) Aging and KIBRA/WWC1 genotype affect spatial memory processes in a virtual navigation task. Hippocampus 23(10):919–930. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22148
Shing YL, Rodrigue KM, Kennedy KM, Fandakova Y, Bodammer, N, Werkle-Bergner M, Lindenberger U, Raz N (2011) Hippocampal subfield volumes: age vascular risk and correlation with associative memory. Front Aging Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2011.00002
Stickel A, Kawa K, Walther K, Glisky E, Richholt R, Huentelman M, Ryan L (2018) Age-modulated associations between KIBRA, brain volume, and verbal memory among healthy older adults. Front Aging Neurosci 9(JAN):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00431
Van Petten C (2004) Relationship between hippocampal volume and memory ability in healthy individuals across the lifespan: review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia 42(10):1394–1413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2004.04.006
Witte AV, Köbe T, Kerti L, Rujescu D, Flöel A (2016) Impact of KIBRA polymorphism on memory function and the hippocampus in older adults. Neuropsychopharmacol 41(3):781–790. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.203
Zhang H, Kranzler HR, Poling J, Gruen JR, Gelernter J (2009) Cognitive flexibility is associated with KIBRA variant and modulated by recent tobacco use. Neuropsychopharmacol 34(12):2508–2516. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.80
Acknowledgements
We thank Qin Yin, Sruthi Ramesh, Bryn Thompson, Lingfei Tang, Dana McCall, David Zhijian Chen, and Pavan Jella Kumar for assistance in data collection.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health (grant R01-MH107512 to PI NO, and grant R01-AG011230 to multi-PI NR and AMD) and Blue Cross Blue Shield Michigan (BCBSMI) Foundation award to RH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization (RH, QJ, NO), Methodology (RH, QJ, NO), Formal Analysis (RH, AMD, NR, NO), Visualization (RH, AMD, NO), Investigation (RH, AMD, NO), Writing Original Draft (RH, AMD, NR, NO), Writing Review and Editing (RH, AMD, NR, NO), Supervision and Funding Acquisition (NO).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Homayouni, R., Daugherty, A.M., Yu, Q. et al. KIBRA single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with hippocampal subfield volumes and cognition across development. Brain Struct Funct 229, 223–230 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02716-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02716-w