Abstract
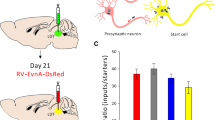
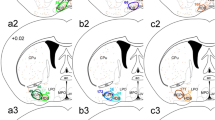
The axonal projections and synaptic input of the C1 adrenergic neurons of the rostral ventrolateral medulla (VLM) were examined using transgenic dopamine-beta hydroxylase Cre mice and modified rabies virus. Cre-dependent viral vectors expressing TVA (receptor for envelopeA) and rabies glycoprotein were injected into the left VLM. EnvelopeA-pseudotyped rabies-EGFP glycoprotein-deficient virus (rabies-EGFP) was injected 4–6 weeks later in either thoracic spinal cord (SC) or hypothalamus. TVA immunoreactivity was detected almost exclusively (95 %) in VLM C1 neurons. In mice with SC injections of rabies-EGFP, starter cells (expressing TVA + EGFP) were found at the rostral end of the VLM; in mice with hypothalamic injections starter C1 cells were located more caudally. C1 neurons innervating SC or hypothalamus had other terminal fields in common (e.g., dorsal vagal complex, locus coeruleus, raphe pallidus and periaqueductal gray matter). Putative inputs to C1 cells with SC or hypothalamic projections originated from the same brain regions, especially the lower brainstem reticular core from spinomedullary border to rostral pons. Putative input neurons to C1 cells were also observed in the nucleus of the solitary tract, caudal VLM, caudal spinal trigeminal nucleus, cerebellum, periaqueductal gray matter and inferior and superior colliculi. In sum, regardless of whether they innervate SC or hypothalamus, VLM C1 neurons receive input from the same general brain regions. One interpretation is that many types of somatic or internal stimuli recruit these neurons en bloc to produce a stereotyped acute stress response with sympathetic, parasympathetic, vigilance and neuroendocrine components.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott SB, Stornetta RL, Socolovsky CS, West GH, Guyenet PG (2009) Photostimulation of channelrhodopsin-2 expressing ventrolateral medullary neurons increases sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in rats. J Physiol 587(Pt 23):5613–5631
Abbott SB, Kanbar R, Bochorishvili G, Coates MB, Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG (2012) C1 neurons excite locus coeruleus and A5 noradrenergic neurons along with sympathetic outflow in rats. J Physiol 590(Pt 12):2897–2915
Abbott SB, Depuy SD, Nguyen T, Coates MB, Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG (2013) Selective optogenetic activation of rostral ventrolateral medullary catecholaminergic neurons produces cardiorespiratory stimulation in conscious mice. J Neurosci 33:3164–3177
Abbott SB, Holloway BB, Viar KE, Guyenet PG (2014a) Vesicular glutamate transporter 2 is required for the respiratory and parasympathetic activation produced by optogenetic stimulation of catecholaminergic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of mice in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 39(1):98–106
Abbott SB, Holloway BB, Viar KE, Guyenet PG (2014b) Vesicular glutamate transporter 2 is required for the respiratory and parasympathetic activation produced by optogenetic stimulation of catecholaminergic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of mice in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 39(1):98–106
Agassandian K, Shan Z, Raizada M, Sved AF, Card JP (2012) C1 catecholamine neurons form local circuit synaptic connections within the rostroventrolateral medulla of rat. Neuroscience 227:247–259
Aicher SA, Saravay RH, Cravo S, Jeske I, Morrison SF, Reis DJ, Milner TA (1996) Monosynaptic projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii to C1 adrenergic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: comparison with input from the caudal ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol 373(1):62–75
Aicher SA, Schreihofer AM, Kraus JA, Sharma S, Milner TA, Guyenet PG (2001) Mu-opioid receptors are present in functionally identified sympathoexcitatory neurons in the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol 433:34–47
Burke PG, Abbott SB, Coates MB, Viar KE, Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG (2014) Optogenetic stimulation of adrenergic C1 neurons causes sleep state-dependent cardiorespiratory stimulation and arousal with sighs in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190(11):1301–1310. doi:10.1164/rccm.201407-1262OC
Callaway EM, Luo L (2015) Monosynaptic circuit tracing with glycoprotein-deleted rabies viruses. J Neurosci 35(24):8979–8985. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0409-15.2015
Card JP, Sved JC, Craig B, Raizada M, Vazquez J, Sved AF (2006) Efferent projections of rat rostroventrolateral medulla C1 catecholamine neurons: implications for the central control of cardiovascular regulation. J Comp Neurol 499(5):840–859
Card JP, Kobiler O, McCambridge J, Ebdlahad S, Shan Z, Raizada MK, Sved AF, Enquist LW (2011) Microdissection of neural networks by conditional reporter expression from a Brainbow herpesvirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(8):3377–3382
Carrive P, Bandler R, Dampney RA (1988) Anatomical evidence that hypertension associated with the defence reaction in the cat is mediated by a direct projection from a restricted portion of the midbrain periaqueductal grey to the subretrofacial nucleus of the medulla. Brain Res 460:339–345
Chan RKW, Sawchenko PE (1994) Spatially and temporally differentiated patterns of c-fos expression in the brainstem catecholaminergic cell groups induced by cardiovascular challenges in the rat. J Comp Neurol 348(3):433–460
Chan RKW, Sawchenko PE (1995) Hemodynamic regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase messenger RNA in medullary catecholamine neurons: a c-fos-guided hybridization histochemical study. Neurosci 66:377–390
Chan RKW, Sawchenko PE (1998) Organization and transmitter specificity of medullary neurons activated by sustained hypertension: implications for understanding baroreceptor reflex circuitry. J Neurosci 18:371–387
Chen D, Bassi JK, Walther T, Thomas WG, Allen AM (2010) Expression of angiotensin type 1A receptors in C1 neurons restores the sympathoexcitation to angiotensin in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of angiotensin type 1A knockout mice. Hypertension 56(1):143–150
Clement CI, Keay KA, Bandler R (1998) Medullary catecholaminergic projections to the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray region activated by halothane anaesthesia. Neuroscience 86(4):1273–1284
Comer AM, Qi J, Christie DL, Gibbons HM, Lipski J (1998) Noradrenaline transporter expression in the pons and medulla oblongata of the rat: localisation to noradrenergic and some C1 adrenergic neurones. Mol Brain Res 62:65–76
Dampney RAL, McAllen RM (1988) Differential control of sympathetic fibres supplying hindlimb skin and muscle by subretrofacial neurones in the cat. J Physiol 395:41–56
Dayas CV, Buller KM, Crane JW, Xu J, Day TA (2001) Stressor categorization: acute physical and psychological stressors elicit distinctive recruitment patterns in the amygdala and in medullary noradrenergic cell groups. Eur J Neurosci 14(7):1143–1152
Dun SL, Ng YK, Brailoiu GC, Ling EA, Dun NJ (2002) Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide-immunoreactivity in adrenergic C1 neurons projecting to the intermediolateral cell column of the rat. J Chem Neuroanat 23(2):123–132
Erickson JT, Millhorn DE (1994) Hypoxia and electrical stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve induce c-Fos-like immunoreactivity within catecholaminergic and serotinergic neurons of the rat brainstem. J Comp Neurol 348:161–182
Ericsson A, Kovacs KJ, Sawchenko PE (1994) A functional anatomical analysis of central pathways subserving the effects of interleukin-1 on stress-related neuroendocrine neurons. J Neurosci 14(2):897–913
Ericsson A, Arias C, Sawchenko PE (1997) Evidence for an intramedullary prostaglandin-dependent mechanism in the activation of stress-related neuroendocrine circuitry by intravenous interleukin-1. J Neurosci 17(18):7166–7179
Esser MJ, Pronych SP, Allen GV (1998) Trigeminal-reticular connections: possible pathways for nociception-induced cardiovascular reflex responses in the rat. J Comp Neurol 391(4):526–544
Farkas E, Jansen AS, Loewy AD (1998) Periaqueductal gray matter input to cardiac-related sympathetic premotor neurons. Brain Res 792(2):179–192
Farnham MM, Li Q, Goodchild AK, Pilowsky PM (2008) PACAP is expressed in sympathoexcitatory bulbospinal C1 neurons of the brain stem and increases sympathetic nerve activity in vivo. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294(4):R1304–R1311
Gluska S, Zahavi EE, Chein M, Gradus T, Bauer A, Finke S, Perlson E (2014) Rabies Virus Hijacks and accelerates the p75NTR retrograde axonal transport machinery. PLoS Pathog 10(8):e1004348. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004348
Guyenet PG, Stornetta RL, Weston MC, McQuiston T, Simmons JR (2004) Detection of amino acid and peptide transmitters in physiologically identified brainstem cardiorespiratory neurons. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin 114(1–2):1–10
Guyenet PG, Stornetta RL, Bochorishvili G, Depuy SD, Burke PG, Abbott SB (2013) C1 neurons: the body’s EMTs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305(3):R187–R204. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00054.2013
Haselton JR, Guyenet PG (1989a) Central respiratory modulation of medullary sympathoexcitatory neurons in rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 256:R739–R750
Haselton JR, Guyenet PG (1989b) Electrophysiological characterization of putative C1 adrenergic neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 30:199–214
Haselton JR, Guyenet PG (1990) Ascending collaterals of medullary barosensitive neurons and C1 cells in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 258:R1051–R1063
Herbert H, Saper CB (1992) Organization of medullary adrenergic and noradrenergic projections to the periaqueductal gray matter in the rat. J Comp Neurol 315(1):34–52
Holloway BB, Stornetta RL, Bochorishvili G, Erisir A, Viar KE, Guyenet PG (2013) Monosynaptic glutamatergic activation of locus coeruleus and other lower brainstem noradrenergic neurons by the c1 cells in mice. J Neurosci 33(48):18792–18805
Holstein GR, Friedrich VL Jr, Kang T, Kukielka E, Martinelli GP (2011) Direct projections from the caudal vestibular nuclei to the ventrolateral medulla in the rat. Neuroscience 175:104–117. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.12.011
Holstein GR, Friedrich VL Jr, Martinelli GP (2014) Projection neurons of the vestibulo-sympathetic reflex pathway. J Comp Neurol 522(9):2053–2074. doi:10.1002/cne.23517
Huangfu D, Verberne AJM, Guyenet PG (1992) Rostral ventrolateral medullary neurons projecting to locus coeruleus have cardiorespiratory inputs. Brain Res 598:67–75
Jansen ASP, Nguyen XV, Karpitskiy V, Mettenleiter TC, Loewy AD (1995) Central command neurons of the sympathetic nervous system: basis of the fight-or flight response. Science 270:644–646
Koji K, Simon M, Tina L, Ann KG, Paul MP (2008) Neuropeptide Y in the rostral ventrolateral medulla blocks somatosympathetic reflexes in anesthetized rats. Auton Neurosci 142(1):64–70
Kwiat GC, Basbaum AI (1990) Organization of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive and serotonin-immunoreactive brainstem neurons with axon collaterals to the periaqueductal gray and the spinal cord in the rat. Brain Res 528:83–94
Lafon M (2005) Rabies virus receptors. J Neurovirol 11(1):82–87. doi:10.1080/13550280590900427
Li HY, Ericsson A, Sawchenko PE (1996) Distinct mechanisms underlie activation of hypothalamic neurosecretory neurons and their medullary catecholaminergic afferents in categorically different stress paradigms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2359–2364
Li T, Gao W, Rao ZR (1998) Noxious somatic stimulation-induced expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in catecholaminergic neurons with habenular nucleus projection in the medullary visceral zone of rat. Brain Res 783(1):51–56
Li AJ, Wang Q, Dinh TT, Ritter S (2009) Simultaneous silencing of Npy and Dbh expression in hindbrain A1/C1 catecholamine cells suppresses glucoprivic feeding. J Neurosci 29(1):280–287
Li AJ, Wang Q, Davis H, Wang R, Ritter S (2015a) Orexin-A enhances feeding in male rats by activating hindbrain catecholamine neurons. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 00065:02015. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00065.2015
Li AJ, Wang Q, Elsarelli MM, Brown RL, Ritter S (2015b) Hindbrain catecholamine neurons activate orexin neurons during systemic glucoprivation in male rats. Endocrinology. doi:10.1210/en.2015-1138
Lipski J, Kanjhan R, Kruszewska B, Smith M (1995) Barosensitive neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat in vivo: morphological properties and relationship to C1 adrenergic neurons. Neuroscience 69(2):601–618
Lonergan T, Goodchild AK, Christie MJ, Pilowsky PM (2003) Mu opioid receptors in rat ventral medulla: effects of endomorphin-1 on phrenic nerve activity. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 138(2–3):165–178
Lovick TA (1992a) Inhibitory modulation of the cardiovascular defence response by the ventrolateral periaqueductal grey matter in rats. Exp Brain Res 89:133–139
Lovick TA (1992b) Midbrain influences on ventrolateral medullo-spinal neurones in the rat. Exp Brain Res 90:147–152
Luppi P-H, Fort P, Kitahama K, Denoroy L, Jouvet M (1989) Adrenergic input from medullary ventrolateral C1 cells to the nucleus raphe pallidus of the cat, as demonstrated by a double immunostaining technique. Neurosci Lett 106(1–2):29–35
Marina N, Abdala AP, Korsak A, Simms AE, Allen AM, Paton JF, Gourine AV (2011) Control of sympathetic vasomotor tone by catecholaminergic C1 neurones of the rostral ventrolateral medulla oblongata. Cardiovasc Res 91(4):703–710
McAllen RM (1985) Mediation of the fastigial pressor reflex and a somatosympathetic reflex by ventral medullary neurones in the cat. J Physiol 368:423–433
McAllen RM, Dampney RA (1990) Vasomotor neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla are organized topographically with respect to type of vascular bed but not body region. Neurosci Lett 110:91–96
McAllen RM, May CN, Campos RR (1997) The supply of vasomotor drive to individual classes of sympathetic neuron. Clin Exp Hypertens 19(5–6):607–618
McCulloch PF, Panneton WM (2003) Activation of brainstem catecholaminergic neurons during voluntary diving in rats. Brain Res 984(1–2):42–53
Milner TA, Abate C, Reis DJ, Pickel VM (1989) Ultrastructural localization of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase-like immunoreactivity in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res 478:1–15
Miyawaki T, Goodchild AK, Pilowsky PM (2002) Activation of mu-opioid receptors in rat ventrolateral medulla selectively blocks baroreceptor reflexes while activation of delta opioid receptors blocks somato-sympathetic reflexes. Neuroscience 109(1):133–144
Mtui EP, Anwar M, Reis DJ, Ruggiero DA (1995) Medullary visceral reflex circuits: local afferents to nucleus tractus solitarii synthesize catecholamines and project to thoracic spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 351:5–26
Mueller PJ, Mischel NA, Scislo TJ (2011) Differential activation of adrenal, renal, and lumbar sympathetic nerves following stimulation of the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300(5):R1230–R1240. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00713.2010
Muller-Ribeiro FC, Dampney RA, McMullan S, Fontes MA, Goodchild AK (2014) Disinhibition of the midbrain colliculi unmasks coordinated autonomic, respiratory, and somatomotor responses to auditory and visual stimuli. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 307(8):R1025–R1035. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00165.2014
Nicholas AP, Hancock MB (1990) Evidence for projections from the rostral medullary raphe onto medullary catecholamine neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett 108(1–2):22–28
Panneton WM, Gan Q, Le J, Livergood RS, Clerc P, Juric R (2012) Activation of brainstem neurons by underwater diving in the rat. Front Physiol 3:111
Paton JF, Boscan P, Pickering AE, Nalivaiko E (2005) The yin and yang of cardiac autonomic control: vago-sympathetic interactions revisited. Brain Res Rev 49(3):555–565
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2013) The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 4th edn. Academic Press, New York
Pearson RJ, Gatti PJ, Sahibzada N, Massari VJ, Gillis RA (2007) Ultrastructural evidence for selective noradrenergic innervation of CNS vagal projections to the fundus of the rat. Auton Neurosci 136(1–2):31–42
Petrov T, Krukoff TL, Jhamandas JH (1993) Branching projections of catecholaminergic brainstem neurons to the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus and the central nucleus of the amygdala in the rat. Brain Res 609(1–2):81–92
Pickel VM, Chan J, Park DH, Joh TH, Milner TA (1986) Ultrastructural localization of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in sensory and motor nuclei of the vagus nerve. J Neurosci Res 15(4):439–456
Puskas N, Papp RS, Gallatz K, Palkovits M (2010) Interactions between orexin-immunoreactive fibers and adrenaline or noradrenaline-expressing neurons of the lower brainstem in rats and mice. Peptides 31(8):1589–1597
Pyner S, Coote JH (1994) Evidence that sympathetic preganglionic neurones are arranged in target-specific columns in the thoracic spinal cord of the rat. J Comp Neurol 342:15–22
Ritter S, Llewellyn-Smith I, Dinh TT (1998) Subgroups of hindbrain catecholamine neurons are selectively activated by 2-deoxy-d-glucose induced metabolic challenge. Brain Res 805(1–2):41–54
Ritter S, Bugarith K, Dinh TT (2001) Immunotoxic destruction of distinct catecholamine subgroups produces selective impairment of glucoregulatory responses and neuronal activation. J Comp Neurol 432(2):197–216
Ross CA, Armstrong DM, Ruggiero DA, Pickel VM, Joh TH, Reis DJ (1981) Adrenaline neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla innervate thoracic spinal cord: a combined immunocytochemical and retrograde transport demonstration. Neurosci Lett 25:257–262
Ross CA, Ruggiero DA, Joh TH, Park DH, Reis DJ (1984) Rostral ventrolateral medulla: selective projections to the thoracic autonomic cell column from the region containing C1 adrenaline neurons. J Comp Neurol 228:168–185
Rukhadze I, Kubin L (2007) Differential pontomedullary catecholaminergic projections to hypoglossal motor nucleus and viscerosensory nucleus of the solitary tract. J Chem Neuroanat 33(1):23–33. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2006.10.001
Saper CB, Loewy AD (1980) Efferent connections of the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. Brain Res 197(2):291–317
Sartor DM, Verberne AJ (2003) Phenotypic identification of rat rostroventrolateral medullary presympathetic vasomotor neurons inhibited by exogenous cholecystokinin. J Comp Neurol 465(4):467–479
Sawchenko PE, Bohn MC (1989) Glucocorticoid receptor-immunoreactivity in C1, C2, and C3 adrenergic neurons that project to the hypothalamus or to the spinal cord in the rat. J Comp Neurol 285(1):107–116
Sawchenko PE, Swanson LW (1982) The organization of noradrenergic pathways from the brainstem to the paraventricular and supraoptic nucleus in the rat. Brain ResearchRev 4:275–325
Sawchenko PE, Swanson LW, Grzanna R, Howe PR, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1985) Colocalization of neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity in brainstem catecholaminergic neurons that project to the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol 241(2):138–153
Schreihofer AM, Guyenet PG (1997) Identification of C1 presympathetic neurons in rat rostral ventrolateral medulla by juxtacellular labeling in vivo. J Comp Neurol 387:524–536
Schreihofer AM, Guyenet PG (2002) The baroreflex and beyond: control of sympathetic vasomotor tone by GABAergic neurons in the ventrolateral medulla. Clin Exp Pharm Phys 29(5–6):514–521
Sevigny CP, Bassi J, Teschemacher AG, Kim KS, Williams DA, Anderson CR, Allen AM (2008) C1 neurons in the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla differentially express vesicular monoamine transporter 2 in soma and axonal compartments. Eur J Neurosci 28(8):1536–1544
Stornetta RL (2009) Neurochemistry of bulbospinal presympathetic neurons of the medulla oblongata. J Chem Neuroanat 38(3):222–230
Stornetta RL, Morrison SF, Ruggiero DA, Reis DJ (1989) Neurons of rostral ventrolateral medulla mediate somatic pressor reflex. Am J Physiol 256:R448–R462
Stornetta R, Adam N, Guyenet PG (1990) Neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA is co-localized in catecholamine (CA) synthesizing neurons in rat brain. FASEB J 4:A882
Stornetta RL, Akey PJ, Guyenet PG (1999) Location and electrophysiological characterization of rostral medullary adrenergic neurons that contain neuropeptide Y mRNA in rat. J Comp Neurol 415:482–500
Stornetta RL, Schreihofer AM, Pelaez NM, Sevigny CP, Guyenet PG (2001) Preproenkephalin mRNA is expressed by C1 and non-C1 barosensitive bulbospinal neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat. J Comp Neurol 435(1):111–126
Stornetta RL, Sevigny CP, Schreihofer AM, Rosin DL, Guyenet PG (2002) Vesicular glutamate transporter DNPI/GLUT2 is expressed by both C1 adrenergic and nonaminergic presympathetic vasomotor neurons of the rat medulla. J Comp Neurol 444(3):207–220
Stornetta RL, McQuiston TJ, Guyenet PG (2004) GABAergic and glycinergic presympathetic neurons of rat medulla oblongata identified by retrograde transport of pseudorabies virus and in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol 479(3):257–270
Stornetta RL, Macon CJ, Nguyen TM, Coates MB, Guyenet PG (2013) Cholinergic neurons in the mouse rostral ventrolateral medulla target sensory afferent areas. Brain Struct Funct 218(2):455–475
Teppema LJ, Veening JG, Kranenburg A, Dahan A, Berkenbosch A, Olievier C (1997) Expression of c-fos in the rat brainstem after exposure to hypoxia and to normoxic and hyperoxic hypercapnia. J Comp Neurol 388(2):169–190
Tucker DC, Saper CB, Ruggiero DA, Reis DJ (1987) Organization of central adrenergic pathways: I. Relationships of ventrolateral medullary projections to the hypothalamus and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 259:591–603
Van Bockstaele EJ, Aston-Jones G, Pieribone VA, Ennis M, Shipley MT (1991) Subregions of the periaqueductal gray topographically innervate the rostral ventral medulla in the rat. J Comp Neurol 309(3):305–327. doi:10.1002/cne.903090303
VanderHorst VG, Ulfhake B (2006) The organization of the brainstem and spinal cord of the mouse: relationships between monoaminergic, cholinergic, and spinal projection systems. J Chem Neuroanat 31(1):2–36
Verberne AJM, Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG (1999) Properties of C1 and other ventrolateral medullary neurones with hypothalamic projections in the rat. J Physiol 517:477–494
Wall NR, Wickersham IR, Cetin A, De La PM, Callaway EM (2010) Monosynaptic circuit tracing in vivo through Cre-dependent targeting and complementation of modified rabies virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(50):21848–21853
Weible AP, Schwarcz L, Wickersham IR, Deblander L, Wu H, Callaway EM, Seung HS, Kentros CG (2010) Transgenic targeting of recombinant rabies virus reveals monosynaptic connectivity of specific neurons. J Neurosci 30(49):16509–16513
Westlund KN, Craig AD (1996) Association of spinal lamina I projections with brainstem catecholamine neurons in the monkey. Exp Brain Res 110(2):151–162
Wickersham IR, Finke S, Conzelmann KK, Callaway EM (2007a) Retrograde neuronal tracing with a deletion-mutant rabies virus. Nat Methods 4(1):47–49. doi:10.1038/nmeth999
Wickersham IR, Lyon DC, Barnard RJ, Mori T, Finke S, Conzelmann KK, Young JA, Callaway EM (2007b) Monosynaptic restriction of transsynaptic tracing from single, genetically targeted neurons. Neuron 53(5):639–647
Zanzinger J, Czachurski J, Offner B, Seller H (1994) Somato-sympathetic reflex transmission in the ventrolateral medulla oblongata: spatial organization and receptor types. Brain Res 656:353–358
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Institutes of Health (HL 074011 and HL 028785 to PGG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stornetta, R.L., Inglis, M.A., Viar, K.E. et al. Afferent and efferent connections of C1 cells with spinal cord or hypothalamic projections in mice. Brain Struct Funct 221, 4027–4044 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1143-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1143-3