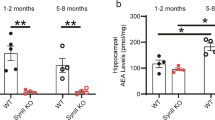
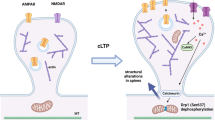
Abstract
The Ly-6 superfamily of proteins, which affects diverse processes in the immune system, has attracted renewed attention due to the ability of some Ly-6 proteins to bind to and modulate the function of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). However, there is a scarcity of knowledge regarding the distribution and developmental regulation of these proteins in the brain. We use protein cross-linking and synaptosomal fractions to demonstrate that the Ly-6 proteins Lynx1 and Ly6H are membrane-bound proteins in the brain, which are present on the cell surface and localize to synaptic compartments. We further estimate the amount of Lynx1 in the rat cortex using known amounts of a heterologously expressed soluble Lynx1 variant (ws-Lynx1) to be approximately 8.6 ng/μg total protein, which is in line with the concentrations of ws-Lynx1 required to affect nAChR function. In addition, we demonstrate that Lynx1 and Ly6H are expressed in cultured neurons, but not cultured micro- or astroglial cultures. In addition, Lynx1, but not Ly6H was detected in the CSF. Finally, we show that the Ly-6 proteins Lynx1, Lynx2, Ly6H, and PSCA, display distinct expression patterns during postnatal development in the rat frontal cortex and hippocampus at the mRNA and protein level, and that this is paralleled to some degree by the expression of the nAChR subunits α2, α4, α7 and β2. Our results demonstrate a developmental pattern, localization, and concentration of Ly-6 proteins in the brain, which support a role for these proteins in the modulation of signaling at synaptic membranes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- aCSF:
-
Artificial cerebrospinal fluid
- BS3 :
-
Bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DIV:
-
Day in vitro
- FC:
-
Frontal cortex
- HIP:
-
Hippocampus
- NAChR:
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
- ws-Lynx1:
-
Water-soluble variant of human Lynx1
References
Adermann K, Wattler F, Wattler S, Heine G, Meyer M, Forssmann WG, Nehls M (1999) Structural and phylogenetic characterization of human SLURP-1, the first secreted mammalian member of the Ly-6/uPAR protein superfamily. Protein Sci 8:810–819
Albuquerque EX, Pereira EFR, Alkondon M, Rogers SW (2009) Mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 89:73–120
Apostolopoulos J, Chisholm LJ, Sandrin MS (1999) Identification of mouse Ly6H and its expression in normal tissue. Immunogenetics 49:987–990
Bamezai A (2004) Mouse Ly-6 proteins and their extended family: markers of cell differentiation and regulators of cell signaling. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 52:255–266
Broide RS, O’Connor LT, Smith MA, Smith JA, Leslie FM (1995) Developmental expression of alpha 7 neuronal nicotinic receptor messenger RNA in rat sensory cortex and thalamus. Neuroscience 67:83–94
Carino C, Fibuch EE, Mao L-M, Wang JQ (2012) Dynamic loss of surface-expressed AMPA receptors in mouse cortical and striatal neurons during anesthesia. J Neurosci Res 90:315–323
Chimienti F, Hogg RC, Plantard L, Lehmann C, Brakch N, Fischer J, Huber M, Bertrand D, Hohl D (2003) Identification of SLURP-1 as an epidermal neuromodulator explains the clinical phenotype of Mal de Meleda. Hum Mol Genet 12:3017–3024
Choo YM, Lee BH, Lee KS, Kim BY, Li J, Kim JG, Lee JH, Sohn HD, Nah SY, Jin BR (2008) Pr-lynx1, a modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the insect. Mol Cell Neurosci 38:224–235
Darvas M, Morsch M, Racz I, Ahmadi S, Swandulla D, Zimmer A (2009) Modulation of the Ca2+ conductance of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by Lypd6. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 19:670–681
Dessaud E, Salaün D, Gayet O, Chabbert M, DeLapeyrière O (2006) Identification of lynx2, a novel member of the ly-6/neurotoxin superfamily, expressed in neuronal subpopulations during mouse development. Mol Cell Neurosci 31:232–242
Fu XW, Rekow SS, Spindel ER (2012) The Ly-6 protein, lynx1 is an endogenous inhibitor of nicotinic signaling in airway epithelium. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 303(8):L661–L668
Grosshans DR, Clayton DA, Coultrap SJ, Browning MD (2002) LTP leads to rapid surface expression of NMDA but not AMPA receptors in adult rat CA1. Nat Neurosci 5:27–33
Herber DL, Severance EG, Cuevas J, Morgan D, Gordon MN (2004) Biochemical and histochemical evidence of nonspecific binding of alpha7 nAChR antibodies to mouse brain tissue. J Histochem Cytochem 52:1367–1376
Hill JA, Zoli M, Bourgeois JP, Changeux JP (1993) Immunocytochemical localization of a neuronal nicotinic receptor: the beta 2-subunit. J Neurosci 13:1551–1568
Horie M, Okutomi K, Taniguchi Y, Ohbuchi Y, Suzuki M, Takahashi E (1998) Isolation and characterization of a new member of the human Ly6 gene family (LY6H). Genomics 53:365–368
Hruska M, Keefe J, Wert D, Tekinay AB, Hulce JJ, Ibañez-Tallon I, Nishi R (2009) Prostate stem cell antigen is an endogenous Lynx1-like prototoxin that antagonizes alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors and prevents programmed cell death of parasympathetic neurons. J Neurosci 29:14847–14854
Ibañez-Tallon I, Miwa JM, Wang HL, Adams NC, Crabtree GW, Sine SM, Heintz N (2002) Novel modulation of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by association with the endogenous prototoxin lynx1. Neuron 33:893–903
Kuryatov A, Luo J, Cooper J, Lindstrom J (2005) Nicotine acts as a pharmacological chaperone to up-regulate human alpha4beta2 acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol 68:1839–1851
Lester HA, Xiao C, Srinivasan R, Son CD, Miwa J, Pantoja R, Banghart MR, Dougherty DA, Goate AM, Wang JC (2009) Nicotine is a selective pharmacological chaperone of acetylcholine receptor number and stoichiometry. Implications for drug discovery. AAPS J 11:167–177
Liu Z, Cao G, Li J, Bao H, Zhang Y (2009) Identification of two Lynx proteins in Nilaparvata lugens and the modulation on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurochem 110:1707–1714
Lozada AF, Wang X, Gounko NV, Massey KA, Duan J, Liu Z, Berg DK (2012a) Glutamatergic synapse formation is promoted by α7-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurosci 32:7651–7661
Lozada AF, Wang X, Gounko NV, Massey KA, Duan J, Liu Z, Berg DK (2012b) Induction of dendritic spines by β2-containing nicotinic receptors. J Neurosci 32:8391–8400
Lyukmanova EN, Shenkarev ZO, Shulepko MA, Mineev KS, D’Hoedt D, Kasheverov IE, Filkin SY, Krivolapova AP, Janickova H, Dolezal V, Dolgikh DA, Arseniev AS, Bertrand D, Tsetlin VI, Kirpichnikov MP (2011) NMR structure and action on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of water-soluble domain of human LYNX1. J Biol Chem 286:10618–10627
Mielke JG, Mealing GA (2009) Cellular distribution of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Res 65:296–306
Miwa JM, Walz A (2012) Enhancement in motor learning through genetic manipulation of the Lynx1 gene. PLoS One 7:e43302
Miwa JM, Ibanez-Tallon I, Crabtree GW, Sánchez R, Sali A, Role LW, Heintz N (1999) Lynx1, an endogenous toxin-like modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the mammalian CNS. Neuron 23:105–114
Miwa JM, Stevens TR, King SL, Caldarone BJ, Ibanez-Tallon I, Xiao C, Fitzsimonds RM, Pavlides C, Lester HA, Picciotto MR, Heintz N (2006) The prototoxin lynx1 acts on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to balance neuronal activity and survival in vivo. Neuron 51:587–600
Miwa JM, Freedman R, Lester HA (2011) Neural systems governed by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: emerging hypotheses. Neuron 70:20–33
Miwa JM, Lester HA, Walz A (2012) Optimizing cholinergic tone through lynx modulators of nicotinic receptors: implications for plasticity and nicotine addiction. Physiology (Bethesda) 27:187–199
Morishita H, Miwa JM, Heintz N, Hensch TK (2010) Lynx1, a cholinergic brake, limits plasticity in adult visual cortex. Science 330:1238–1240
Moser N et al (2007) Evaluating the suitability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies for standard immunodetection procedures. J Neurochem 102:479–492
Nirogi R, Kandikere V, Mudigonda K, Bhyrapuneni G, Muddana N, Saralaya R, Benade V (2009) A simple and rapid method to collect the cerebrospinal fluid of rats and its application for the assessment of drug penetration into the central nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 178:116–119
Sarter M, Parikh V, Howe WM (2009) nAChR agonist-induced cognition enhancement: integration of cognitive and neuronal mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol 78:658–667
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Shacka JJ, Robinson SE (1998) Postnatal developmental regulation of neuronal nicotinic receptor subunit alpha 7 and multiple alpha 4 and beta 2 mRNA species in the rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 109:67–75
Soliakov L, Gallagher T, Wonnacott S (1995) Anatoxin-a-evoked [3H]dopamine release from rat striatal synaptosomes. Neuropharmacology 34:1535–1541
Srivastava S, Osten P, Vilim FS, Khatri L, Inman G, States B, Daly C, DeSouza S, Abagyan R, Valtschanoff JG, Weinberg RJ, Ziff EB (1998) Novel anchorage of GluR2/3 to the postsynaptic density by the AMPA receptor-binding protein ABP. Neuron 21:581–591
Tekinay AB, Nong Y, Miwa JM, Lieberam I, Ibanez-Tallon I, Greengard P, Heintz N (2009) A role for LYNX2 in anxiety-related behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4477–4482
Thomsen MS, Mikkelsen JD (2012a) The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor complex: one, two or multiple drug targets? Curr Drug Targets 13(5):707–720
Thomsen MS, Mikkelsen JD (2012b) The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands methyllycaconitine, NS6740 and GTS-21 reduce lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α release from microglia. J Neuroimmunol 251:65–72
Thomsen MS, Hansen HH, Timmermann DB, Mikkelsen JD (2010) Cognitive improvement by activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from animal models to human pathophysiology. Curr Pharm Des 16:323–343
Thomsen MS, El-Sayed M, Mikkelsen JD (2011) Differential immediate and sustained memory enhancing effects of alpha7 nicotinic receptor agonists and allosteric modulators in rats. PLoS One 6:e27014
Tsetlin V (1999) Snake venom alpha-neurotoxins and other “three-finger” proteins. Eur J Biochem 264:281–286
Tsuji H, Okamoto K, Matsuzaka Y, Iizuka H, Tamiya G, Inoko H (2003) SLURP-2, a novel member of the human Ly-6 superfamily that is up-regulated in psoriasis vulgaris. Genomics 81:26–33
Wilson EH, Weninger W, Hunter CA (2010) Trafficking of immune cells in the central nervous system. J Clin Invest 120:1368–1379
Zhang X, Liu C, Miao H, Gong Z, Nordberg A (1998) Postnatal changes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 2, α3, α4, α7 and β2 subunits genes expression in rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 16:507–518
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Cecilia Gotti for kindly providing the β2 antibody, Felix Eckenstein for providing the Lynx1 knock-out mouse tissue, and Imad Damaj for providing the α7 and β2 knock-out mouse tissue. This work was supported by the Danish Medical Research Council, the Danish Strategic Research Council, the Lundbeck Foundation, the NOVO Nordisk Foundation, the Danish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Higher Education, the Russian Academy of Sciences (Program “Molecular and Cell Biology”), the Ministry of Science and Education (contract No. 8268), and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomsen, M.S., Cinar, B., Jensen, M.M. et al. Expression of the Ly-6 family proteins Lynx1 and Ly6H in the rat brain is compartmentalized, cell-type specific, and developmentally regulated. Brain Struct Funct 219, 1923–1934 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0611-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0611-x