Abstract
Researchers working with rodent models of neurological disease often require an accurate map of the anatomical organization of the white matter of the rodent brain. With the increasing popularity of small animal MRI techniques, including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), there is considerable interest in rapid segmentation methods of neurological structures for quantitative comparisons. DTI-derived tractography allows simple and rapid segmentation of major white matter tracts, but the anatomic accuracy of these computer-generated fibers is open to question and has not been rigorously evaluated in the rat brain. In this study, we examine the anatomic accuracy of tractography-based segmentation in the adult rat brain. We analysed 12 major white matter pathways using semi-automated tractography-based segmentation alongside manual segmentation of Gallyas silver-stained histology sections. We applied four fiber-tracking algorithms to the DTI data—two integration methods and two deflection methods. In many cases, tractography-based segmentation closely matched histology-based segmentation; however different tractography algorithms produced dramatically different results. Results suggest that certain white matter pathways are more amenable to tractography-based segmentation than others. We believe that these data will help researchers decide whether it is appropriate to use tractography-based segmentation of white matter structures for quantitative DTI-based analysis of neurologic disease models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallyas F (1971) A principle for silver staining of tissue elements by physical development. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung 19(1):57–71
Gallyas F (1979) Silver staining of myelin by means of physical development. Neurol Res 1(2):203−209
Hasan KM, Halphen C, Sankar A, Eluvathingal TJ, Kramer L, Stuebing KK, Ewing-Cobbs L, Fletcher JM (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging-based tissue segmentation: validation and application to the developing child and adolescent brain. Neuroimage 34(4):1497–1505. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.10.029
Johnson GA, Calabrese E, Badea A, Paxinos G, Watson C (2012a) A multidimensional magnetic resonance histology atlas of the Wistar rat brain. Neuroimage 62(3):1848–1856. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.05.041
Johnson GA, Calabrese E, Badea A, Paxinos G, Watson C (2012b) A multidimensional magnetic resonance histology atlas of the Wistar rat brain. Neuroimage. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.05.041
Koenig SH (1990) Paramagnetic agents as tracers in magnetic resonance imaging. Extrapolations from Gd-DTPA to everything. Acta Radiol Suppl 374:17–23
Konig JFR, Klippel RA (1963) The rat brain A stereotaxic atlas of the forebrain and the lower parts of the brain stem. The Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore
Mukherjee P, Chung SW, Berman JI, Hess CP, Henry RG (2008) Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: technical considerations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(5):843–852. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1052
Niogi SN, Mukherjee P, McCandliss BD (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging segmentation of white matter structures using a Reproducible Objective Quantification Scheme (ROQS). Neuroimage 35(1):166–174. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.10.040
O’Donnell LJ, Westin CF (2007) Automatic tractography segmentation using a high-dimensional white matter atlas. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26(11):1562–1575. doi:10.1109/TMI.2007.906785
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Pistorio AL, Hendry SH, Wang X (2006) A modified technique for high-resolution staining of myelin. J Neurosci Methods 153(1):135–146. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.10.014
Renshaw PF, Owen CS, McLaughlin AC, Frey TG, Leigh JS Jr (1986) Ferromagnetic contrast agents: a new approach. Magn Reson Med 3(2):217–225
Savadjiev P, Campbell JS, Pike GB, Siddiqi K (2008) Streamline flows for white matter fibre pathway segmentation in diffusion MRI. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 11(Pt 1):135–143
Tago H, Kimura H, Maeda T (1986) Visualization of detailed acetylcholinesterase fiber and neuron staining in rat brain by a sensitive histochemical procedure. J Histochem Cytochem 34(11):1431–1438
Tuch DS (2004) Q-ball imaging. Magn Reson Med 52(6):1358–1372. doi:10.1002/mrm.20279
Tuch DS, Reese TG, Wiegell MR, Makris N, Belliveau JW, Wedeen VJ (2002) High angular resolution diffusion imaging reveals intravoxel white matter fiber heterogeneity. Magn Reson Med 48(4):577–582. doi:10.1002/mrm.10268
Van Hecke W, Leemans A, Sijbers J, Vandervliet E, Van Goethem J, Parizel PM (2008) A tracking-based diffusion tensor imaging segmentation method for the detection of diffusion-related changes of the cervical spinal cord with aging. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(5):978–991. doi:10.1002/jmri.21338
Wedeen VJ, Wang RP, Schmahmann JD, Benner T, Tseng WY, Dai G, Pandya DN, Hagmann P, D’Arceuil H, de Crespigny AJ (2008) Diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging (DSI) tractography of crossing fibers. Neuroimage 41(4):1267–1277. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.036
Yendiki A, Panneck P, Srinivasan P, Stevens A, Zollei L, Augustinack J, Wang R, Salat D, Ehrlich S, Behrens T, Jbabdi S, Gollub R, Fischl B (2011) Automated probabilistic reconstruction of white-matter pathways in health and disease using an atlas of the underlying anatomy. Front Neuroinform 5:23. doi:10.3389/fninf.2011.00023
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an Australia Fellowship awarded to Professor George Paxinos by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) (466028) and the Duke Center for In Vivo Microscopy, an NIH/NCRR/NIBIB national Biomedical Technology Resource Center (P41 EB015897).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Erika Gyengesi and Evan Calabrese contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
429_2013_516_MOESM2_ESM.tif
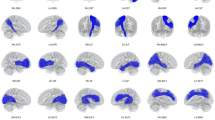
Fig 1. Three-dimensional rendering of the rest of the analyzed structures, including the anterior commissure, the corpus callosum, the cingulate, the fasciculus retroflexus, the medial lemniscus, the medial longitudinal fasciculus, the mammillothalamic tract, and the optic tract, and the stria medullaris. The figures show the frontal, lateral, and dorsal views. (TIFF 7106 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gyengesi, E., Calabrese, E., Sherrier, M.C. et al. Semi-automated 3D segmentation of major tracts in the rat brain: comparing DTI with standard histological methods. Brain Struct Funct 219, 539–550 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0516-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0516-8