Abstract
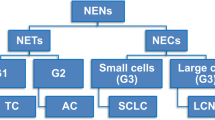
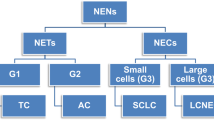
Neuroendocrine (NE) tumours of the lung include pure and mixed forms. In the former group, a continuum of lesions is recognised ranging from benign typical carcinoids to atypical carcinoids (having a low-grade behaviour, although often associated with regional and distant metastases), to the highly aggressive poorly differentiated carcinomas of the small and large cell types. In the mixed tumour group, the NE component is extensively represented in association with any of the non-small cell carcinoma subtypes (so-called combined carcinomas), or the NE component is restricted to a cell population scattered among adenocarcinoma cells (or more rarely within squamous or large cell carcinomas). The molecular profile of NE tumours has been widely investigated to identify features helpful for the diagnosis, prognosis and even therapy for this special lung tumour category. Specific chromosomal alterations, oncogene mutations and cell cycle molecule disregulation has been documented in NE tumours of the lung, as well as the expression of specific receptors or enzymes implicated in the response to biotherapies or to chemotherapeutic agents. The “molecular classification” of NE tumours should be integrated to morphology, for a better definition of the different histological types and a more appropriate selection of the therapeutic strategy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbona G, Papotti M, Viberti L, Macri L, Stella A, Bussolati G (1998) Chromogranin A gene expression in non-small cell lung carcinomas. J Pathol 186:151–156
Aguayo SM, King TE Jr, Waldron JA Jr, Sherritt KM, Kane MA, Miller YE (1990) Increased pulmonary neuroendocrine cells with bombesin-like immunoreactivity in adult patients with eosinophilic granuloma. J Clin Invest 86:838–844
Anbazhagan R, Tihan T, Bornman DM, Johnston JC, Saltz JH, Weigering A, Piantadosi S, Gabrielson E (1999) Classification of small cell lung cancer and pulmonary carcinoid by gene expression profiles. Cancer Res 59:5119–5122
Arrigoni MG, Woolner LB, Bernatz PE (1972) Atypical carcinoid tumors of the lung. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 64:413–421
Asamura H, Kameya T, Matsuno Y, Noguchi M, Tada H, Ishikawa Y, Yokose T, Jiang SX, Inoue T, Nakagawa K, Tajima K, Nagai K (2006) Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung: a prognostic spectrum. J Clin Oncol 24:70–76
Berendsen HH, de Leij L, Poppema S, Postmus PE, Boes A, Sluiter HJ, The H (1989) Clinical characterization of non-small-cell lung cancer tumors showing neuroendocrine differentiation features. J Clin Oncol 7:1614–1620
Berruti A, Mosca A, Tucci M, Terrone C, Torta M, Tarabuzzi R, Russo L, Cracco C, Bollito E, Scarpa RM, Angeli A, Dogliotti L (2005) Independent prognostic role of circulating chromogranin A in prostate cancer patients with hormone-refractory disease. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:109–117
Bhattacharjee A, Richards WG, Staunton J, Li C, Monti S, Vasa P, Ladd C, Beheshti J, Bueno R, Gillette M, Loda M, Weber G, Mark EJ, Lander ES, Wong W, Johnson BE, Golub TR, Sugarbaker DJ, Meyerson M (2001) Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13790–13795
Brambilla C, Brambilla E (eds) (1999) Lung tumors. Fundamental biology and clinical managment. Marcel Dekker, New York
Chejfec G, Cosnow I, Gould NS, Husain AN, Gould VE (1990) Pulmonary blastoma with neuroendocrine differentiation in cell morules resembling neuroepithelial bodies. Histopathology 17:353–358
Cooper CS, Nicholson AG, Foster C, Dodson A, Edwards S, Fletcher A, Roe T, Clark J, Joshi A, Norman A, Feber A, Lin D, Gao Y, Shipley J, Cheng SJ (2006) Nuclear overexpression of the E2F3 transcription factor in human lung cancer. Lung Cancer 54:155–162
Dancey JE (2005) Inhibitors of the mammalian target of rapamycin. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 14:313–328
Eymin B, Gazzeri S, Brambilla C, Brambilla E (2001) Distinct pattern of E2F1 expression in human lung tumors: E2F1 is up regulated in small cell lung carcinoma. Oncogene 20:1678–1687
Friedkin M, Crawford EJ, Donovan E, Pastore EJ (1962) The enzymatic synthesis of thymidylate. III. The further purification of thymidylate synthetase and its separation from natural fluorescent inhibitors. J Biol Chem 237:3811–3814
Garber ME, Troyanskaya OG, Schluens K, Petersen S, Thaesler Z, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, van de Rijn M, Rosen GD, Perou CM, Whyte RI, Altman RB, Brown PO, Botstein D, Petersen I (2001) Diversity of gene expression in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13784–13789
Gillan JE, Cutz E (1993) Abnormal pulmonary bombesin immunoreactive cells in Wilson-Mikity syndrome (pulmonary dysmaturity) and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pathol 13:165–180
Gould VE, Linnoila RI, Memoli VA, Warren WH (1983) Neuroendocrine components of the bronchopulmonary tract: hyperplasias, dysplasias, and neoplasms. Lab Invest 49:519–537
He P, Varticovski L, Bowman ED, Fukuoka J, Welsh JA, Miura K, Jen J, Gabrielson E, Brambilla E, Travis WD, Harris CC (2004) Identification of carboxypeptidase E and gamma-glutamyl hydrolase as biomarkers for pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors by cDNA microarray. Hum Pathol 35:1196–1209
Howe MC, Chapman A, Kerr K, Dougal M, Anderson H, Hasleton PS (2005) Neuroendocrine differentiation in non-small cell lung cancer and its relation to prognosis and therapy. Histopathology 46:195–201
Igarashi T, Jiang SX, Kameya T, Asamura H, Sato Y, Nagai K, Okayasu I (2004) Divergent cyclin B1 expression and Rb/p16/cyclin D1 pathway aberrations among pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Mod Pathol 17:1259–1267
Jiang SX, Kameya T, Asamura H, Umezawa A, Sato Y, Shinada J, Kawakubo Y, Igarashi T, Nagai K, Okayasu I (2004) hASH1 expression is closely correlated with endocrine phenotype and differentiation extent in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Mod Pathol 17:222–229
Jiang SX, Mikami T, Umezawa A, Saegusa M, Kameya T, Okayasu I (2006) Gastric large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Am J Surg Pathol 30:945–953
Jones MH, Virtanen C, Honjoh D, Miyoshi T, Satoh Y, Okumura S, Nakagawa K, Nomura H, Ishikawa Y (2004) Two prognostically significant subtypes of high-grade lung neuroendocrine tumors independent of small-cell and large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas identified by gene expression profiles. Lancet 363:775–781
Kaye FJ (2002) RB and cyclin dependent kinase pathways: defining a distinction between RB and p16 loss in lung cancer. Oncogene 21:6908–6914
Lantuejoul S, Moro D, Michalides RJ, Brambilla C, Brambilla E (1998) Neural cell adhesion molecules (NCAM) and NCAM-PSA expression in neuroendocrine lung tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 22:1267–1276
Lantuejoul S, Soria JC, Moro-Sibilot D, Morat L, Veyrenc S, Lorimier P, Brichon PY, Sabatier L, Brambilla C, Brambilla E (2004) Differential expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) in lung tumors. Br J Cancer 90:1222–1229
Lantuejoul S, Salon C, Soria JC, Brambilla E (2007) Telomerase expression in lung preneoplasia and neoplasia. Int J Cancer 120:1835–1841
Miller RR, Muller NL (1995) Neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia and obliterative bronchiolitis in patients with peripheral carcinoid tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 19:653–658
Navalgund LG, Rossana C, Muench AJ, Johnson LF (1980) Cell cycle regulation of thymidylate synthetase gene expression in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 255:7386–7390
Nishio Y, Nakanishi K, Ozeki Y, Jiang SX, Kameya T, Hebisawa A, Mukai M, Travis WD, Franks TJ, Kawai T (2007) Telomere length, telomerase activity, and expressions of human telomerase mRNA component (hTERC) and human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) mRNA in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:16–22
Oliveira AM, Tazelaar HD, Wentzlaff KA, Kosugi NS, Hai N, Benson A, Miller DL, Yang P (2001) Familial pulmonary carcinoid tumors. Cancer 91:2104–2109
Onuki N, Wistuba II, Travis WD, Virmani AK, Yashima K, Brambilla E, Hasleton P, Gazdar AF (1999) Genetic changes in the spectrum of neuroendocrine lung tumors. Cancer 85:600–607
Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yatabe Y, Horio Y, Takahashi T (2005) ASH1 gene is a specific therapeutic target for lung cancers with neuroendocrine features. Cancer Res 65:10680–10685
Pandya K, Levy D, Hidalgo M (2005) A randomized, phase II ECOG trial of two dose levels of temsirolimus (CCI-779) in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer in remission after induction chemotherapy. A preliminary report. ASCO annual meeting proceedings, Abstract 7005, pp 622s
Papotti M, Croce S, Macri L, Funaro A, Pecchioni C, Schindler M, Bussolati G (2000) Correlative immunohistochemical and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis of somatostatin receptor type 2 in neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Diagn Mol Pathol 9:47–57
Papotti M, Sapino A, Righi L, Chiappone S, Bussolati G (2001) 34betaE12 cytokeratin immunodetection in the differential diagnosis of neuroendocrine carcinomas of the breast. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 9:229–233
Papotti M, Croce S, Bello M, Bongiovanni M, Allia E, Schindler M, Bussolati G (2001) Expression of somatostatin receptor types 2, 3 and 5 in biopsies and surgical specimens of human lung tumors. Correlation with preoperative octreotide scintigraphy. Virchows Arch 439:787–797
Pelosi G, Pasini F, Sonzogni A, Maffini F, Maisonneuve P, Iannucci A, Terzi A, De Manzoni G, Bresaola E, Viale G (2003) Prognostic implications of neuroendocrine differentiation and hormone production in patients with Stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 97:2487–2497
Pelosi G, Scarpa A, Puppa G, Veronesi G, Spaggiari L, Pasini F, Maisonneuve P, Iannucci A, Arrigoni G, Viale G (2005) Alteration of the E-cadherin/beta-catenin cell adhesion system is common in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors and is an independent predictor of lymph node metastasis in atypical carcinoids. Cancer 103:1154–1164
Pelosi G, Volante M, Papotti M, Sonzogni A, Masullo M, Viale G (2006) Peptide receptors in neuroendocrine tumors of the lung as potential tools for radionuclide diagnosis and therapy. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 50:272–287
Petersen I, Hidalgo A, Petersen S, Schluns K, Schewe C, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, Goeze A, Krebber B, Knosel T, Kaufmann O, Szymas J, von Deimling A (2000) Chromosomal imbalances in brain metastases of solid tumors. Brain Pathol 10:395–401
Pilmane M, Luts A, Sundler F (1995) Changes in neuroendocrine elements in bronchial mucosa in chronic lung disease in adults. Thorax 50:551–554
Reubi JC, Kappeler A, Waser B, Laissue J, Hipkin RW, Schonbrunn A (1998) Immunohistochemical localization of somatostatin receptors sst2A in human tumors. Am J Pathol 153:233–245
Reubi JC (2003) Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr Rev 24:389–427
Salon C, Moro D, Lantuejoul S, Brichon Py P, Drabkin H, Brambilla C, Brambilla E (2004) E-cadherin, beta-catenin adhesion complex in neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: a suggested role upon local invasion and metastasis. Hum Pathol 35:1148–1155
Salon C, Merdzhanova G, Brambilla C, Brambilla E, Gazzeri S, Eymin B (2007) E2F-1, Skp2 and cyclin E oncoproteins are upregulated and directly correlated in high-grade neuroendocrine lung tumors. Oncogene
Schleusener JT, Tazelaar HD, Jung SH, Cha SS, Cera PJ, Myers JL, Creagan ET, Goldberg RM, Marschke RF Jr (1996) Neuroendocrine differentiation is an independent prognostic factor in chemotherapy-treated nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 77:1284–1291
Shivapurkar N, Toyooka S, Eby MT, Huang CX, Sathyanarayana UG, Cunningham HT, Reddy JL, Brambilla E, Takahashi T, Minna JD, Chaudhary PM, Gazdar AF (2002) Differential inactivation of caspase-8 in lung cancers. Cancer Biother 1:65–69
Spears CP, Gustavsson BG, Mitchell MS, Spicer D, Berne M, Bernstein L, Danenberg PV (1984) Thymidylate synthetase inhibition in malignant tumors and normal liver of patients given intravenous 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Res 44:4144–4150
Sturm N, Rossi G, Lantuejoul S, Papotti M, Frachon S, Claraz C, Brichon PY, Brambilla C, Brambilla E (2002) Expression of thyroid transcription factor-1 in the spectrum of neuroendocrine cell lung proliferations with special interest in carcinoids. Hum Pathol 33:175–182
Sugita M, Geraci M, Gao B, Powell RL, Hirsch FR, Johnson G, Lapadat R, Gabrielson E, Bremnes R, Bunn PA, Franklin WA (2002) Combined use of oligonucleotide and tissue microarrays identifies cancer/testis antigens as biomarkers in lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 62:3971–3979
Sunday ME, Kaplan LM, Motoyama E, Chin WW, Spindel ER (1988) Gastrin-releasing peptide (mammalian bombesin) gene expression in health and disease. Lab Invest 59:5–24
Takeuchi T, Minami Y, Iijima T, Kameya T, Asamura H, Noguchi M (2006) Characteristics of loss of heterozygosity in large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung and small cell lung carcinomas. Pathol Int 56:434–439
Travis WD, Linnoila RI, Tsokos MG, Hitchcock CL, Cutler GB Jr, Nieman L, Chrousos G, Pass H, Doppman J (1991) Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung with proposed criteria for large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. An ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric study of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 15:529–553
Travis WD, Gal AA, Colby TV, Klimstra DS, Falk R, Koss MN (1998) Reproducibility of neuroendocrine lung tumor classification. Hum Pathol 29:272–279
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, Harris CC (eds) (2004) World Health Organization classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. IARC, Lyon, France
Tsurutani J, West KA, Sayyah J, Gills JJ, Dennis PA (2005) Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway but not the MEK/ERK pathway attenuates laminin-mediated small cell lung cancer cellular survival and resistance to imatinib mesylate or chemotherapy. Cancer Res 65:8423–8432
Vageli D, Daniil Z, Dahabreh J, Karagianni E, Liloglou T, Koukoulis G, Gourgoulianis K (2006) Microsatellite instability and loss of heterozygosity at the MEN1 locus in lung carcinoid tumors: a novel approach using real-time PCR with melting curve analysis in histopathologic material. Oncol Rep 15:557–564
Viberti L, Bongiovanni M, Croce S, Bussolati G (2000) 34betaE12 Cytokeratin immunodetection in the differential diagnosis of small cell tumors of lung. Int J Surg Pathol 8:317–322
Volante M, Fulcheri E, Allia E, Cerrato M, Pucci A, Papotti M (2002) Ghrelin expression in fetal, infant, and adult human lung. J Histochem Cytochem 50:1013–1021
Yokomizo A, Tindall DJ, Drabkin H, Gemmill R, Franklin W, Yang P, Sugio K, Smith DI, Liu W (1998) PTEN/MMAC1 mutations identified in small cell, but not in non-small cell lung cancers. Oncogene 17:475–479
Zaffaroni N, Villa R, Pastorino U, Cirincione R, Incarbone M, Alloisio M, Curto M, Pilotti S, Daidone MG (2005) Lack of telomerase activity in lung carcinoids is dependent on human telomerase reverse transcriptase transcription and alternative splicing and is associated with long telomeres. Clin Cancer Res 11:2832–2839
Zitzmann K, De Toni EN, Brand S, Goke B, Meinecke J, Spottl G, Meyer HH, Auernhammer CJ (2007) The novel mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) induces antiproliferative effects in human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cells. Neuroendocrinology 85:54–60
Acknowledgements
Work partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Research (MIUR, Rome; grant ex-60% to MP).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of Interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Righi, L., Volante, M., Rapa, I. et al. Neuro-endocrine tumours of the lung. A review of relevant pathological and molecular data. Virchows Arch 451 (Suppl 1), 51–59 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0445-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0445-0