Abstract
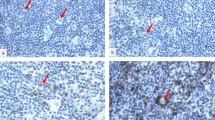
No reliable marker still exists for predicting those patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) who may experience a fatal outcome. Among the factors tested in the literature, it has been suggested that the number of activated cytotoxic T cells may represent a prognostic marker in HL. In 244 samples from patients with stage-IIIB/IV HL issued from the GELA H89 trial, we have analysed TiA1 expression on Reed Sternberg (RS) cells as well as the percentage of positive reactive lymphocytes. There were 34 cases (13.7%) that showed TiA1 expression on tumour cells; whereas, in 32 cases (13.1%), TiA1-positive reactive lymphocytes represented more than 30% of the reactive lymphocytes. LMP-1 was found co-expressed with TiA1 in 10 of the 22 positive cases tested. Our study confirms that a subset of classical HL expresses cytotoxic proteins, with occasional co-expression of CD20. In stage-IIIB/IV disease, neither TiA1 expression by RS cells nor a high percentage of TiA1-positive reactive lymphocytes have a prognostic impact on outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson P, Nagler-Anderson C, O’Brien C et al (1990) A monoclonal antibody reactive with a 15-kDa cytoplasmic granule-associated protein defines a subpopulation of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 144:574–582
Felgar RE, Macon WR, Kinney MC et al (1997) TIA-1 expression in lymphoid neoplasms. Identification of subsets with cytotoxic T lymphocyte or natural killer cell differentiation. Am J Pathol 150:1893–1900
Fermé C, Sebban C, Hennequin C et al (2000) Comparison of chemotherapy to radiotherapy as consolidation of complete or good partial response after six cycles of chemotherapy for patients with advanced Hodgkin’s disease: results of the Groupe d’étude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte H89 trial. Blood 95:2246–2252
Kanavaros P, Vlychou M, Stefanaki K et al (1999) Cytotoxic protein expression in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and Hodgkin’s disease. Anticancer Res 19:1209–1216
Krenacs L, Wellmann A, Sorbara L et al (1997) Cytotoxic cell antigen expression in anaplastic large cell lymphomas of T- and null-cell type and Hodgkin’s disease: evidence for distinct cellular origin. Blood 89:980–989
Mantel N (1966) Evaluation for survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep 50:163
Muschen M, Rajewsky K, Brauninger A et al (2000) Rare occurrence of classical Hodgkin’s disease as a T cell lymphoma. J Exp Med 191:387–394
Oudejans JJ, Jiwa NM, Kummer JA et al (1997) Activated cytotoxic T cells as prognostic marker in Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 89:1376–1382
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank J. Diebold for his helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camilleri-Broët, S., Fermé, C., Berger, F. et al. TiA1 in advanced-stage classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: no prognostic impact for positive tumour cells or number of cytotoxic cells. Virchows Arch 445, 344–346 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-1057-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-1057-6