Abstract
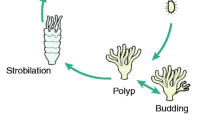
Strobilation is a unique asexual reproduction mode of scyphozoan jellyfish, through which benthic polyp develops into pelagic medusa. It is an orderly metamorphosis process triggered by environmental signals. However, the knowledges of molecular mechanisms under the drastic morphological and physiological changes are still limited. In this study, the transcriptomes from polyps to juvenile medusae at different stages were characterized by RNA-seq in scyphozoan jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Among 96,076 de novo assembled unigenes, 7090 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified during the developmental stages. The co-expression pattern analysis of DEGs yielded 15 clusters with different expression patterns. Among them, a cluster with 388 unigenes was related to strobila. In this specific cluster, the GO terms related to “sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity” and “sequence-specific DNA binding” were significantly enriched. Transcription factors, including segmentation protein even-skipped-like, segmentation polarity protein engrailed-like, homeobox proteins Otx-like, Twist-like and Cnox2-Pc-like, as well as genes such as RxR-like and Dmrtf-like, were identified to be potentially involved in strobilation. Their expression patterns and the other 11 TFs/genes involved in strobilation were confirmed with qRT-PCR methods. The present study pointed out the role of transcription factors in strobilation and produced a list of novel candidate genes for further studies. It could provide valuable information for understanding the molecular mechanisms of jellyfish strobilation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J (2010) topGO: enrichment analysis for gene ontology. R Package Version 2 18:0
Berking S, Czech N, Gerharz M, Herrmann K, Hoffmann U, Raifer H, Sekul G, Siefker B, Sommerei A, Vedder F (2005) A newly discovered oxidant defence system and its involvement in the development of Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria): reactive oxygen species and elemental iodine control medusa formation. Int J Dev Biol 49:969–976
Brekhman V, Malik A, Haas B, Sher N, Lotan T (2015) Transcriptome profiling of the dynamic life cycle of the scypohozoan jellyfish Aurelia aurita. BMC Genomics 16:74
Ceh J, Gonzalez J, Pacheco AS, Riascos JM (2015) The elusive life cycle of scyphozoan jellyfish—metagenesis revisited. Sci Rep 5:491–492
Chen J, Ding G (1983) Effect of temperature on the strobilation of jellyfish (Rhopilema esculenta Kishinouye-Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Acta Zool Sin 29:195–206 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Damen WGM (2010) Evolutionary conservation and divergence of the segmentation process in arthropods. Dev Dynam 236:1379–1391
D'Amico LA, Boujard D, Coumailleau P (2013) The neurogenic factor NeuroD1 is expressed in post-mitotic cells during juvenile and adult Xenopus neurogenesis and not in progenitor or radial glial cells. PLoS One 8:e66487
Ding G, Chen J (1981) The life history of Rhopilema esculenta Kishinouye. J Fish China 5:93–104 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dong Z, Liu D, Keesing JK (2010) Jellyfish blooms in China: dominant species, causes and consequences. Mar Pollut Bull 60:954–963
Eddy SR (1998) Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 14:755–763
Fuchs B, Wang W, Graspeuntner S, Li Y, Insua S, Herbst EM, Dirksen P, Böhm AM, Hemmrich G, Sommer F, Domazet-Lošo T, Klostermeier UC, Anton-Erxleben F, Rosenstiel P, Bosch TCG, Khalturin K (2014) Regulation of polyp-to-jellyfish transition in Aurelia aurita. Curr Biol 24:263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.12.003
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, di Palma F, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1883
Helm RR (2018) Evolution and development of scyphozoan jellyfish. Biol Rev 93:1228–1250
Helm RR, Tiozzo S, Lilley MKS, Lombard F, Dunn CW (2015) Comparative muscle development of scyphozoan jellyfish with simple and complex life cycles. Evodevo 6:1–10
Kopp A (2012) Dmrt genes in the development and evolution of sexual dimorphism. Trends Genet 28:175–184
Kostrouch Z, Kostrouchova M, Love W, Jannini E, Piatigorsky J, Rall JE (1998) Retinoic acid X receptor in the diploblast, Tripedalia cystophora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:13442–13447
Kraus JEM, Fredman D, Wang W, Khalturin K, Technau U (2015) Adoption of conserved developmental genes in development and origin of the medusa body plan. Evodevo 6:23
Kroiher M, Siefker B, Berking S (2000) Induction of segmentation in polyps of Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria) into medusae and formation of mirror-image medusa anlagen. Int J Dev Biol 44:485
Kuniyoshi HI, Okumura R, Kuroda N, Tsujita K, Arakawa J, Shoji TS, Osada H (2012) Indomethacin induction of metamorphosis from the asexual stage to sexual stage in the moon jellyfish, Aurelia aurita. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:1397–1400
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25
Li B, Dewey CN (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12:323
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei L (2005) Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 21:3787–3793
Masuda-Nakagawa LM, Gröer H, Aerne BL, Schmid V (2000) The Hox-like gene Cnox2-Pc is expressed at the anterior region in all life cycle stages of the jellyfish Podocoryne carnea. Dev Genes Evol 210:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270050022
Müller P, Yanze N, Schmid V, Spring J (1999) The homeobox gene Otx of the jellyfish Podocoryne carnea: role of a head gene in striated muscle and evolution. Dev Biol 216:582–594
Nakanishi N, Hartenstein V, Jacobs DK (2009) Development of the rhopalial nervous system in Aurelia sp.1 (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). Dev Genes Evol 219:301–317
Omori M, Nakano E (2001) Jellyfish fisheries in Southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia 451:19–26
Parlier D, Moers V, van Campenhout C, Preillon J, Leclère L, Saulnier A, Sirakov M, Busengdal H, Kricha S, Marine JC, Rentzsch F, Bellefroid EJ (2013) The Xenopus doublesex-related gene Dmrt5 is required for olfactory placode neurogenesis. Dev Biol 373:39–52
Picard MA et al (2015) The roles of Dmrt (double sex/male-abnormal-3 related transcription factor) genes in sex determination and differentiation mechanisms: ubiquity and diversity across the animal kingdom. C R Biol 338:451–462
Prieto L, Astorga D, Navarro G, Ruiz J (2012) Environmental control of phase transition and polyp survival of a massive-outbreaker jellyfish. PLoS One 5:e13793
Purcell JE, Uye SI, Lo WT (2007) Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for human: a review. Mar Ecol Prog 350:153–174
Robinson MD, Oshlack A (2010) A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol 11:1–9
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140
Spangenberg DB (1967) Iodine induction of metamorphosis in Aurelia. J Exp Zool 165:441–449
Spangenberg DB (1974) Thyroxine in early strobilation in Aurelia aurita. Am Zool 14:825–831
Spring J, Yanze N, Middel AM, Stierwald M, Gröger H, Schmid V (2000) The mesoderm specification factor twist in the life cycle of jellyfish. Dev Biol 228:363–375
Storey JD (2003) The positive false discovery rate: a Bayesian interpretation and the q-value. Ann Stat 31:2013–2035
Tresser J, Chiba SM, El ND, Newman SE, Horie T, Tsuda M, Smith WC (2010) Doublesex/mab3 related-1 (dmrt1) is essential for development of anterior neural plate derivatives in Ciona. Development 137:2197–2203
Uye SI (2014) The giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai in east Asian marginal seas. In: Pitt KA, Lucas CH (eds) Jellyfish blooms. Springer, Dordrecht
You K, Ma CH, Gao HW, Li FQ, Zhang MZ, Qiu YT, Wang B (2007) Research on the jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye) and associated aquaculture techniques in China: current status. Aquacult Int 15:479–488
Zhao C, Emmons SW (1995) A transcription factor controlling development of peripheral sense organs in C. elegans. Nature 373:74–78
Acknowledgments
We thank BMK Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for help with the Illumina sequencing of the cDNA library and bio-informatic analysis.
Funding
This study received grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31702327) and Key Program for International S&T Cooperation Projects of China (2017YFE0111100-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Mark Q. Martindale
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
The saturation curve of transcriptome sequencing data in the 6 libraries. The x-axis is the number of reads (in units of 10^6) and the y-axis is the number of genes detected (in units of 10^3). (DOCX 211 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
The 20 most enriched GO terms in the strobila specific cluster. The number on the top of each bar indicates the gene number in each GO terms. (DOCX 85 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Classification of differentially expressed TFs according to their family group. (DOCX 17 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOCX 14 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(XLSX 8696 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
(XLSX 322 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
(XLSX 849 kb)
Supplementary Table 6
(DOCX 17 kb)
Supplementary Table 7
(XLSX 102 kb)
Supplementary Table 8
(XLSX 29 kb)
Supplementary Table 9
(XLSX 37 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, J., Liu, C., Tan, J. et al. Transcriptome analysis of scyphozoan jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum from polyp to medusa identifies potential genes regulating strobilation. Dev Genes Evol 228, 243–254 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-018-0621-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-018-0621-z