Abstract
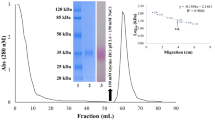
Analysis of nectar from leek (Allium porrum) flowers by SDS-PAGE revealed the presence of two major polypeptide bands of 50 kDa and 13 kDa, respectively. Using a combination of agglutination tests, enzyme assays and N-terminal sequencing, the polypeptides have been identified as subunits of alliin lyase (alliinase, EC 4.4.1.4) and mannose-binding lectin, respectively. The latter protein is particularly abundant since it represents about 75% of the total nectar protein. Honey produced by bees foraging on flowering leek plants still contains biologically active lectin and alliinase. However, the levels of both proteins are strongly reduced as compared to those in the original nectar. It is evident, therefore, that the lectin as well as the alliinase are inactivated/degraded during the conversion of nectar into honey.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
Brewster JL, ed (1994) Onions and other vegetable Alliums. CAB International, Wallingford, UK
Collinge DB, Kragh KM, Mikkelsen JD, Nielsen KK, Rasmussen U, Vad K (1993) Plant chitinases. Plant J 3: 31–40
Hilder VA, Powell KS, Gatehouse AMR, Gatehouse JA, Gatehouse LN, Shi Y, Hamilton WDO, Merryweather A, Newell C, Timans JC, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM, Boulter D (1995) Expression of snowdrop lectin in transgenic tobacco plants results in added protection against aphids. Transgen Res 4: 18–25
Jansen H, Müller B, Knobloch K (1989) Characterization of an alliin lyase preparation from garlic (Allium sativum). Planta Med 55: 434–439
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Lancaster JE, Collin HA (1981) Presence of alliinase in isolated vacuoles and of alkyl cysteine sulfoxides in the cytoplasm of bulbs of onion (Allium cepa). Plant Sci Lett 22: 169–176
Landshuter J, Lohmüller E, Knobloch K (1994) Purification and characterization of a C-S-lyase from ramson, the wild garlic, Allium ursinum. Planta Med 60: 343–347
Lohmüller E-M, Landshuter J, Knobloch K (1994) On the isolation and characterization of a C-S-lyase preparation from leek, Allium porrum. Planta Med 60: 337–342
Mo H, Van Damme EJM, Peumans WJ, Goldstein IJ (1993) Purification and characterization of a mannose-specific lectin from shallot (Allium ascalonicum) bulbs. Arch Biochem Biophys 306: 431–438
Nock PL, Mazelis M (1986) The C-S lyases of higher plants: preparation and properties of homogeneous alliin lyase from garlic (Allium sativum). Arch Biochem Biophys 249: 27–33
Powell KS, Gatehouse AMR, Hilder VA, Van Damme EJM, Peumans WJ, Boonjawat J, Horsham K, Gatehouse JA (1995) Different antimetabolic effects of related lectins towards nymphal stages of Nilaparvata lugens. Entomol Exp Appl 75: 61–65
Rabinkov A, Zhu X, Grafi G, Galili G, Mirelman D. (1994) Alliin lyase (alliinase) from garlic (Allium sativum). Appl Biochem Biotech 48: 149–171
Rahbé Y, Sauvion N, Febvay G, Peumans WJ, Gatehouse AMR (1995) Toxicity of lectins and processing of ingested proteins in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Entomol Exp Appl 76: 143–155
Schwimmer S, Guadagni DG (1962) Relation between olfactory threshold concentration and pyruvic acid content of onion juice. J Food Sci 27: 94–97
Shibuya N, Goldstein IJ, Van Damme EJM, Peumans WJ (1988) Binding properties of a mannose-specific lectin from the snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis) bulb. J Biol Chem 263: 728–734
Smeets K, Van Damme EJM, Peumans WJ (1994) Comparative study of the post-translational processing of the mannosebinding lectins in the bulbs of garlic (Allium sativum) and ramsons (Allium ursinum). Glycoconjugate J 11: 309–320
Van Damme EJM, Allen AK, Peumans WJ (1987) Isolation and characterization of a lectin with exclusive specificity towards mannose from snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis) bulbs. FEBS Lett 215: 140–144
Van Damme EJM, Goldstein IJ, Peumans WJ (1991a) A comparative study of related mannose-binding lectins from the Amaryllidaceae and Alliaceae. Phytochemistry 30: 509–514
Van Damme EJM, Kaku H, Perini F, Goldstein IJ, Peeters B, Yagi F, Decock B, Peumans WJ (1991b) Biosynthesis, primary structure and molecular cloning of snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis L.) lectin. Eur J Biochem 202: 23–30
Van Damme EJM, Goldstein IJ, Vercammen G, Vuylsteke J, Peumans WJ (1992a) Lectins of members of the Amaryllidaceae are encoded by multigene families which show extensive homologies. Physiol Plant 86: 245–252
Van Damme EJM, Smeets K, Torrekens S, Van Leuven F, Peumans WJ (1992b) Isolation and characterization of alliinase cDNA clones from garlic (Allium sativum L.) and related species. Eur J Biochem 209: 751–757
Van Damme EJM, Smeets K, Balzarini J, Pusztai A, Van Leuven F, Goldstein IJ, Peumans WJ (1993) Cloning and characterization of the lectin cDNA clones from onion, shallot and leek. Plant Mol Biol 23: 365–376
Van Damme EJM, Balzarini J, Smeets K, Van Leuven F, Peumans WJ (1994) The monomeric and dimeric mannose-binding proteins from the Orchidaceae species Listera ovata and Epipactis helleborine: sequence homologies and differences in biological activities. Glycoconjugate J 11: 321–332
Van Damme EJM, Briké F, Winter HC, Van Leuven F, Goldstein IJ, Peumans WJ (1996) Molecular cloning of two different mannose-binding lectins from tulip bulbs. Eur J Biochem 236: 419–427
Wirth SJ, Wolf GA (1990) Dye-labelled substrates for the assay and detection of chitinase and lysozyme activity. J Microbiol Methods 12: 197–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by grants from the KULeuven and the National Fund for Scientific Research (Belgium). E.V.D is a Senior Research Assistant and W.P. a Research Director of the National Fund for Scientific Research (Belgium).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peumans, W.J., Smeets, K., Van Nerum, K. et al. Lectin and alliinase are the predominant proteins in nectar from leek (Allium porrum L.) flowers. Planta 201, 298–302 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050070
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050070