Abstract.
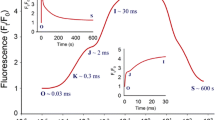
Dissipation of light energy was studied in the moss Rhytidiadelphus squarrosus (Hedw.) Warnst., and in leaves of Spinacia oleracea L. and Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh., using chlorophyll fluorescence as an indicator reaction. Maximum chlorophyll fluorescence of 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (DCMU)-treated spinach leaves, as produced by saturating light and studied between +5 and −20 °C, revealed an activation energy ΔE of 0.11 eV. As this suggested recombination fluorescence produced by charge recombination between the oxidized primary donor of photosystem II and reduced pheophytin, a mathematical model explaining fluorescence, and based in part on known characteristics of primary electron-transport reactions, was developed. The model permitted analysis of different modes of fluorescence quenching, two localized in the reaction center of photosystem II and one in the light-harvesting system of the antenna complexes. It predicted differences in the relationship between quenching of variable fluorescence F v and quenching of basal, so-called F 0 fluorescence depending on whether quenching originated from antenna complexes or from reaction centers. Such differences were found experimentally, suggesting antenna quenching as the predominant mechanism of dissipation of light energy in the moss Rhytidiadelphus, whereas reaction-center quenching appeared to be important in spinach and Arabidopsis. Both reaction-center and antenna quenching required activation by thylakoid protonation but only antenna quenching depended on or was strongly enhanced by zeaxanthin. De-protonation permitted relaxation of this quenching with half-times below 1 min. More slowly reversible quenching, tentatively identified as so-called q I or photoinhibitory quenching, required protonation but persisted for prolonged times after de-protonation. It appeared to originate in reaction centers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 April 2000 / Accepted: 31 August 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bukhov, N., Heber, U., Wiese, C. et al. Energy dissipation in photosynthesis: Does the quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence originate from antenna complexes of photosystem II or from the reaction center?. Planta 212, 749–758 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250000486
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250000486