Abstract
Main conclusion
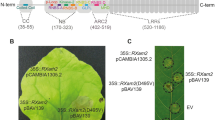
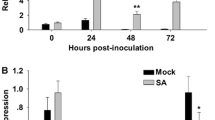
The overexpression of RXam1 leads to a reduction in bacterial growth of XamCIO136, suggesting that RXam1 might be implicated in strain-specific resistance.
Cassava bacterial blight (CBB) caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis (Xam) is a prevalent disease in all regions, where cassava is cultivated. CBB is a foliar and vascular disease usually controlled through host resistance. Previous studies have found QTLs explaining resistance to several Xam strains. Interestingly, one QTL called XM5 that explained 13% of resistance to XamCIO136 was associated with a similar fragment of the rice Xa21-resistance gene called PCR250. In this study, we aimed to further identify and characterize this fragment and its role in resistance to CBB. Screening and hybridization of a BAC library using the molecular marker PCR250 as a probe led to the identification of a receptor-like kinase similar to Xa21 and were called RXam1 (Resistance to Xam 1). Here, we report the functional characterization of susceptible cassava plants overexpressing RXam1. Our results indicated that the overexpression of RXam1 leads to a reduction in bacterial growth of XamCIO136. This suggests that RXAM1 might be implicated in strain-specific resistance to XamCIO136.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- dpi:
-
Days post inoculation
- LRR:
-
Leucine-rich repeats
- CBB:
-
Cassava bacterial blight
- EFR:
-
Elongation factor receptor
- MAMP:
-
Microbe-associated molecular pattern
- PRR:
-
Pattern-recognition receptors
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RLK:
-
Receptor-like kinase
- Xam :
-
Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bart R, Cohn M, Kassen A et al (2012) High-throughput genomic sequencing of cassava bacterial blight strains identifies conserved effectors to target for durable resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E1972–E1979
Boutrot F, Segonzac C, Chang KN, Qiao H, Ecker JR, Zipfel C (2010) Direct transcriptional control of the Arabidopsis immune receptor FLS2 by the ethylene-dependent transcription factors EIN3 and EIL1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:14502–14507
Bull SE, Owiti JA, Niklaus M, Beeching JR, Gruissem W, Vanderschuren H (2009) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of friable embryogenic calli and regeneration of transgenic cassava. Nat Protoc 4(12):1845–1854
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Kioke T et al (2003) Multiple sequence aligment with the clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3497–3500
Chinchilla D, Bauer Z, Regenass M, Boller T, Felix G (2006) The Arabidopsis receptor kinase FLS2 binds flg22 and determines the specificity of flagellin perception. Plant Cell 18:465–476
Contreras E, Lopez C (2008) Expresión de dos genes candidatos a resistencia contra la bacteriosis vascular en yuca. Acta Biol Colom 13:175–188
Couto D, Zipfel C (2016) Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling in plants. Nature Rev Immunol 16:537–552
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1(4):19–21
Duxbury Z, Ma Y, Furzer OJ et al (2016) Pathogen perception by NLRs in plants and animals: parallel worlds. BioEssays 38:769–781
Fregene M, Angel F, Gomez R et al (1997) A molecular genetic map of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Theor Appl Genet 95:431–441
French E, Kim B, Iyer-Pascuzzi A (2016) Mechanisms of quantitative disease resistance in plants. Semin Cell Dev Biol 56:201–208
Gedil M, Kumar M, Igwe D (2012) Isolation and characterization of resistant gene analogs in cassava, wild Manihot species, and castor bean (Ricinus communis). Afr J Biotechnol 11:15111–15123
Godfrey D, Rathjen JP (2012) Recognition and response in plant PAMP-triggered immunity. In: eLS. Wiley, London. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0023725
Greshoff PM, Doy CH (1972) Development and differentiation of haploid Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Planta 107:161–170
Gurr SJ, Rushton PJ (2005) Engineering plants with increased disease resistance: how are we going to express it? Trends Biotechnol 23:283–290
Hahn SK, Terry ER, Leuschner K, Akobundu IO, Okali C, Lal R (1979) Cassava improvement in Africa. Field Crops Res 2:193–226
Hahn SK, Howland AK, Terry ER (1980) Correlated resistance of cassava to mosaic and bacterial blight diseases. Euphytica 29:305–311
Hurni S, Scheuermann D, Krattinger SG et al (2015) The maize disease resistance gene Htn1 against northern corn leaf blight encodes a wall-associated receptor-like kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:8780–8785
Jacob F, Vernaldi S, Maekawa T (2013) Evolution and conservation of plant NLR functions. Front Immunol 4:1–16
Jorge V, Fregene MA, Duque MC, Bonierbale MW, Tohme J, Verdier V (2000) Genetic mapping of resistance to bacterial blight disease in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Theor Appl Genet 101:865–872
Jorge V, Verdier V (2002) Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of cassava bacterial blight resistance in F1 progeny of a cross between elite cassava clones. Euphytica 123:41–48
Kou Y, Wang S (2010) Broad-spectrum and durability: understanding of quantitative disease resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:181–185
Lacombe S, Rougon-Cardoso A, Sherwood E et al (2010) Interfamily transfer of a plant pattern-recognition receptor confers broad-spectrum bacterial resistance. Nat Biotechnol 28:365–369
Li B, Meng X, Shan L, He P (2016) Transcriptional regulation of pattern-triggered immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 19:641–650
Liu B, Li JF, Ao Y et al (2012) Lysin motif-containing proteins LYP4 and LYP6 play dual toles in peptidoglycan and chitin perception in rice innate immunity. Plant Cell 24:3406–3419
López CE, Bernal AJ (2012) Cassava bacterial blight: using genomics for the elucidation and management of an old problem. Trop Plant Biol 5:117–126
López CE, Zuluaga AP, Cooke R, Delseny M, Tohme J, Verdier V (2003) Isolation of resistance gene candidates (RGCs) and characterization of an RGC cluster in cassava. Mol Genet Genom 269:658–671
López CE, Quesada-Ocampo LM, Bohorquez A et al (2007) Mapping EST-derived SSRs and ESTs involved in resistance to bacterial blight in Manihot esculenta. Genome 50:1078–1088
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S et al (2012) Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:614–629
Marone D, Russo M, Laidò G, De Leonardis A, Mastrangelo A (2013) Plant nucleotide binding site–leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes: active guardians in host defense responses. Int J Mol Sci 14:7302–7326
Mba RE, Stephenson P, Edwards K et al (2001) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers survey of the cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) genome: towards an SSR-based molecular genetic map of cassava. Theor Appl Genet 102:21–31
McCallum EJ, Anjanappa RB, Gruissem W (2017) Tackling agriculturally relevant diseases in the staple crop cassava (Manihot esculenta). Curr Opin Plant Biol 38:50–58
Miya A, Albert P, Shinya T et al (2007) CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19613–19618
Moreno I, Gruissem W, Vanderschuren H (2011) Reference genes for reliable potyvirus quantitation in cassava and analysis of Cassava brown streak virus load in host varieties. J Virol Methods 177:49–54
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497
Poland JA, Balint-Kurti PJ, Wisser RJ, Pratt RC, Nelson RJ (2009) Shades of gray: the world of quantitative disease resistance. Trends Plant Sci 14:21–29
Pruitt RN, Schwessinger B, Joe A et al (2015) The rice immune receptor XA21 recognizes a tyrosine-sulfated protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Sci Adv 1:e1500245
Qi D, Innes RW (2013) Recent advances in plant NLR structure, function, localization, and signaling. Front Immunol 4:1–10
Rabbi IY, Hamblin MT, Kumar PL, Gedil MA, Ikpan AS, Jannink JL et al (2014) High-resolution mapping of resistance to cassava mosaic geminiviruses in cassava using genotyping-by-sequencing and its implications for breeding. Virus Res 186:87–96
Ranf S, Gisch N, Schaffer M et al (2015) A lectin S-domain receptor kinase mediates lipopolysaccharide sensing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Immunol 16:426–433
Restrepo S, Verdier V (1997) Geographical differentiation of the population of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Colombia. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4427–4434
Roux F, Voisin D, Badet T et al (2014) Resistance to phytopathogens e tutti quanti: placing plant quantitative disease resistance on the map. Mol Plant Pathol 15:427–432
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386
Shimizu T, Nakano T, Takamizawa D et al (2010) Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice. Plant J 64:204–214
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen LL et al (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 270:1804–1806
Soto JC, Ortiz JF, Perlaza-Jiménez L et al (2015) A genetic map of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) with integrated physical mapping of immunity-related genes. BMC Genomics 16:190. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1397-4
St. Clair DA (2010) Quantitative disease resistance and quantitative resistance loci in breeding. Annu Rev Phytopathol 48:247–268
Takken FLW, Goverse A (2012) How to build a pathogen detector: structural basis of NB-LRR function. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15:375–384
Taylor N, Gaitán-Solís E, Moll T et al (2012) A high-throughput platform for the production and analysis of transgenic cassava (Manihot esculenta) plants. Tropical Plant Biol 5(1):127–139
Tomkins J, Fregene M, Main D, Kim H, Wing R, Tohme J (2004) Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library resource for positional cloning of pest and disease resistance genes in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Plant Mol Biol 56(4):555–561
Trujillo CA, Ochoa JC, Mideros MF, Restrepo S, López CE, Bernal A (2014) A complex population structure of the cassava pathogen Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in recent years in the caribbean region of Colombia. Microb Ecol 68:155–167
Wu Y, Zhou JM (2013) Receptor-like kinases in plant innate immunity. J Integr Plant Biol 55:1271–1286
Wu S, Shan L, He P (2014) Microbial signature-triggered plant defense responses and early signaling mechanisms. Plant Sci 228:118–126
Wydra K, Zinsou V, Jorge V, Verdier V (2004) Identification of pathotypes of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Africa and detection of quantitative trait loci and markers for resistance to bacterial blight of cassava. Phytopathology 94:1084–1093
Zipfel C, Kunze G, Chinchilla D et al (2006) Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 125:749–760
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Colciencias (110152128399). PADT was supported with a scholarship for graduated students from Universidad Nacional de Colombia. The authors would like to acknowledge Rosa Juliana Gil for careful and critical reading of the manuscript, Camilo Dorado for his support on the statistical analysis and Fabio Gómez for his support on the molecular cloning of RXam1. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz Tatis, P.A., Herrera Corzo, M., Ochoa Cabezas, J.C. et al. The overexpression of RXam1, a cassava gene coding for an RLK, confers disease resistance to Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis. Planta 247, 1031–1042 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2863-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2863-4