Abstract
Main conclusion
MdPUB29 is a positive regulator of the defense response to the fungal pathogen Botryosphaeria dothidea possibly by directly regulating the salicylic acid (SA) content as well as SA synthesis-related and signaling-related gene transcription.
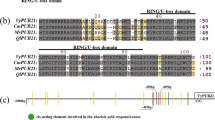
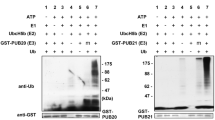
In plants, ubiquitin E3 ligases containing a U-box domain (PUBs, Plant U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase) have been identified as key regulators of fundamental cellular processes, such as cellular growth, development, and apoptosis, as well as biotic and abiotic stress responses. However, the function of PUBs in apple ring rot remains elusive. Here, we isolated the U-box E3 ligase MdPUB29 from the apple cultivar ‘Royal Gala’ and characterized its function in plant pathogen defense against Botryosphaeria dothidea. qRT-PCR showed that the expression of MdPUB29 was significantly induced in apple fruits after B. dothidea infection. Overexpression of the MdPUB29 gene in apple calli increased the resistance to B. dothidea infection. In contrast, silencing MdPUB29 in apple calli resulted in reduced resistance. Ectopic expression of MdPUB29 in Arabidopsis also exhibited enhanced resistance to B. dothidea infection compared to that of the wild-type (Col) control. In addition, it was found that the increase of plant pathogen defense was correlated with the increased salicylic acid (SA) content, as well as SA synthesis-related and signaling-related gene transcription in comparison to the wild type. We elucidated the mechanism by which MdPUB29 elevates plant pathogen defense against B. dothidea possibly by regulating the SA pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PTI:
-
PAMPs-triggered immunity
- PUB:
-
Plant U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
References
Adams EH, Spoel SH (2018) The ubiquitin-proteasome system as a transcriptional regulator of plant immunity. J Exp Bot 69:4529–4537. https://academic.oup.com/jxb/article/69/19/4529/5033092
Berndsen CE, Wolberger C (2014) New insights into ubiquitin E3 ligase mechanism. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:301. https://www.nature.com/articles/nsmb.2780
Bonito G, Isikhuemhen OS, Vilgalys R (2010) Identification of fungi associated with municipal compost using DNA-based techniques. Bioresour Technol 101:1021–1027
Crous PW, Slippers B, Wingfield MJ, Rheeder J, Marasas WF, Philips AJ, Alves A, Burgess T, Barber P, Groenewald JZ (2006) Phylogenetic lineages in the Botryosphaeriaceae. Stud Mycol 55:235–253
Diaz-Vivancos P, Bernal-Vicente A, Cantabella D, Petri C, Hernández JA (2017) Metabolomics and biochemical approaches link salicylic acid biosynthesis to cyanogenesis in peach plants. Plant Cell Physiol 58:2057–2066. https://academic.oup.com/pcp/article/58/12/2057/4222594
Duan Y, Jiang Y, Ye S, Karim A, Ling Z, He Y, Yang S, Luo K (2015) PtrWRKY73, a salicylic acid-inducible poplar WRKY transcription factor, is involved in disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 34:831–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1745-5
Duplan V, Rivas S (2014) E3 ubiquitin-ligases and their target proteins during the regulation of plant innate immunity. Front Plant Sci 5:42. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00042/full
Fu ZQ, Dong X (2013) Systemic acquired resistance: turning local infection into global defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:839–863. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105606
He Q, McLellan H, Boevink PC, Sadanandom A, Xie C, Birch PR, Tian Z (2015) U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase PUB17 acts in the nucleus to promote specific immune pathways triggered by Phytophthora infestans. J Exp Bot 66:3189–3199. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25873665
He X, Huo Y, Liu X, Zhou Q, Feng S, Shen X, Chen X (2018) Activation of disease resistance against Botryosphaeria dothidea by downregulating the expression of MdSYP121 in apple. Hortic Res 5:24. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41438-018-0030-5
Herrera-Vásquez A, Salinas P, Holuigue L (2015) Salicylic acid and reactive oxygen species interplay in the transcriptional control of defense genes expression. Front Plant Sci 6:171. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00171/full
Hu D, Sun C, Ma Q, You C, Cheng L, Hao Y (2016a) MdMYB1 regulates anthocyanins and malate accumulation by directly facilitating their transport into the vacuole in apples. Plant Physiol 170:1315–1330. http://www.plantphysiol.org/content/early/2015/12/04/pp.15.01333
Hu D, Ma Q, Sun C, Sun M, You C, Hao Y (2016b) Overexpression of MdSOS2L1, a CIPK protein kinase, increases the antioxidant metabolites to enhance salt tolerance in apple and tomato. Physiol Plant 156:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12354
Kang L, Hao H, Yang Z, Li X, Kang G (2009) The advances in the research of apple ring rot. Chin Agric Bull 25:188–191. http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-zntb200909039.htm
Klessig DF, Choi HW, Dempsey DMA (2018) Systemic acquired resistance and salicylic acid: past, present, and future. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 31:871–888. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-03-18-0067-CR
Kumar SS, Manoj P, Giridhar P (2015) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis, chlorophyll content and antioxidant properties of native and defatted foliage of green leafy vegetables. J Food Sci 52:8131–8139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1959-0
Liu X, Liang Y, Zhang W, Huo Y, Feng S, Qiu H, He X, Wu S, Chen X (2018) MdFLS2 recognizes bacterial flagellin flg22 and enhances immune resistance against apple ring rot causal fungi in Arabidopsis fls2 mutant. Acta Hortic Sin 45:827–844. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYXB201805002.htm (in Chinese)
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Loake G, Grant M (2007) Salicylic acid in plant defence-the players and protagonists. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:466–472
Lu D, Lin W, Gao X, Wu S, Cheng C, Avila J, Shan L (2011) Direct ubiquitination of pattern recognition receptor FLS2 attenuates plant innate immunity. Science 332:1439–1442. http://science.sciencemag.org/content/332/6036/1439
Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2014) The transcriptional regulatory network in the drought response and its crosstalk in abiotic stress responses including drought, cold, and heat. Front Plant Sci 5:170. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00170/full
O’neill LA (2011) Innate immunity in plants goes to the PUB. Science 332:1386–1387. http://science.sciencemag.org/content/332/6036/1386
Rietz S, Stamm A, Malonek S, Wagner S, Becker D, Medina-Escobar N, Parker JE (2011) Different roles of enhanced disease susceptibility 1 (EDS1) bound to and dissociated from phytoalexin deficient 4 (PAD4) in Arabidopsis immunity. New Phytol 191:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03675.x
Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M (2012) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jb/2012/217037/abs/
Slippers B, Crous PW, Denman S, Coutinho TA, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ (2004) Combined multiple gene genealogies and phenotypic characters differentiate several species previously identified as Botryosphaeria dothidea. Mycologia 96:83–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/15572536.2005.11833000
Sun M, Ma Q, Hu D, Zhu X, You C, Shu H, Hao Y (2018) The glucose sensor MdHXK1 phosphorylates a tonoplast Na+/H+ exchanger to improve salt tolerance. Plant Physiol 176:2977–2990. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01472
Tang W, Ding Z, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Guo L (2012) Phylogenetic and pathogenic analyses show that the causal agent of apple ring rot in China is Botryosphaeria dothidea. Plant Dis 96:486–496. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-08-11-0635
Tateda C, Zhang Z, Shrestha J, Jelenska J, Chinchilla D, Greenberg JT (2014) Salicylic acid regulates Arabidopsis microbial pattern receptor kinase levels and signaling. Plant Cell 26:4171–4187. http://www.plantcell.org/content/early/2014/10/14/tpc.114.131938.short
Trujillo M (2017) News from the PUB: plant U-box type E3 ubiquitin ligases. J Exp Bot 69:371–384. https://academic.oup.com/jxb/article/69/3/371/4718587
Trujillo M, Shirasu K (2010) Ubiquitination in plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:402–408
Trujillo M, Ichimura K, Casais C, Shirasu K (2008) Negative regulation of PAMP-triggered immunity by an E3 ubiquitin ligase triplet in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 18:1396–1401
Vicente MRS, Plasencia J (2011) Salicylic acid beyond defence: its role in plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 62:3321–3338. https://academic.oup.com/jxb/article/62/10/3321/479369
Wang X, Sager R, Cui W, Zhang C, Lu H, Lee JY (2013) Salicylic acid regulates plasmodesmata closure during innate immune responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell tpc-113. http://www.plantcell.org/content/25/6/2315.short
Wang B, Liang X, Gleason ML, Zhang R, Sun G (2018) Comparative genomics of Botryosphaeria dothidea and B. kuwatsukai, causal agents of apple ring rot, reveals both species expansion of pathogenicity-related genes and variations in virulence gene content during speciation. IMA Fungus 9: 243–257. https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ima/imafung/pre-prints/content-p2_vol9_no2_article2
Xu C, Wang C, Ju L, Zhang R, Biggs AR, Tanaka E, Li B, Sun G (2015) Multiple locus genealogies and phenotypic characters reappraise the causal agents of apple ring rot in China. Fungal Divers 71:215–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-014-0306-5
Yan S, Dong X (2014) Perception of the plant immune signal salicylic acid. Curr Opin Plant Biol 20:64–68
Yee D, Goring DR (2009) The diversity of plant U-box E3 ubiquitin ligases: from upstream activators to downstream target substrates. J Exp Bot 60:1109–1121. https://academic.oup.com/jxb/article/60/4/1109/566266
Zhang Q, Yong D, Zhang Y, Shi X, Li B, Li G, Liang W, Wang C (2016) Streptomyces rochei A-1 induces resistance and defense-related responses against Botryosphaeria dothidea in apple fruit during storage. Postharvest Biol Tec 115:30–37
Zhu Y, Li Y, Fei F, Wang Z, Wang W, Cao A, Chen W (2015) E3 ubiquitin ligase gene CMPG 1–V from Haynaldia villosa L. contributes to powdery mildew resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant J 84:154–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12966
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Prof. Takaya Moriguchi of National Institute of Fruit Tree Science, Japan, for ‘Orin’ apple calli. We also would like to thank TopEdit English Editing LLC for providing linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31601728, 31471854 and 31772288), Ministry of Education of China (IRT15R42), Shandong Province (ZR2016CQ13 and SDAIT-06-03), and Shandong Agricultural University (564024, 24024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, PL., Dong, YH., Gu, KD. et al. The apple U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase MdPUB29 contributes to activate plant immune response to the fungal pathogen Botryosphaeria dothidea. Planta 249, 1177–1188 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-03069-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-03069-z