Abstract
Main conclusion
Young Seedling Stripe1 (YSS1) was characterized as an important regulator of plastid-encoded plastid RNA polymerase (PEP) activity essential for chloroplast development at rice seedling stage.
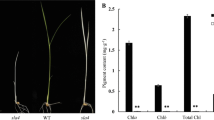
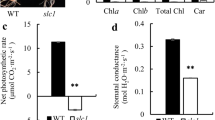
Chloroplast development is coordinately regulated by plastid- and nuclear-encoding genes. Although a few regulators have been reported to be involved in chloroplast development, new factors remain to be identified, given the complexity of this process. Here, we report the characterization of a temperature-sensitive young seedling stripe1 (yss1) rice mutant, which develops striated leaves at the seedling stage, particularly in leaf 3, but produces wild-type leaves in leaf 5 and onwards. The chlorotic leaves have decreased chlorophyll (Chls) accumulation and impaired chloroplast structure. Positional cloning combined with sequencing demonstrated that aberrant splicing of the 8th intron in YSS1 gene, due to a single nucleotide deletion around splicing donor site, leads to decreased expression of YSS1 and accumulation of an 8th intron-retained yss1 transcript. Furthermore, complementation test revealed that downregulation of YSS1 but not accumulation of yss1 transcript confers yss1 mutant phenotype. YSS1 encodes a chloroplast nucleoid-localized protein belonging to the DUF3727 superfamily. Expression analysis showed that YSS1 gene is more expressed in newly expanded leaves, and distinctly up-regulated as temperatures increase and by light stimulus. PEP- and nuclear-encoded phage-type RNA polymerase (NEP)-dependent genes are separately down-regulated and up-regulated in yss1 mutant, indicating that PEP activity may be impaired. Furthermore, levels of chloroplast proteins are mostly reduced in yss1 seedlings. Together, our findings identify YSS1 as a novel regulator of PEP activity essential for chloroplast development at rice seedling stage.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DUF:
-
Domain of unknown function
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- NEP:
-
Nuclear-encoded phage-type RNA polymerase
- PEP:
-
Plastid-encoded plastid RNA polymerase
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- yss1 :
-
Young seedling stripe1
References
Allison LA (2000) The role of sigma factors in plastid transcription. Biochimie 82:537–548
Börner T, Aleynikova AY, Zubo YO, Kusnetsov VV (2015) Chloroplast RNA polymerases: role in chloroplast biogenesis. BBA-Bioenergetics 1847:761–769
Chen S, Tao L, Zeng L, Vega-Sanchez ME, Umemura K, Wang GL (2006) A highly efficient transient protoplast system for analyzing defence gene expression and protein–protein interactions in rice. Mol Plant Pathol 7:417–427
Dong H, Fei GL, Wu CY et al (2013) A rice virescent-yellow leaf mutant reveals new insights into the role and assembly of plastid caseinolytic protease in higher plants. Plant Physiol 162:1867–1880
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, von Heijne G (1999) ChloroP, a neural network-based method for predicting chloroplast transit peptides and their cleavage sites. Protein Sci 8:978–984
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (2000) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol 300:1005–1016
Fujiwara M, Nagashima A, Kanamaru K, Tanaka K, Takahashi H (2000) Three new nuclear genes, sigD, sigE and sigF, encoding putative plastid RNA polymerase sigma factors in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 481:47–52
Grennan AK, Ort DR (2007) Cool temperatures interfere with D1 synthesis in tomato by causing ribosomal pausing. Photosynth Res 94:375–385
Hajdukiewicz PT, Allison LA, Maliga P (1997) The two RNA polymerases encoded by the nuclear and the plastid compartments transcribe distinct groups of genes in tobacco plastids. EMBO J 16:4041–4048
Hedtke B, Börner T, Weihe A (1997) Mitochondrial and chloroplast phage-type RNA polymerases in Arabidopsis. Science 277:809–811
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282
Hiratsuka J, Shimada H, Whittier R et al (1989) The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet 217:185–194
Hricova A, Quesada V, Micol JL (2006) The SCABRA3 nuclear gene encodes the plastid RpoTp RNA polymerase, which is required for chloroplast biogenesis and mesophyll cell proliferation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:942–956
Ishizaki Y, Tsunoyama Y, Hatano K, Ando K, Kato K, Shinmyo A, Kobori M, Takeba G, Nakahira Y, Shiina T (2005) A nuclear-encoded sigma factor, Arabidopsis SIG6, recognizes sigma-70 type chloroplast promoters and regulates early chloroplast development in cotyledons. Plant J 42:133–144
Isken O, Maquat LE (2007) Quality control of eukaryotic mRNA: safeguarding cells from abnormal mRNA function. Gene Dev 21:1833–1856
Isono K, Shimizu M, Yoshimoto K, Niwa Y, Satoh K, Yokota A, Kobayashi H (1997) Leaf-specifically expressed genes for polypeptides destined for chloroplasts with domain sigma 70 factors of bacterial RNA polymerases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14948–14953
Isshiki M, Morino K, Nakajima M, Okagaki RJ, Wessler SR, Izawa T, Shimamoto K (1998) A naturally occurring functional allele of the rice waxy locus has a GT to TT mutation at the 5′ splice site of the first intron. Plant J 15:133–138
Kasai K, Kawagishi-Kobayashi M, Teraishi M, Ito Y, Ochi K, Wakasa K, Tozawa Y (2004) Differential expression of three plastidial sigma factors, OsSIG1, OsSIG2A, and OsSIG2B, during leaf development in rice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:973–977
Kindgren P, Kremnev D, Blanco NE et al (2012) The plastid redox insensitive 2 mutant of Arabidopsis is impaired in PEP activity and high light-dependent plastid redox signalling to the nucleus. Plant J 70:279–291
Kubota Y, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Tozawa Y, Yasuda H, Tsunoyama Y, Niwa Y, Imamura S, Shirai M, Asayama M (2007) Two novel nuclear genes, OsSIG5 and OsSIG6, encoding potential plastid sigma factors of RNA polymerase in rice: tissue-specific and light-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell Physiol 48:186–192
Kühn K, Richter U, Meyer EH, Delannoy E, de Longevialle AF, Borner T, Millar AH, Small I, Whelan J (2009) Phage-type RNA polymerase RPOTmp performs genespecific transcription in mitochondria of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21:2762–2779
Kusumi K, Mizutani A, Nishimura M, Iba K (1997) A virescent gene V1 determines the expression timing of plastid genes for transcription/translation apparatus during early leaf development in rice. Plant J 12:1241–1250
Kusumi K, Sakata C, Nakamura T, Kawasaki S, Yoshimura A, Iba K (2011) A plastid protein NUS1 is essential for build-up of the genetic system for early chloroplast development under cold stress conditions. Plant J 68:1039–1050
Liu X, Rodermel SR, Yu F (2010) A var2 leaf variegation suppressor locus, SUPPRESSOR OF VARIEGATION3, encodes a putative chloroplast translation elongation factor that is important for chloroplast development in the cold. BMC Plant Biol 10:287
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Majeran W, Friso G, Asakura Y, Qu X, Huang M, Ponnala L, Watkins KP, Barkan A, van Wijk KJ (2012) Nucleoiden-riched proteomes in developing plastids and chloroplasts from maize leaves: a new conceptual framework for nucleoid functions. Plant Physiol 158:156–189
Mao B, Cheng Z, Lei C et al (2012) Wax crystal-sparse leaf2, a rice homologue of WAX2/GL1, is involved in synthesis of leaf cuticular wax. Planta 235:39–52
Moreira D, Le Guyader H, Philippe H (2000) The origin of red algae and the evolution of chloroplasts. Nature 405:69–72
Mullet JE (1993) Dynamic regulation of chloroplast transcription. Plant Physiol 103:309–313
Nishiyama Y, Nishiyama Y, Allakhverdiev S, Murata N (2006) A new paradigm for the action of reactive oxygen species in the photoinhibition of photosystem II. BBA-Bioenergetics 1757:742–749
Pfalz J, Pfannschmidt T (2013) Essential nucleoid proteins in early chloroplast development. Trends Plant Sci 18:186–194
Pfalz J, Liere K, Kandlbinder A, Dietz KJ, Oelmüller R (2006) pTAC2, -6, and -12 are components of the transcriptionally active plastid chromosome that are required for plastid gene expression. Plant Cell 18:176–197
Quesada V, Sarmiento-Manus R, Gonzalez-Bayon R et al (2011) Arabidopsis RUGOSA2 encodes an mTERF family member required for mitochondrion, chloroplast and leaf development. Plant J 68:738–753
Ren YL, Wang YH, Liu F et al (2014) GLUTELIN PRECURSOR ACCUMULATION3 encodes a regulator of post-Golgi vesicle traffic essential for vacuolar protein sorting in rice endosperm. Plant Cell 26:410–425
Reumann S, Inoue K, Keegstra K (2005) Evolution of the general protein import pathway of plastids (review). Mol Membr Biol 22:73–86
Rogalski M, Schottler MA, Thiele W, Schulze WX, Bock R (2008) Rpl33, a nonessential plastid-encoded ribosomal protein in tobacco, is required under cold stress conditions. Plant Cell 20:2221–2237
Sakamoto W, Miyagishima S, Jarvis P (2008) Chloroplast biogenesis: control of plastid development, protein import, division and inheritance. Arabidopsis Book 6:e0110
Steiner S, Schroter Y, Pfalz J, Pfannschmidt T (2011) Identification of essential subunits in the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase complex reveals building blocks for proper plastid development. Plant Physiol 157:1043–1055
Su N, Hu ML, Wu DX et al (2012) Disruption of a rice pentatricopeptide repeat protein causes a seedling-specific albino phenotype and its utilization to enhance seed purity in hybrid rice production. Plant Physiol 159:227–238
Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Tozawa Y, Yazaki J, Kishimoto N, Kikuchi S, Iba K (2004) The virescent-2 mutation inhibits translation of plastid transcripts for the plastid genetic system at an early stage of chloroplast differentiation. Plant Cell Physiol 45:985–996
Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K (2007) The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2, is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria. Plant J 52:512–527
Terasawa K, Sato N (2005) Visualization of plastid nucleoids in situ using the PEND-GFP fusion protein. Plant Cell Physiol 46:649–660
Tozawa Y, Hasegawa H, Terakawa T, Wakasa K (2001) Characterization of rice anthranilate synthase alpha-subunit genes OASA1 and OASA2. Tryptophan accumulation in transgenic rice expressing a feedback-insensitive mutant of OASA1. Plant Physiol 126:1493–1506
Wang ZY, Zheng FQ, Shen GZ, Gao JP, Snustad DP, Li MG, Zhang JL, Hong MM (1995) The amylose content in rice endosperm is related to the post-transcriptional regulation of the waxy gene. Plant J 7:613–622
Wu ZM, Zhang X, He B et al (2007) A chlorophyll-deficient rice mutant with impaired chlorophyllide esterification in chlorophyll biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 145:29–40
Xu YZ, Arrieta-Montiel MP, Virdi KS et al (2011) MutS HOMOLOG1 is a nucleoid protein that alters mitochondrial and plastid properties and plant response to high light. Plant Cell 23:3428–3441
Yagi Y, Ishizaki Y, Nakahira Y, Tozawa Y, Shiina T (2012) Eukaryotic-type plastid nucleoid protein pTAC3 is essential for transcription by the bacterial-type plastid RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:7541–7546
Yoo SC, Cho SH, Sugimoto H, Li J, Kusumi K, Koh HJ, Iba K, Paek NC (2009) Rice Virescent3 and Stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development. Plant Physiol 150:388–401
Zhang L, Ren YL, Lu BY et al (2016) FLOURY ENDOSPERM7 encodes a regulator of starch synthesis and amyloplast development essential for peripheral endosperm development in rice. J Exp Bot 67:633–647
Zhong L, Zhou W, Wang H, Ding S, Lu Q, Wen X, Peng L, Zhang L, Lu C (2013) Chloroplast small heat shock protein HSP21 interacts with plastid nucleoid protein pTAC5 and is essential for chloroplast development in Arabidopsis under heat stress. Plant Cell 25:2925–2943
Zhou KN, Ren YL, Lv J et al (2013) Young Leaf Chlorosis 1, a chloroplast-localized gene required for chlorophyll and lutein accumulation during early leaf development in rice. Planta 237:279–292
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from the Fundamental Research Funds for Excellent Young Scientists of ICS-CAAS (Grant to YR, 2014JB04-009; 1610092015003-08), the 973 Program of China (2011CB100102), the High Technology Program from NDRC ([2012]1961), the 863 Program of China (2014AA10A604-4), and Jiangsu Science and Technology Development Program (BE2014394). We thank Dr. Bing Hu (Nanjing Agricultural University) for assistance in transmission electron microscopy analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Zhou, Y. Ren, F. Zhou and Y. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, K., Ren, Y., Zhou, F. et al. Young Seedling Stripe1 encodes a chloroplast nucleoid-associated protein required for chloroplast development in rice seedlings. Planta 245, 45–60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2590-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2590-7