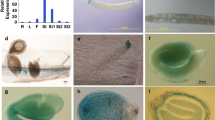
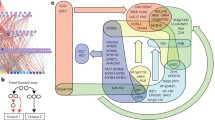
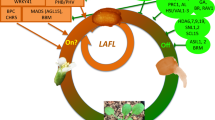
Abstract
The Arabidopsis thaliana KNAT7 (KNOX family) and MYB75 (MYB family) transcription factors were each shown earlier to interact in yeast two-hybrid assays, and to modulate secondary cell wall formation in inflorescence stems. We demonstrate here that their interaction also occurs in vivo, and that specific domains of each protein mediate this process. The participation of these interacting transcription factors in secondary cell wall formation was then extended to the developing seed coat through the use of targeted transcript analysis and SEM in single loss-of-function mutants. Novel genetic and protein–protein interactions of MYB75 and KNAT7 with other transcription factors known to be involved in seed coat regulation were also identified. We propose that a MYB75-associated protein complex is likely to be involved in modulating secondary cell wall biosynthesis in both the Arabidopsis inflorescence stem and seed coat, and that at least some parts of the transcriptional regulatory network in the two tissues are functionally conserved.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Y2H:
-
Yeast two-hybrid
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron micrograph
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
An YQ, McDowell JM, Huang S, McKinney EC, Chambliss S, Meagher RB (1996) Strong, constitutive expression of the Arabidopsis ACT2/ACT8 actin subclass in vegetative tissues. Plant J 10:107–121
Baudry A, Heim MA, Dubreucq B, Caboche M, Weisshaar B, Lepiniec L (2004) TT2, TT8, and TTG1 synergistically specify the expression of BANYULS and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 39:366–380
Beeckman T, De Rycke R, Viane R, Inzé D (2000) Histological study of seed coat development in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res 113:139–148
Bellaoui M, Pidkowich MS, Samach A, Kushalappa K, Kohalmi SE, Modrusan Z, Crosby WL, Haughn GW (2001) The Arabidopsis BELL1 and KNOX TALE homeodomain proteins interact through a domain conserved between plants and animals. Plant Cell 13:2455–2470
Bhargava A, Mansfield SD, Hall HC, Douglas CJ, Ellis BE (2010) MYB75 functions in regulation of secondary cell wall formation in the Arabidopsis inflorescence stem. Plant Physiol 154:1428–1438
Borevitz JO, Xia Y, Blount J, Dixon RA, Lamb C (2000) Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 12:2383–2394
Broun P (2005) Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis: a complex network of conserved regulators involved in multiple aspects of differentiation in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:272–279
Brown DM, Zeef LA, Ellis J, Goodacre R, Turner SR (2005) Identification of novel genes in Arabidopsis involved in secondary cell wall formation using expression profiling and reverse genetics. Plant Cell 17:2281–2295
Burglin TR (1997) Analysis of TALE superclass homeobox genes (MEIS, PBC, KNOX, Iroquois, TGIF) reveals a novel domain conserved between plants and animals. Nucleic Acids 25(21):4173–4180
Dallman JE, Allopenna J, Bassett A, Travers A, Mandel G (2004) A conserved role but different partners for the transcriptional corepressor CoREST in fly and mammalian nervous system formation. J Neurosci 24:7186–7193
Dean G, Cao Y, Xiang D, Provart NJ, Ramsay L, Ahad A, White R, Selvaraj G, Datla R, Haughn G (2011) Analysis of gene expression patterns during seed coat development in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 4(6):1074–1091
Debeaujon I, Nesi N, Perez P, Devic M, Grandjean O, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2003) Proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells in Arabidopsis testa: regulation of differentiation and role in seed development. Plant Cell 15:2514–2531
Demura T, Ye ZH (2010) Regulation of plant biomass production. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:299–304
Dilkes BP, Spielman M, Weizbauer R, Burkart-Waco D, Watson B, Scott RJ, Comai L (2008) The maternally expressed WRKY transcription factor TTG2 controls lethality in interploidy crosses of Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol 6:2707–2720
Dixon R, Xie DY, Sharma S (2005) Proanthocyanidins—a final frontier in flavonoid research? New Phytol 165:9–28
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 10:573–581
Frampton J, Gibson TJ, Ness SA, Doderlein G, Graf T (1991) Proposed structure for the DNA-binding domain of the Myb oncoprotein based on model building and mutational analysis. Protein Eng 4:891–901
Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Leavitt JM, Lloyd AM (2008) Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 53:814–827
Gonzalez A, Mendenhall J, Huo Y, Lloyd A (2009) TTG1 complex MYBs, MYB5 and TT2, control outer seed coat differentiation. Dev Biol 325:412–421
Greenbaum S, Lazorchak AS, Zhuang Y (2004) Differential functions for the transcription factor E2A in positive and negative gene regulation in pre-B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 279:4502–4503
Guimil S, Dunand C (2006) Patterning of Arabidopsis epidermal cells: epigenetic factors regulate the complex epidermal cell fate pathway. Trends Plant Sci 11:601–609
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Pelloux J, Bellini C, Van Wuytswinkel O (2008) Towards a systematic validation of references in real-time RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20:1734–1735
Hackbusch J, Richter K, Muller J, Salamini F, Uhrig JF (2005) A central role of Arabidopsis thaliana ovate family proteins in networking and subcellular localization of 3-aa loop extension homeodomain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:4908–4912
Harpaz-Saad S, McFarlane HE, Xu S, Divi UK, Forward B, Western TL, Kieber JJ (2011) Cellulose synthesis via the FEI2 RLK/SOS5 pathway and CELLULOSE SYNTHASE 5 is required for the structure of seed coat mucilage in Arabidopsis. Plant J 68:941–953
Haughn G, Chaudhury A (2005) Genetic analysis of seed coat development in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 10:472–477
Ishida T, Hattori S, Sano R, Inoue K, Shirano Y, Hayashi H, Shibata D, Sato S, Kato T, Tabata S, Okada K, Wada T (2007) Arabidopsis TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2 is directly regulated by R2R3 MYB transcription factors and is involved in regulation of GLABRA2 transcription in epidermal differentiation. Plant Cell 19:2531–2543
Johnson CS, Kolevski B, Smyth DR (2002) TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2, a trichome and seed coat development gene of Arabidopsis, encodes a WRKY transcription factor. Plant Cell 14(6):1359–1375
Kanei-Ishii C, Sarai A, Sawazaki T, Nakagoshi H, He DN, Ogata K, Nishimura Y, Ishii S (1990) The tryptophan cluster: a hypothetical structure of the DNA-binding domain of the myb protooncogene product. J Biol Chem 265:19990–19995
Kanei-Ishii C, Tanikawa J, Nakai A, Morimoto RI, Ishii S (1997) Activation of heat shock transcription factor 3 by c-Myb in the absence of cellular stress. Science 277:246–248
Koes R, Verweij W, Quattrocchio F (2005) Flavonoids: a colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci 10:236–242
Koornneef M (1981) The complex syndrome of ttg mutants. Arabidopsis Inf Serv 18:45–51
Kumar R (2006) The roles of BEL1-like proteins in organ morphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. PhD thesis, University of British Columbia (UBC), Vancouver
Le BH et al. (2010) Global analysis of gene activity during Arabidopsis seed development and identification of seed-specific transcription factors. PNAS 107:8063–8070
Lea US, Slimestad R, Smedvig P, Lillo C (2007) Nitrogen deficiency enhances expression of specific MYB and bHLH transcription factors and accumulation of end products in the flavonoid pathway. Planta 225:1245–1253
Li E (2009) Identification and characterization of regulatory genes associated with secondary wall formation in Populus and Arabidopsis thaliana. PhD thesis, University of British Columbia
Li SF, Milliken ON, Pham H, Seyit R, Napoli R, Preston J, Koltunow AM, Parish RW (2009) The Arabidopsis MYB5 transcription factor regulates mucilage synthesis, seed coat development, and trichome morphogenesis. Plant Cell 21:72–89
Li E, Wang S, Liu Y, Chen JG, Douglas CJ (2011) OVATE FAMILY PROTEIN4 (OFP4) interaction with KNAT7 regulates secondary cell wall formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 67:328–341
Li E, Bhargava A, Qiang W, Friedmann MC, Forneris N, Savidge RA, Johnson LA, Mansfield SD, Ellis BE, Douglas CJ (2012) The Class II KNOX gene KNAT7 negatively regulates secondary wall formation in Arabidopsis and is functionally conserved in Populus. New Phytol 194:102–115
Marles MA, Ray H, Gruber MY (2003) New perspectives on proanthocyanidin biochemistry and molecular regulation. Phytochemistry 64:367–383
Martin C, Glover BJ (2007) Functional aspects of cell patterning in aerial epidermis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:70–82
Matsui K, Tanaka H, Ohme-Takagi M (2004) Suppression of the biosynthesis of proanthocyanidin in Arabidopsis by a chimeric PAP1 repressor. Plant Biotechnol J 2:487–493
Mendu V, Griffiths J, Persson S, Stork J, Downie B, Vioniciuc C, Haughn G, Debolt S (2011) Subfunctionalization of cellulose synthases in seed coat epidermal cells mediate secondary radial wall synthesis and mucilage attachment. Plant Physiol 157:441–453
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nesi N, Debeaujon I, Jond C, Pelletier G, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2000) The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell 12:1863–1878
Nesi N, Jond C, Debeaujon I, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2001) The Arabidopsis TT2 gene encodes an R2R3 MYB domain protein that acts as a key determinant for proanthocyanidin accumulation in developing seed. Plant Cell 13:2099–2114
Penfield S, Meissner RC, Shoue DA, Carpita NC, Bevan MW (2001) MYB61 is required for mucilage deposition and extrusion in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Cell 13:2777–2791
Pooma W, Gersos C, Grotewold E (2002) Transposon insertions in the promoter of the Zea mays a1 gene differentially affect transcription by the Myb factors P and C1. Genetics 161(2):793–801
Qi T, Song S, Ren Q, Wu D, Huang H, Chen Y, Fan M, Peng W, Ren C, Xie D (2011) The Jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 23:1795–1814
Ramsay NA, Glover BJ (2005) MYB-bHLH-WD40 protein complex and the evolution of cellular diversity. Trends Plant Sci 10:63–70
Romano JM, Dubos C, Prouse MB, Wilkins O, Hong H, Poole M, Kang K-Y, Li E, Douglas CJ, Western TL, Mansfield SD, Campbell MM (2012) AtMYB61, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor, functions as a pleiotropic regulator via a small gene network. New Phytol. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04201.x
Schellmann S, Hulskamp M (2005) Epidermal differentiation: trichomes in Arabidopsis as a model system. Int J Dev Biol 49:579–584
Serna L (2005) Epidermal cell patterning and differentiation throughout the apical-basal axis of the seedling. J Exp Bot 56:1983–1989
Serna L, Martin C (2006) Trichomes: different regulatory networks lead to convergent structures. Trends Plant Sci 11:274–280
Stork J, Harris D, Griffiths J, Williams B, Beisson F, Li-Beisson Y, Mendu V, Haughn G, Debolt S (2010) CELLULOSE SYNTHASE9 serves a nonredundant role in secondary cell wall synthesis in Arabidopsis epidermal testa cells. Plant Physiol 153:580–589
Sullivan S, Ralet MC, Berger A, Diatloff E, Bischoff V, Gonneau M, Marion-Poll A, North HM (2011) CESA5 is required for the synthesis of cellulose with a role in structuring the adherent mucilage of Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol 156:1725–1739
Teng S, Keurentjes J, Bentsink L, Koornneef M, Smeekens S (2005) Sucrose-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis requires the MYB75/PAP1 gene. Plant Physiol 139:1840–1852
Timmermans MC, Hudson A, Becraft PW, Nelson T (1999) ROUGH SHEATH2: a MYB protein that represses KNOX homeobox genes in maize lateral organ primordia. Science 284:151–153
Tohge T, Matsui K, Ohme-Takagi M, Yamazaki M, Saito K (2005) Enhanced radical scavenging activity of genetically modified Arabidopsis seeds. Biotechnol Lett 27:297–303
Viola IL, Gonzalez DH (2006) Interaction of the BELL-like protein ATH1 with DNA: role of homeodomain residue 54 in specifying the different binding properties of BELL and KNOX proteins. Biol Chem 387:31–40
Wang S, Chang Y, Guo J, Chen JG (2007) Arabidopsis Ovate Family Protein 1 is a transcriptional repressor that suppresses cell elongation. Plant J 50:858–872
Western TJ (2006) Changing spaces: the Arabidopsis mucilage secretory cells as a novel system to dissect cell wall production in differentiating cells. Can J Bot 84:622–630
Western TL, Skinner DJ, Haughn GW (2000) Differentiation of mucilage secretory cells of the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Physiol 122:345–356
Western TL, Young DS, Dean GH, Tan WL, Samuels AL, Haughn GW (2004) MUCILAGE-MODIFIED4 encodes a putative pectin biosynthetic enzyme developmentally regulated by APETALA2, TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1, and GLABRA2 in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Physiol 134:296–306
Winter D, Vinegar B, Nahal H, Ammar R, Wilson GV, Provart NJ (2007) An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS One 2(8):e718. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000718
Wolberger C (1999) Multiprotein-DNA complexes in transcriptional regulation. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 28:29–56
Yamaguchi M, Ohtani M, Mitsuda N, Kubo M, Ohme-Takagi M, Fukuda H, Demura T (2010) VND-INTERACTING2, a NAC domain transcription factor, negatively regulates xylem vessel formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:1249–1263
Zhang F, Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Payne CT, Lloyd A (2003) A network of redundant bHLH proteins functions in all TTG1-dependent pathways of Arabidopsis. Development 130:4859–4869
Zhao M, Morohashi K, Hatlestad G, Grotewold E, Lloyd A (2008) The TTG1-bHLH-MYB complex controls trichome cell fate and patterning through direct targeting of regulatory loci. Development 135:1991–1999
Zheng Z, Mosher S, Fan B, Klessig D, Chen Z (2007) Functional analysis of Arabidopsis WRKY25 transcription factor in plant defense against Pseudomonas syringae. BMC Plant Biol 7:2
Zhong R, Ye ZH (2007) Regulation of cell wall biosynthesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:564–572
Zhong R, Lee C, Zhou J, McCarthy RL, Ye ZH (2008) A battery of transcription factors involved in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:2763–2782
Zhong R, Lee C, Ye ZH (2010) Evolutionary conservation of the transcriptional network regulating secondary cell wall biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci 15:625–631
Zimmermann IM, Heim MA, Weisshaar B, Uhrig JF (2004) Comprehensive identification of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB transcription factors interacting with R/B-like BHLH proteins. Plant J 40:22–34
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Brad Ross and the UBC Bioimaging facility for SEM support. We gratefully acknowledge Dr Joachim Ührig (Botanical Institute, Universität Köln) for the kind gift of the pBatTL vectors used for the BiFC assays. Funding for this work was provided by Discovery Grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) to SDM, GWH, CJD, and BEE, the NSERC Green Crops Network and by NSERC scholarship support to AB.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhargava, A., Ahad, A., Wang, S. et al. The interacting MYB75 and KNAT7 transcription factors modulate secondary cell wall deposition both in stems and seed coat in Arabidopsis. Planta 237, 1199–1211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1821-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1821-9