Abstract
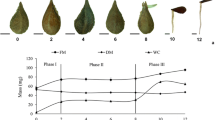
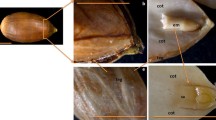
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE), coupled with mass spectroscopy, was used to study seed abortion in Dimocarpus longan Lour. (cv. Minjiao 64-1) by comparing normal and aborted seeds at three developmental stages. More than 1,000 protein spots were reproducibly detected in 2-DE gels, with 43 protein spots being significantly altered in their intensity between normal and aborted seeds at least at one stage. Thirty-five proteins were identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight-tandem mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS/MS) analysis and protein database searching. Most of the identified proteins were associated with a variety of functions, including energy and metabolism (30%), programed cell death (9%), antioxidative processes (14%), chaperonin (23%), cell division, amino acid metabolism, secondary metabolism, and other functional classes. Furthermore, the expression patterns of HSP70 and cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (cAPX) were validated by immunoblotting analysis. This study provides a novel, global insight into proteomic differences between normal and aborted seeds in longan. We anticipate that identification of the differentially expressed proteins may lead to a better understanding of the molecular basis for seed abortion in longan.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAP:
-
Days after pollination
- 2-DE:
-
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
- MALDI-TOF-MS/MS:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight-tandem mass spectrometry
- IEF:
-
Isoelectric focusing
- IPG:
-
Immobilized pH gradient
- pI:
-
Isoelectric point
- PCD:
-
Programed cell death
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- PTM:
-
Post-translational modification
References
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Arathi HS, Ganeshaiah KN, Shaanker RU, Hegde SG (1999) Seed abortion in Pongamia pinnata (Fabaceae). Am J Bot 86:659–662
Baba AI, Nogueira FCS, Pinheiro CB, Brasil JN, Jereissati ES, Juca TL, Soares AA, Santos MF, Domont GB, Campos FAP (2008) Proteome analysis of secondary somatic embryogenesis in cassava (Manihot esculenta). Plant Sci 175:717–723
Beers EP, Woffenden BJ, Zhao C (2000) Plant proteolytic enzymes: possible roles during programmed cell death. Plant Mol Biol 44:399–415
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 7:248–254
Chen Z, Gallie DR (2005) Increasing tolerance to ozone by elevating foliar ascorbic acid confers greater protection against ozone than increasing avoidance. Plant Physiol 138:1673–1689
Dam S, Laursen BS, Ornfelt JH, Jochimsen B, Staerfeldt HH, Friis C, Nielsen K, Goffard N, Besenbacher S, Krusell L, Sato S, Tabata S, Thogersen IB, Enghild JJ, Stougaard J (2009) The proteome of seed development in the model legume Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol 149:1325–1340
Dat JF, Pellinen R, Beeckman T, Van De Cotte B, Langebartels C, Kangasjarvi J, Inze D, Van Breusegem F (2003) changes in hydrogen peroxide homeostasis trigger an active cell death process in tobacco. Plant J 33:621–632
Ellis RJ, Van der Vies SM (1988) The rubisco subunit binding protein. Photosynth Res 16:101–115
Finnie C, Melchior S, Roepstorff P, Svensson B (2002) Proteome analysis of grain filling and seed maturation in barley. Plant Physiol 129:1308–1319
Franks RG, Wang C, Levin JZ, Liu Z (2002) SEUSS, a member of a novel family of plant regulatory proteins, represses floral homeotic gene expression with LEUNIG. Development 129:253–263
Gallardo K, Le Signor C, Vandekerckhove J, Thompson RD, Burstin J (2003) Proteomics of Medicago truncatula seed development establishes the time frame of diverse metabolic processes related to reserve accumulation. Plant Physiol 133:664–682
Gallie DR, Le H, Caldwell C, Tanguay RL, Hoang NX, Browning KS (1997) The phosphorylation state of translation initiation factors is regulated developmentally and following heat shock in wheat. J Biol Chem 272:1046–1053
Ghazoul J, Satake A (2009) Nonviable seed set enhances plant fitness: the sacrificial sibling hypothesis. Ecology 90:369–377
Hajduch M, Ganapathy A, Stein JW, Thelen JJ (2005) A systematic proteomic study of seed filling in soybean: establishment of high resolution two-dimensional reference maps, expression profiles, and an interactive proteome database. Plant Physiol 137:1397–1419
Hajduch M, Casteel JE, Hurrelmeyer KE, Song Z, Agrawal GK, Thelen JJ (2006) Proteomic analysis of seed filling in Brassica napus. Developmental characterization of metabolic isozymes using high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol 141:32–46
Hashimoto M, Komatsu S (2007) Proteomic analysis of rice seedlings during cold stress. Proteomics 7:1293–1302
Hauser BA, Sun K, Oppenheimer DG, Sage TL (2006) Changes in mitochondrial membrane potential and accumulation of reactive oxygen species precede ultrastructural changes during ovule abortion. Planta 223:492–499
Helenurm K, Schaal BA (1996) Genetic load, nutrient limitation, and seed production in Lupinus texensis (Fabaceae). Am J Bot 83:1585–1595
Ho SL, Tong WF, Yu SM (2000) Multiple mode regulation of a cysteine proteinase gene expression in rice. Plant Physiol 122:57–66
Hossaert M, Valero M (1988) Effect of ovule position in the pod on patterns of seed formation in two species of Lathyrus (Leguminosae: Papilionoideae). Am J Bot 75:1714–1731
Ishikawa A, Tanaka H, Nakai M, Asahi T (2003) Deletion of a chaperonin 60 beta gene leads to cell death in the Arabidopsis lesion initiation 1 mutant. Plant Cell Physiol 44:255–261
Jones-Rhoades MW, Borevitz JO, Preuss D (2007) Genome-wide expression profiling of the Arabidopsis female gametophyte identifies families of small, secreted proteins. PLoS Genet 3:1848–1861
Locato V, de Pinto MC, De Gara L (2009) Different involvement of the mitochondrial, plastidial and cytosolic ascorbate-glutathione redox enzymes in heat shock responses. Physiol Plant 135:296–306
Marshall DL, Levin DA, Fowler NL (1985) Plasticity in yield components in response to fruit predation and date of fruit initiation in three species of Sesbania (Leguminosae). J Ecol 73:71–81
Marsoni M, Bracale M, Espen L, Prinsi B, Negri AS, Vannini C (2008) Proteomic analysis of somatic embryogenesis in Vitis vinifera. Plant Cell Rep 27:347–356
Mechin V, Thevenot C, Le Guilloux M, Prioul JL, Damerval C (2007) Developmental analysis of maize endosperm proteome suggests a pivotal role for pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase. Plant Physiol 143:1203–1219
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Miyajima D (2006) Ovules that failed to form seeds in zinnia (Zinnia violacea Cav). Sci Hortic 107:176–182
Nadeau JA, Zhang XS, Li J, O’Neill SD (1996) Ovule development: identification of stage-specific and tissue-specific cDNAs. Plant Cell 8:213–239
Nelson RJ, Ziegelhoffer T, Nicolet C, Werner-Washburne M, Craig EA (1992) The translation machinery and 70 kd heat shock protein cooperate in protein synthesis. Cell 71:97–105
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279
Patterson BD, MacRae EA, Ferguson IB (1984) Estimation of hydrogen peroxide in plant extracts using titanium (IV). Anal Biochem 139:487–492
Puigderrajols P, Jofre A, Mir G, Pla M, Verdaguer D, Huguet G, Molinas M (2002) Developmentally and stress-induced small heat shock proteins in cork oak somatic embryos. J Exp Bot 373:1445–1452
Qureshi MI, Qadir S, Zolla L (2007) Proteomics-based dissection of stress-responsive pathways in plants. J Plant Physiol 164:1239–1260
Roe JL, Nemhauser JL, Zambryski PC (1997) TOUSLED participates in apical tissue formation during gynoecium development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 9:335–353
Saravanan RS, Rose JK (2004) A critical evaluation of sample extraction techniques for enhanced proteomics analysis of recalcitrant plant tissues. Proteomics 4:2522–2532
Seavy SR, Carter SK (1996) Ovule fates in Epilobium obcordatum (Onagraceae). Am J Bot 83:316–325
Shulaev V, Oliver DJ (2006) Metabolic and proteomic markers for oxidative stress. New tools for reactive oxygen species research. Plant Physiol 141:367–372
Sin SF, Yeung EC, Chye ML (2006) Downregulation of Solanum americanum genes encoding proteinase inhibitor II causes defective seed development. Plant J 45:58–72
Skinner DJ, Hill TA, Gasser CS (2004) Regulation of ovule development. Plant Cell 16:S32–S45
Stephenson AG (1981) Flower and fruit abortion: proximate causes and ultimate functions. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 12:253–279
Sun K, Hunt K, Hauser BA (2004) Ovule abortion in Arabidopsis triggered by stress. Plant Physiol 135:2358–2367
Sun K, Cui Y, Hauser BA (2005) Environmental stress alters genes expression and induces ovule abortion: reactive oxygen species appear as ovules commit to abort. Planta 222:632–642
Teixeira FK, Menezes-Benavente L, Galvão VC, Margis R, Margis-Pinheiro M (2006) Rice ascorbate peroxidase gene family encodes functionally diverse isoforms localized in different subcellular compartments. Planta 224:300–314
Thibaud-Nissen F, Shealy RT, Khanna A, Vodkin LO (2003) Clustering of microarray data reveals transcript patterns associated with somatic embryogenesis in soybean. Plant Physiol 132:118–136
Tischner T, Allphin L, Chase K, Orf JH, Lark KG (2003) Genetics of seed abortion and reproductive traits in soybean. Crop Sci 43:464–473
Ueda T, Seo S, Ohashi Y, Hashimoto J (2000) Circadian and senescence-enhanced expression of a tobacco cysteine protease gene. Plant Mol Biol 44:649–657
Vacca RA, de Pinto MC, Valenti D, Passarella S, Marra E, De Gara L (2004) Production of reactive oxygen species, alteration of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase, and impairment of mitochondrial metabolism are early events in heat shock-induced programmed cell death in tobacco Bright-Yellow 2 cells. Plant Physiol 134:1100–1112
Van Breusegem F, Dat JF (2006) Reactive oxygen species in plant cell death. Plant Physiol 141:384–390
Villanueva JM, Broadhvest J, Hauser BA, Meister RJ, Schneitz K, Gasser CS (1999) INNER NO OUTER regulates abaxial-adaxial patterning in Arabidopsis ovules. Genes Dev 13:3160–3169
Wang TL, Hadavizideh A, Harwood A, Welham TJ, Harwood WA, Faulks R, Hedley CL (1990) An analysis of seed development in Pisum sativum. XIII. The chemical induction of storage product mutants. Plant Breed 105:311–320
Wang J, Zhang H, Allen RD (1999) Overexpression of an Arabidopsis peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase gene in tobacco increases protection against oxidative stress. Plant Cell Physiol 40:725–732
Wang XQ, Yan PF, Gao Q, Liu XL, Kuang TY, Shen SH, He YK (2008) Proteomic analysis of the response to high-salinity stress in Physcomitrella patens. Planta 228:167–177
Watson BS, Asirvatham VS, Wang L, Sumner LW (2003) Mapping the proteome of barrel medic (Medicago truncatula). Plant Physiol 131:1104–1123
Wehmeyer N, Vierling E (2000) The expression of small heat shock proteins in seeds responds to discrete developmental signals and suggests a general protective role in desiccation tolerance. Plant Physiol 122:1099–1108
Wei WH, Chen B, Yan XH, Wang LJ, Zhang HF, Cheng JP, Zhou XA, Sha AH, Shen H (2008) Identification of differentially expressed genes in soybean seeds differing in oil content. Plant Sci 175:663–673
Weretilnyk EA, Hanson AD (1990) Molecular cloning of a plant betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme implicated in adaptation to salinity and drought. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2745–2749
Wiederanders B (2003) Structure-function relationship in class CA1 cysteine peptidase propeptides. Acta Biochim Polonica 50:691–713
Winkelmann T, Heintz D, Van Dorsselaer A, Serek M, Braun HP (2006) Proteomic analyses of somatic and zygotic embryos of Cyclamen persicum Mill. reveal new insights into seed and germination physiology. Planta 224:508–519
Wolucka BA, Van Montagu M (2003) GDP-mannose 3′, 5′-epimerase forms GDP-l-gulose, a putative intermediate for the de novo biosynthesis of vitamin C in plants. J Biol Chem 278:47483–47490
Xu FX, Chye ML (1999) Expression of cysteine proteinase during developmental events associated with programmed cell death in brinjal. Plant J 17:321–327
Yang PF, Chen H, Liang Y, Shen SH (2007) Proteomic analysis of de-etiolated rice seedlings upon exposure to light. Proteomics 7:2459–2468
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Grant of China (Award no. 30370999) and the Provincial Natural Science Grant of Fujian, PR China (Award no. 2009J01084). We also would like to thank Professor Jonathan E. Poulton of the Department of Biology at The University of Iowa (USA) for the critical reviewing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Liu, Yz., Zheng, Sq. et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) seed abortion. Planta 231, 847–860 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-1093-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-1093-1