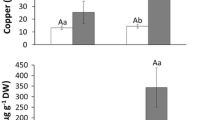
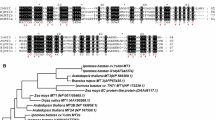
Abstract
Plant metallothioneins (MTs) are extremely diverse and are thought to be involved in metal homeostasis or detoxification. Thlaspi caerulescens is a model Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator and thus constitutes an ideal system to study the variability of these MTs. Two T. caerulescens cDNAs (accession: 665511; accession: 665515), that are highly homologous to type 1 and type 2 Arabidopsis thaliana MTs, have been isolated using a functional screen for plant cDNAs that confer Cd tolerance to yeast. However, TcMT1 has a much shorter N-terminal domain than that of A. thaliana and so lacks Cys motifs conserved through all the plant MTs classified as type 1. A systematic search in plant databases allowed the detection of MT-related sequences. Sixty-four percent fulfil the criteria for MT classification described in Cobbett and Goldsbrough (2002) and further extend our knowledge about other conserved residues that might play an important role in plant MT structure. In addition, 34% of the total MT-related sequences cannot be classified strictly as they display modifications in the conserved residues according to the current plant MTs’ classification. The significance of this variability in plant MT sequences is discussed. Functional complementation in yeast was used to assess whether these variations may alter the MTs’ function in T. caerulescens. Regulation of the expression of MTs in T. caerulescens was also investigated. TcMT1 and TcMT2 display higher expression in T. caerulescens than in A. thaliana. Moreover, their differential expression patterns in organs and in response to metal exposure, suggest that the two types of MTs may have diverse roles and functions in T. caerulescens.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Assunção AGL, Schat H, Aarts MGM (2003) Thlaspi caerulescens, an attractive model species to study heavy metal hyperaccumulation in plants. New Phytol 159 (2):351–360
Babiychuk E, Kushnir S, Belles-Boix E, Van Montagu M, Inzé D (1995) Arabidopsis thaliana NADPH oxidoreductase homologs confer tolerance of yeasts toward the thiol-oxidizing drug diamide. J Biol Chem 270:26224–26231
Baker AJM (1981) Accumulators and excluders—strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. J Plant Nutr 3:643–654
Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Wheeler DL (2003) GenBank Nucleic Acids Res 31:23–27
Bernard C, Roosens N, Czernic P, Lebrun M, Verbruggen N (2004) A novel CPx-ATPase from the cadmium hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. FEBS Lett 569(1–3):140–148
Binz PA, Kägi JHR (2001) Metallothionein. http://www.unizh.ch/~mtpage/MT.html
Boeckmann B, Bairoch A, Apweiler R, Blatter MC, Estreicher A, Gasteiger E, Martin MJ, Michoud K, O’Donovan C, Phan I, Pilbout S, Schneider M (2003) The SWISS-PROT protein knowledgebase and its supplement TrEMBL in 2003. Nucleic Acids Res 31:365–370
Butt A, Mousley C, Morris K, Beynon J, Can C (1998) Differential expression of senescence-enhanced metallothionein gene in Arabidopsis in response to isolates of Peronospora parasitica and Pseudomonas syringae. Plant J 16:209–221
Chatthai M, Kaukinen KH, Tranbarger TJ, Gupta PK, Misra S (1997) The isolation of a novel metallothionein-related cDNA expressed in somatic and zygotic embryos of Douglas-fir, regulation by ABA, osmoticum and metal ions. Plant Mol Biol 34:243–254
Chen H-J, Hou W-C, Yang C-Y, Huang D-J, Liu J-S, Lin Y-H (2003) Molecular cloning of two metallothionein-like protein genes with differential expression patterns from sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). J Plant Physiol 160:547–555
Clemens S (2001) Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis. Planta 212:475–486
Clendennen S, May GD (1997) Differential gene expression in ripening banana fruit. Plant Physiol 115:463–469
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002). Phytochelatins and metallothioneins : roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182
Cullen JT, Lane TW, Morel FMM, Sherrell RM (1999) Modulation of cadmium uptake in phytoplankton by seawater CO2 concentration. Nature 402:165–167
Escarré J, Lefèbvre C, Gruber W, Leblanc M, Lepart J, Rivière Y, Delay B (2000) Zinc and cadmium hyperaccumulation by Thlaspi caerulescens from metalliferous and nonmetalliferous sites in the Mediterranean area: implications for phytoextraction. New Phytol 145:429–437
Foley RC, Singh KB (1994) Isolation of a Vicia faba metallothionein-like gene - expression in foliar trichomes. Plant Mol Biol 26:435–444
Giordani T, Natali L, Maserti BE, Taddei S, Cavallini A (2000) Characterization and expression of DNA sequences encoding putative type-II metallothioneins in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Plant Physiol 123(4):1571–1582
Guo W-J, Bundithya W, Goldsbrough PB (2003) Characterization of the Arabidopsis metallothionein gene family: tissue-specific expression and induction during senescence and in response to copper. New Phytol 159:369–381
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53:1–11
Hamer DH (1986) Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem 55:913–951
Hsieh HM, Liu WK, Huang PC (1995) A novel stress-inducible metallothionein-like gene from rice. Plant Mol Biol 28:381–389
Kelley LA, MacCallum RM, Sternberg MJ (2000) Enhanced genome annotation using structural profiles in the program 3D-PSSM. J Mol Biol 299:499–520
Kitashiba H, Iwai T, Toriyama K, Watanabe M, Hinata K (1996) Identification of genes expressed in the shoot apex of Brassica campestris during floral transition. Sex Plant Reprod 9:186–188
Lane TW, Morel FM (2000) A biological function for cadmium in marine diatoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4627–4631
Lane BG, Kajioka R, Kennedy TD (1987) The wheat germ Ec protein is a zinc-containing metallothionein. Biochem Cell Biol 65:1001–1005
Li W, Jaroszewski L, Godzik A (2001) Clustering of highly homologous sequences to reduce the size of large protein database. Bioinformatics 17:282–283
Mathys W (1977) The role of malate, oxalate and mustard oil glucosides in the evolution of zinc-resistance in herbage plants. Physiologia Plantarum 40:130–136
Meerts P, Van Isacker N (1997) Heavy metal tolerance and accumulation in metallicolous and non-metallicolous populations of Thlaspi caerulescens from continental Europe. Plant Ecol 133:221–231
Murphy A and Taiz L (1995) Comparison of metallothionein genes expression and non-protein thiols in ten Arabidopsis ecotypes. Plant Physiol 113:1293–1301
Murphy A, Zhou JM, Goldsbrough PB, Taiz L (1997) Purification and immunological identification of metallothioneins 1 and 2 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 113:1293–1301
Murzin AG, Brenner SE, Hubbard T, Chothia C (1995) SCOP: a structural classification of proteins database for the investigation of sequences and structures. J Mol Biol 247(4):536–540
Pearson W, Lipman D (1988) Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2444–2448
Peer WA, Mamoudian M, Lahner B, Reeves RD, Murphy AS, Salt DE (2003) Identifying model metal hyperaccumulating plants: germplasm analysis of 20 Brassicaceae accession from a wide geographical area. New Phytol 159(2):411–420
Pollard AJ, Baker AJM (1996) Quantitative genetics of zinc hyperaccumulation in Thlaspi caerulescens. New Phytol 132:113–118
Rauser WE (1999) Structure and function of metal chelators produced by plants: the case for organic acids, amino acids, phytin and metallothioneins. Cell Biochem Biophys 31:19–48
Reeves DR, Schwartz C, Morel JL, Edmondson J (2001) Distribution and metal-accumulating behaviour of Thlaspi caerulescens and associated metallophytes in France. Int J Phytoremediation 3:145–172
Rerie WG, Whietcross M, Higgins T (1991) Developmental and environmental regulation of pea legumin genes in transgenic tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 225:148–157
Robinson NJ, Wilson JR, Turner JS (1996) Expression of type 2 metallothionein-like gene MT2 from Arabidopsis thaliana in Zn2+ -metallothionein deficient Synechococcus PCC 7942: putative role for MT2 in Zn2+ -metabolism. Plant Mol Biol 30:1169–1179
Romero-Isart N, Vasak M (2002) Advances in the structure and chemistry of metallothioneins. J Inorg Biochem 88:388–396
Roosens N, Verbruggen N, Meerts P, Ximénez-Embùn P, Smith JAC (2003) Natural variation in cadmium tolerance and its relationship to metal hyperaccumulation for seven populations of Thlaspi caerulescens from Western Europe. Plant Cell Environ 26:1657–1672
Roosens NH, Bernard C, Leplae R, Verbruggen N (2004) Evidence for copper homeostasis function of metallothionein (MT3) in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. FEBS Lett 577:9–16
Schafer HJ, Greiner S, Rausch T, HaagKerwer A (1997) In seedlings of the heavy metal accumulator Brassica juncea Cu2+ differentially affects transcript amounts for g-glutamylcysteine synthetase (g-ECS) and metallothionein (MT2). FEBS letters 404:216–220
Schat H, Llugany M, Vooijs R, Hartley-Whitaker J, Bleeker PM (2002) The role of phytochelatins in constitutive and adaptive heavy metal tolerances in hyperaccumulator and non-hyperaccumulator metallophytes. J Exp Bot 53:2381–2392
Shen ZG, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (1997) Uptake and transport of zinc in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens and the non-hyperaccumulator Thlaspi ochroleucum. Plant Cell Environ 20:898–906
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Van Hoof NALM, Hassinen VH, Hakvoort HWJ, Ballintijn KF, Schat H, Verkleij JAC, Ernst WHO, Karenlampi SO, Tervahauta AI (2001) Enhanced copper tolerance in Silene vulgaris (Moench) Garcke populations from copper mines is associated with increased transcript levels of 2b-type metallothionein gene. Plant Physiol 126:1519–1526
Vasak M, Hasler DW (2000) Metallothioneins: new functional and structural insights. Curr Opin Chem Biol 4:177–183
Zhao F-J, Hamon RE, Lombi E, McLaughlin MJ, McGrath SP (2002) Characteristics of cadmium uptake in two contrasting ecotypes of the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. J Exp Bot 53:535–543
Zhou JM, Goldsbrough PB (1994) Functional homologs of fungal metallothionein genes from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 6:875–884
Zhou JM, Goldsbrough PB (1995) Structure, organization and expression of the metallothionein gene family in Arabidopsis. Mol Gen Genet 248:318–328
Acknowledgements
N.R. and C.B. are indebted to the National Foundation (FNRS) for “Chargée de Recherche” and “Aspirant”, respectively. N.R. is indebted to the Belgian Science Policy. The authors thank P. Salis for his technical assistance and Y. Massin for her help in collecting the sequences from the database. The authors thank P. Meerts for the use of the ICP-OES. The authors are grateful to C. Krack and U. Krämer, who generated the zrc1cot1Δ mutant. The authors thank L. Moore for checking the manuscript and L. Bovet for helpful discussions. This research was supported by grants from the Belgian Programme on Interuniversity Poles (Science Policy Program V/13) and the European Research Network Metallome (HPRN-CT 2002-00243).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roosens, N.H., Leplae, R., Bernard, C. et al. Variations in plant metallothioneins: the heavy metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens as a study case. Planta 222, 716–729 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0006-1