Abstract
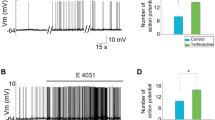
Voltage-gated sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) channels have been found to be regulated by Src family kinases (SFKs). However, how these channels are regulated by SFKs in cochlear spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) remains unknown. Here, we report that altering the activity of endogenous SFKs modulated voltage-gated Na+, but not K+, currents recorded in embryonic SGNs in culture. Voltage-gated Na+ current was suppressed by inhibition of endogenous SFKs or just Src and potentiated by the activation of these enzymes. Detailed investigations showed that under basal conditions, SFK inhibitor application did not significantly affect the voltage-dependent activation, but shifted the steady-state inactivation curves of Na+ currents and delayed the recovery of Na+ currents from inactivation. Application of Src specific inhibitor, Src40–58, not only shifted the inactivation curve but also delayed the recovery of Na+ currents and moved the voltage-dependent activation curve towards the left. The pre-inhibition of SFKs occluded all the effects induced by Src40–58 application, except the left shift of the activation curve. The activation of SFKs did not change either steady-state inactivation or recovery of Na+ currents, but caused the left shift of the activation curve. SFK inhibitor application effectively prevented all the effects induced by SFK activation, suggesting that both the voltage-dependent activation and steady-state inactivation of Na+ current are subjects of SFK regulation. The different effects induced by activation versus inhibition of SFKs implied that under basal conditions, endogenously active and inactive SFKs might be differentially involved in the regulation of voltage-gated Na+ channels in SGNs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Ahern CA, Zhang JF, Wookalis MJ, Horn R (2005) Modulation of the cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5 by Fyn, a Src family tyrosine kinase. Circ Res 96:991–998
Ahn M, Beacham D, Westenbroek RE, Scheuer T, Catterall WA (2007) Regulation of Na(v)1.2 channels by brain-derived neurotrophic factor, TrkB, and associated Fyn kinase. J Neurosci 27:11533–11542
Alioua A, Mahajan A, Nishimaru K, Zarei MM, Stefani E, Toro L (2002) Coupling of c-Src to large conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels as a new mechanism of agonist-induced vasoconstriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:14560–14565
Bain J, McLauchlan H, Elliott M, Cohen P (2003) The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update. Biochem J 371:199–204
Beacham D, Ahn M, Catterall WA, Scheuer T (2007) Sites and molecular mechanisms of modulation of Na(v)1.2 channels by Fyn tyrosine kinase. J Neurosci 27:11543–11551
Bielefeld EC, Hynes S, Pryznosch D, Liu J, Coleman JK, Henderson D (2005) A comparison of the protective effects of systemic administration of a pro-glutathione drug and a Src-PTK inhibitor against noise-induced hearing loss. Noise Health 7:24–30
Blake RA, Broome MA, Liu X, Wu J, Gishizky M, Sun L, Courtneidge SA (2000) SU6656, a selective Src family kinase inhibitor, used to probe growth factor signaling. Mol Cell Biol 20:9018–9027
Bradshaw JM (2010) The Src, Syk, and Tec family kinases: distinct types of molecular switches. Cell Signal 22:1175–1184
Brown MT, Cooper JA (1996) Regulation, substrates and functions of Src. Biochim Biophys Acta 1287:121–149
Cantrell AR, Catterall WA (2001) Neuromodulation of Na+ channels: an unexpected form of cellular plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:397–407
Catterall WA (1991) Structure and function of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1:5–13
Cayabyab FS, Khanna R, Jones OT, Schlichter LC (2000) Suppression of the rat microglia Kv1.3 current by Src-family tyrosine kinases and oxygen/glucose deprivation. Eur J Neurosci 12:1949–1960
Chahine M, Ziane R, Vijayaragavan K, Okamura Y (2005) Regulation of Na v channels in sensory neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:496–502
Cohen P (2002) Protein kinases—the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:309–315
d’Alcantara P, Schiffmann SN, Swillens S (1999) Effect of protein kinase A-induced phosphorylation on the gating mechanism of the brain Na+ channel: model fitting to whole-cell current traces. Biophys J 77:204–216
Davis MJ, Wu X, Nurkiewicz TR, Kawasaki J, Gui P, Hill MA, Wilson E (2001) Regulation of ion channels by protein tyrosine phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H1835–H1862
Fang XQ, Xu J, Feng S, Groveman BR, Lin SX, Yu XM (2011) The NMDA receptor NR1 subunit is critically involved in the regulation of NMDA receptor activity by C-terminal Src kinase (Csk). Neurochem Res 36:319–326
Fekete DM, Wu DK (2002) Revisiting cell fate specification in the inner ear. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:35–42
Feng S, Wei J, Gao M, Tang X, Su J (2010) Inhibition on voltage-gated sodium channels in rat spiral ganglion neurons by salicylate. J Guangxi Med Univ 1:1–4
Fryatt AG, Vial C, Mulheran M, Gunthorpe MJ, Grubb BD (2009) Voltage-gated sodium channel expression in rat spiral ganglion neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 42:399–407
Gamper N, Stockand JD, Shapiro MS (2003) Subunit-specific modulation of KCNQ potassium channels by Src tyrosine kinase. J Neurosci 23:84–95
Groveman BR, Feng S, Fang XQ, Pflueger M, Lin SX, Bienkiewicz EA, Yu XM (2011) The regulation of NMDA receptors by Src kinase. FEBS J 279:20–28
Groveman BR, Xue S, Marin V, Xu J, Ali MK, Bienkiewicz EA, Yu XM (2011) Roles of the SH2 and SH3 domains in the regulation of neuronal Src kinase functions. FEBS J 278:643–653
Gu RM, Wei Y, Falck JR, Krishna UM, Wang WH (2001) Effects of protein tyrosine kinase and protein tyrosine phosphatase on apical K(+) channels in the TAL. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1188–C1195
Harris KC, Hu B, Hangauer D, Henderson D (2005) Prevention of noise-induced hearing loss with Src-PTK inhibitors. Hear Res 208:14–25
Holmes TC, Fadool DA, Ren R, Levitan IB (1996) Association of Src tyrosine kinase with a human potassium channel mediated by SH3 domain. Science 274:2089–2091
Jia Z, Jia Y, Liu B, Zhao Z, Jia Q, Liang H, Zhang H (2008) Genistein inhibits voltage-gated sodium currents in SCG neurons through protein tyrosine kinase-dependent and kinase-independent mechanisms. Pflugers Arch 456:857–866
Kalia LV, Gingrich JR, Salter MW (2004) Src in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Oncogene 23:8007–8016
Karni R, Mizrachi S, Reiss-Sklan E, Gazit A, Livnah O, Levitzki A (2003) The pp 60c-Src inhibitor PP1 is non-competitive against ATP. FEBS Lett 537:47–52
Kotecha SA, MacDonald JF (2003) Signaling molecules and receptor transduction cascades that regulate NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission. Int Rev Neurobiol 54:51–106
Lau CG, Zukin RS (2007) NMDA receptor trafficking in synaptic plasticity and neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:413–426
Lei G, Xue S, Chery N, Liu Q, Xu J, Kwan CL, Fu Y, Lu YM, Liu M, Harder KH, Yu XM (2002) Gain control of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor activity by receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha. EMBO J 21:2977–2989
Li Y, Langlais P, Gamper N, Liu F, Shapiro MS (2004) Dual phosphorylations underlie modulation of unitary KCNQ K(+) channels by Src tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 279:45399–45407
Lin X (1997) Action potentials and underlying voltage-dependent currents studied in cultured spiral ganglion neurons of the postnatal gerbil. Hear Res 108:157–179
Lin X, Chen S, Tee D (1998) Effects of quinine on the excitability and voltage-dependent currents of isolated spiral ganglion neurons in culture. J Neurophysiol 79:2503–2512
Ling S, Sheng JZ, Braun AP (2004) The calcium-dependent activity of large-conductance, calcium-activated K+ channels is enhanced by Pyk2- and Hck-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C698–C706
Ling S, Woronuk G, Sy L, Lev S, Braun AP (2000) Enhanced activity of a large conductance, calcium-sensitive K+ channel in the presence of Src tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 275:30683–30689
Liu X, Brodeur SR, Gish G, Songyang Z, Cantley LC, Laudano AP, Pawson T (1993) Regulation of c-Src tyrosine kinase activity by the Src SH2 domain. Oncogene 8:1119–1126
Liu XJ, Gingrich JR, Vargas-Caballero M, Dong YN, Sengar A, Beggs S, Wang SH, Ding HK, Frankland PW, Salter MW (2008) Treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain by uncoupling Src from the NMDA receptor complex. Nat Med 14:1325–1332
Marin V, Groveman BR, Qiao H, Xu J, Ali MK, Fang XQ, Lin SX, Rizkallah R, Hurt MH, Bienkiewicz EA, Yu XM (2010) Characterization of neuronal Src kinase purified from a bacterial expression system. Protein Expr Purif 74:289–297
Repp H, Birringer J, Koschinski A, Dreyer F (2001) Activation of a Ca2+-dependent K+ current in mouse fibroblasts by sphingosine-1-phosphate involves the protein tyrosine kinase c-Src. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 363:295–301
Rusznak Z, Szucs G (2009) Spiral ganglion neurones: an overview of morphology, firing behaviour, ionic channels and function. Pflugers Arch 457:1303–1325
Salter MW, Kalia LV (2004) Src kinases: a hub for NMDA receptor regulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:317–328
Salter MW, Pitcher GM (2011) Dysregulated Src upregulation of NMDA receptor activity: a common link in chronic pain and schizophrenia. FEBS J 279:2–11
Santos-Sacchi J (1993) Voltage-dependent ionic conductances of type I spiral ganglion cells from the guinea pig inner ear. J Neurosci 13:3599–3611
Sobko A, Peretz A, Attali B (1998) Constitutive activation of delayed-rectifier potassium channels by a Src family tyrosine kinase in Schwann cells. EMBO J 17:4723–4734
Spoendlin H (1988) Neural anatomy of the ear. In: Janh A, Santos-Sacchi J (eds) Physiology of the ear. Raven, New York, pp 201–219
Strauss O, Rosenthal R, Dey D, Beninde J, Wollmann G, Thieme H, Wiederholt M (2002) Effects of protein kinase C on delayed rectifier K+ channel regulation by tyrosine kinase in rat retinal pigment epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1645–1654
Szabo I, Gulbins E, Apfel H, Zhang X, Barth P, Busch AE, Schlottmann K, Pongs O, Lang F (1996) Tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent suppression of a voltage-gated K+ channel in T lymphocytes upon Fas stimulation. J Biol Chem 271:20465–20469
Tang X, Gao M, Feng S, Su J (2010) Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit expression in rat spiral ganglion neurons. Neural Regen Res 5:1–3
Tong Q, Stockand JD (2005) Receptor tyrosine kinases mediate epithelial Na(+) channel inhibition by epidermal growth factor. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F150–F161
Traxler P, Bold G, Frei J, Lang M, Lydon N, Mett H, Buchdunger E, Meyer T, Mueller M, Furet P (1997) Use of a pharmacophore model for the design of EGF-R tyrosine kinase inhibitors: 4-(phenylamino)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines. J Med Chem 40:3601–3616
Trepanier CH, Jackson MF, MacDonald JF (2011) Regulation of NMDA receptors by the tyrosine kinase Fyn. FEBS J 279:12–19
Xu J, Weerapura M, Ali MK, Jackson MF, Li H, Lei G, Xue S, Kwan CL, Manolson MF, Yang K, MacDonald JF, Yu XM (2008) Control of excitatory synaptic transmission by C-terminal Src kinase. J Biol Chem 283:17503–17514
Yu XM, Askalan R, Keil GJI, Salter MW (1997) NMDA channel regulation by channel-associated protein tyrosine kinase Src. Science 275:674–678
Yu XM, Groveman BR (2011) Src family kinases in the nervous system. FEBS J 279:1–1
Acknowledgements
SF is supported by the State Scholarship Fund of China (2009845013). This work was supported by a grant from NIH (5R01 NS053567-04) to XMY. We would like to thank Dr. M. W. Salter for kindly supplying us Src inhibitory peptide (Src40–58), SFK activator peptide (EPQ(pY)EEIPIA), and control peptide (EPQYEEIPIA). We would also like to thank Drs. M. W. Salter, M. Hildebrand, and G. Pitcher for the very constructive discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM doc
(DOC 27.0 KB)
Supplementary Fig. 1
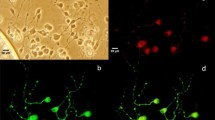
Expression of SFKs in SGNs. N-200: an antibody staining for neurofilament 200; SFKs: an antibody staining for SFKs. Merge: merged image showing co-labeling of neurofilament 200 and SFKs (TIFF 716 KB)
Supplementary Fig. 2
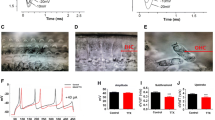
Effects of intracellular application of the SFK activator peptide EPQ(pY)EEIPIA (1 mM) on TTX-resistant inward current. A: example of current traces recorded immediately (0’) and 5 min after breakthrough with electrodes filled with intracellular solution containing the SFK activator peptide, EPQ(pY)EEIPIA (1 mM) from a SGN bathed with extracellular solution containing TTX (1 μM). B: Summary data showing relative changes in TTX-resistant currents recorded from SGNs applied intracellularly with the SFK activator peptide. Values in brackets indicate number of SGNs tested (TIFF 9.10 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S., Pflueger, M., Lin, SX. et al. Regulation of voltage-gated sodium current by endogenous Src family kinases in cochlear spiral ganglion neurons in culture. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 463, 571–584 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1072-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1072-4