Abstract
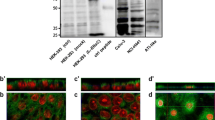
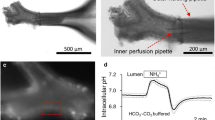
Impairment of lung liquid absorption can lead to severe respiratory symptoms, such as those observed in pulmonary oedema. In the adult lung, liquid absorption is driven by cation transport through two pathways: a well-established amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel (ENaC) and, more controversially, an amiloride-insensitive channel that may belong to the cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channel family. Here, we show robust CNGA1 (but not CNGA2 or CNGA3) channel expression principally in rat alveolar type I cells; CNGA3 was expressed in ciliated airway epithelial cells. Using a rat in situ lung liquid clearance assay, CNG channel activation with 1 mM 8Br-cGMP resulted in an approximate 1.8-fold stimulation of lung liquid absorption. There was no stimulation by 8Br-cGMP when applied in the presence of either 100 μM l-cis-diltiazem or 100 nM pseudechetoxin (PsTx), a specific inhibitor of CNGA1 channels. Channel specificity of PsTx and amiloride was confirmed by patch clamp experiments showing that CNGA1 channels in HEK 293 cells were not inhibited by 100 μM amiloride and that recombinant αβγ-ENaC were not inhibited by 100 nM PsTx. Importantly, 8Br-cGMP stimulated lung liquid absorption in situ, even in the presence of 50 μM amiloride. Furthermore, neither l-cis-diltiazem nor PsTx affected the β2-adrenoceptor agonist-stimulated lung liquid absorption, but, as expected, amiloride completely ablated it. Thus, transport through alveolar CNGA1 channels, located in type I cells, underlies the amiloride-insensitive component of lung liquid reabsorption. Furthermore, our in situ data highlight the potential of CNGA1 as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of diseases characterised by lung liquid overload.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander SP, Mathie A, Peters JA (2008) Guide to receptors and channels (GRAC), 3rd edition. Br J Pharmacol 153(Suppl 2):S1–S209
Althaus M, Fronius M, Buchackert Y, Vadasz I, Clauss WG, Seeger W, Motterlini R, Morty RE (2009) Carbon monoxide rapidly impairs alveolar fluid clearance by inhibiting epithelial sodium channels. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41:639–650
Bernard A, Roels H, Lauwerys R, Witters R, Gielens C, Soumillion A, Van Damme J, De Ley M (1992) Human urinary protein 1: evidence for identity with the Clara cell protein and occurrence in respiratory tract and urogenital secretions. Clin Chim Acta 207:239–249
Borok Z, Liebler JM, Lubman RL, Foster MJ, Zhou B, Li X, Zabski SM, Kim KJ, Crandall ED (2002) Na transport proteins are expressed by rat alveolar epithelial type I cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L599–L608
Bourke S, Mason HS, Borok Z, Kim KJ, Crandall ED, Kemp PJ (2005) Development of a lung slice preparation for recording ion channel activity in alveolar epithelial type I cells. Respir Res 6:40
Brouns I, Van Nassauw L, Van Genechten J, Majewski M, Scheuermann DW, Timmermans JP, Adriaensen D (2002) Triple immunofluorescence staining with antibodies raised in the same species to study the complex innervation pattern of intrapulmonary chemoreceptors. J Histochem Cytochem 50:575–582
Brown MJ, Olver RE, Ramsden CA, Strang LB, Walters DV (1983) Effects of adrenaline and of spontaneous labour on the secretion and absorption of lung liquid in the fetal lamb. J Physiol 344:137–152
Brown RL, Haley TL, West KA, Crabb JW (1999) Pseudechetoxin: a peptide blocker of cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:754–759
Brown RL, Lynch LL, Haley TL, Arsanjani R (2003) Pseudechetoxin binds to the pore turret of cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. J Gen Physiol 122:749–760
Campbell AR, Folkesson HG, Berthiaume Y, Gutkowska J, Suzuki S, Matthay MA (1999) Alveolar epithelial fluid clearance persists in the presence of moderate left atrial hypertension in sheep. J Appl Physiol 86:139–151
Cassin S, Perks AM (1982) Studies of factors which stimulate lung fluid secretion in fetal goats. J Dev Physiol 4:311–325
De Proost I, Brouns I, Pintelon I, Timmermans JP, Adriaensen D (2007) Pulmonary expression of voltage-gated calcium channels: special reference to sensory airway receptors. Histochem Cell Biol 128:301–316
Ding C, Potter ED, Qiu W, Coon SL, Levine MA, Guggino SE (1997) Cloning and widespread distribution of the rat rod-type cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel. Am J Physiol 272:C1335–C1344
Dobbs LG, Williams MC, Brandt AE (1985) Changes in biochemical characteristics and pattern of lectin binding of alveolar type II cells with time in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta 846:155–166
Eaton DC, Helms MN, Koval M, Bao HF, Jain L (2009) The contribution of epithelial sodium channels to alveolar function in health and disease. Annu Rev Physiol 71:403–423
Egli M, Duplain H, Lepori M, Cook S, Nicod P, Hummler E, Sartori C, Scherrer U (2004) Defective respiratory amiloride-sensitive sodium transport predisposes to pulmonary oedema and delays its resolution in mice. J Physiol 560:857–865
Fehrenbach H, Kasper M, Tschernig T, Pan T, Schuh D, Shannon JM, Muller M, Mason RJ (1999) Keratinocyte growth factor-induced hyperplasia of rat alveolar type II cells in vivo is resolved by differentiation into type I cells and by apoptosis. Eur Respir J 14:534–544
Frings S, Seifert R, Godde M, Kaupp UB (1995) Profoundly different calcium permeation and blockage determine the specific function of distinct cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Neuron 15:169–179
Funaki H, Yamamoto T, Koyama Y, Kondo D, Yaoita E, Kawasaki K, Kobayashi H, Sawaguchi S, Abe H, Kihara I (1998) Localization and expression of AQP5 in cornea, serous salivary glands, and pulmonary epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 275:C1151–C1157
Garat C, Carter EP, Matthay MA (1998) New in situ mouse model to quantify alveolar epithelial fluid clearance. J Appl Physiol 84:1763–1767
Gonzalez R, Yang YH, Griffin C, Allen L, Tigue Z, Dobbs L (2005) Freshly isolated rat alveolar type I cells, type II cells, and cultured type II cells have distinct molecular phenotypes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L179–L189
Goodman BE, Crandall ED (1982) Dome formation in primary cultured monolayers of alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 243:C96–C100
Guo Y, DuVall MD, Crow JP, Matalon S (1998) Nitric oxide inhibits Na+ absorption across cultured alveolar type II monolayers. Am J Physiol 274:L369–L377
Helms MN, Jain L, Self JL, Eaton DC (2008) Redox regulation of epithelial sodium channels examined in alveolar type 1 and 2 cells patch-clamped in lung slice tissue. J Biol Chem 283:22875–22883
Hummler E, Barker P, Gatzy J, Beermann F, Verdumo C, Schmidt A, Boucher R, Rossier BC (1996) Early death due to defective neonatal lung liquid clearance in alpha-ENaC-deficient mice. Nat Genet 12:325–328
Icard P, Saumon G (1999) Alveolar sodium and liquid transport in mice. Am J Physiol 277:L1232–L1238
Jain L, Chen XJ, Brown LA, Eaton DC (1998) Nitric oxide inhibits lung sodium transport through a cGMP-mediated inhibition of epithelial cation channels. Am J Physiol 274:L475–L484
Johnson MD, Bao HF, Helms MN, Chen XJ, Tigue Z, Jain L, Dobbs LG, Eaton DC (2006) Functional ion channels in pulmonary alveolar type I cells support a role for type I cells in lung ion transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4964–4969
Johnson MD, Widdicombe JH, Allen L, Barbry P, Dobbs LG (2002) Alveolar epithelial type I cells contain transport proteins and transport sodium, supporting an active role for type I cells in regulation of lung liquid homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1966–1971
Junor RW, Benjamin AR, Alexandrou D, Guggino SE, Walters DV (2000) Lack of a role for cyclic nucleotide gated cation channels in lung liquid absorption in fetal sheep. J Physiol 523:493–502
Junor RW, Benjamin AR, Alexandrou D, Guggino SE, Walters DV (1999) A novel role for cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in lung liquid homeostasis in sheep. J Physiol 520:255–260
Kaupp UB, Niidome T, Tanabe T, Terada S, Bonigk W, Stuhmer W, Cook NJ, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Hirose T (1989) Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of the rod photoreceptor cyclic GMP-gated channel. Nature 342:762–766
Kaupp UB, Seifert R (2002) Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Physiol Rev 82:769–824
Kemp PJ, Kim KJ, Borok Z, Crandall ED (2001) Re-evaluating the Na+ conductance of adult rat alveolar type II pneumocytes: evidence for the involvement of cGMP-activated cation channels. J Physiol 536:693–701
Kerem E, Bistritzer T, Hanukoglu A, Hofmann T, Zhou Z, Bennett W, MacLaughlin E, Barker P, Nash M, Quittell L, Boucher R, Knowles MR (1999) Pulmonary epithelial sodium-channel dysfunction and excess airway liquid in pseudohypoaldosteronism. N Engl J Med 341:156–162
Kingston PA, Zufall F, Barnstable CJ (1999) Widespread expression of olfactory cyclic nucleotide-gated channel genes in rat brain: implications for neuronal signalling. Synapse 32:1–12
Lewis A, Peers C, Ashford ML, Kemp PJ (2002) Hypoxia inhibits human recombinant large conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ (maxi-K) channels by a mechanism which is membrane delimited and Ca2+ sensitive. J Physiol 540:771–780
Liebler JM, Borok Z, Li X, Zhou B, Sandoval AJ, Kim KJ, Crandall ED (2004) Alveolar epithelial type I cells express β2-adrenergic receptors and G-protein receptor kinase 2. J Histochem Cytochem 52:759–767
Martinez-Francois JR, Xu Y, Lu Z (2009) Mutations reveal voltage gating of CNGA1 channels in saturating cGMP. J Gen Physiol 134:151–164
Mason RJ, Williams MC, Widdicombe JH, Sanders MJ, Misfeldt DS, Berry LC Jr (1982) Transepithelial transport by pulmonary alveolar type II cells in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6033–6037
Negoescu A, Labat-Moleur F, Lorimier P, Lamarcq L, Guillermet C, Chambaz E, Brambilla E (1994) F(ab) secondary antibodies: a general method for double immunolabeling with primary antisera from the same species. Efficiency control by chemiluminescence. J Histochem Cytochem 42:433–437
Norlin A, Finley N, Abedinpour P, Folkesson HG (1998) Alveolar liquid clearance in the anesthetized ventilated guinea pig. Am J Physiol 274:L235–L243
Norlin A, Lu LN, Guggino SE, Matthay MA, Folkesson HG (2001) Contribution of amiloride-insensitive pathways to alveolar fluid clearance in adult rats. J Appl Physiol 90:1489–1496
O’Brodovich H, Hannam V, Rafii B (1991) Sodium channel but neither Na+-H+ nor Na-glucose symport inhibitors slow neonatal lung water clearance. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 5:377–384
O’Brodovich H, Hannam V, Seear M, Mullen JB (1990) Amiloride impairs lung water clearance in newborn guinea pigs. J Appl Physiol 68:1758–1762
Olver RE, Ramsden CA, Strang LB, Walters DV (1986) The role of amiloride-blockable sodium transport in adrenaline-induced lung liquid reabsorption in the fetal lamb. J Physiol 376:321–340
Qiao R, Zhou B, Liebler JM, Li X, Crandall ED, Borok Z (2003) Identification of three genes of known function expressed by alveolar epithelial type I cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:98–105
Qiu W, Laheri A, Leung S, Guggino SE (2000) Hormones increase mRNA of cyclic-nucleotide-gated cation channels in airway epithelia. Pflugers Arch 441:69–77
Ramsden CA, Markiewicz M, Walters DV, Gabella G, Parker KA, Barker PM, Neil HL (1992) Liquid flow across the epithelium of the artificially perfused lung of fetal and postnatal sheep. J Physiol 448:579–597
Ridge KM, Olivera WG, Saldias F, Azzam Z, Horowitz S, Rutschman DH, Dumasius V, Factor P, Sznajder JI (2003) Alveolar type 1 cells express the α2 Na, K-ATPase, which contributes to lung liquid clearance. Circ Res 92:453–460
Ruffieux-Daidie D, Poirot O, Boulkroun S, Verrey F, Kellenberger S, Staub O (2008) Deubiquitylation regulates activation and proteolytic cleavage of ENaC. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:2170–2180
Sakuma T, Suzuki S, Usuda K, Handa M, Okaniwa G, Nakada T, Fujimura S, Matthay MA (1996) Preservation of alveolar epithelial fluid transport mechanisms in rewarmed human lung after severe hypothermia. J Appl Physiol 80:1681–1686
Schwiebert EM, Potter ED, Hwang TH, Woo JS, Ding C, Qiu W, Guggino WB, Levine MA, Guggino SE (1997) cGMP stimulates sodium and chloride currents in rat tracheal airway epithelia. Am J Physiol 272:C911–C922
Smedira N, Gates L, Hastings R, Jayr C, Sakuma T, Pittet JF, Matthay MA (1991) Alveolar and lung liquid clearance in anesthetized rabbits. J Appl Physiol 70:1827–1835
Stephens RH, Benjamin AR, Walters DV (1996) Volume and protein concentration of epithelial lining liquid in perfused in situ postnatal sheep lungs. J Appl Physiol 80:1911–1920
Warren EJ, Allen CN, Brown RL, Robinson DW (2006) The light-activated signaling pathway in SCN-projecting rat retinal ganglion cells. Eur J Neurosci 23:2477–2487
Wilson SM, Olver RE, Walters DV (2007) Developmental regulation of lumenal lung fluid and electrolyte transport. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 159:247–255
Xu W, Leung S, Wright J, Guggino SE (1999) Expression of cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in airway epithelial cells. J Membr Biol 171:117–126
Yamazaki Y, Brown RL, Morita T (2002) Purification and cloning of toxins from elapid venoms that target cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Biochemistry 41:11331–11337
Acknowledgements
The authors declare no conflict of interest and would like to thank the Medical Research Council for funding (G0600821) this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
William J. Wilkinson and Audra R. Benjamin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkinson, W.J., Benjamin, A.R., De Proost, I. et al. Alveolar epithelial CNGA1 channels mediate cGMP-stimulated, amiloride-insensitive, lung liquid absorption. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 462, 267–279 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0971-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0971-0