Abstract
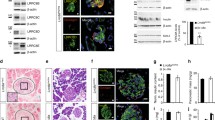
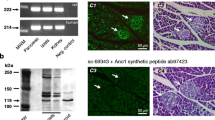
Zinc is stored in insulin-containing dense core vesicles of pancreatic β-cells where it forms crystals together with insulin and calcium ions. Zinc ions are therefore released together with insulin upon exocytosis of these vesicles. Consequently, pancreatic β-cells need to take up large amounts of zinc from the extracellular space across their plasma membrane. The pathways for zinc uptake are only partially understood. TRPM3 channels are present in pancreatic β-cells and can be activated by the endogenous steroid pregnenolone sulfate. We demonstrate here that recombinant TRPM3 channels are highly permeable for many divalent cations, in particular also for zinc ions. Importantly, TRPM3 channels endogenously expressed in pancreatic β-cells are also highly permeable for zinc ions. Using FluoZin3 to image changes of the intracellular zinc concentration, we show that pancreatic β-cells take up zinc through TRPM3 channels even when extracellular zinc concentrations are low and physiological levels of calcium and magnesium are present. Activation of TRPM3 channels also leads to depolarization of β-cells and to additional zinc influx through voltage-gated calcium channels. Our data establish that TRPM3 channels constitute a regulated entry pathway for zinc ions in pancreatic β-cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abràmoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton Int 11:36–42
Asfari M, Janjic D, Meda P, Li G, Halban PA, Wollheim CB (1992) Establishment of 2-mercaptoethanol-dependent differentiated insulin-secreting cell lines. Endocrinology 130:167–178
Bertram R, Pernarowski M (1998) Glucose diffusion in pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Biophys J 74:1722–1731
Chausmer AB (1998) Zinc, insulin and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 17:109–115
Chimienti F, Devergnas S, Favier A, Seve M (2004) Identification and cloning of a β-cell-specific zinc transporter, ZnT-8, localized into insulin secretory granules. Diabetes 53:2330–2337
Dean PM (1973) Ultrastructural morphometry of the pancreatic β-cell. Diabetologia 9:115–119
Dunn MF (2005) Zinc–ligand interactions modulate assembly and stability of the insulin hexamer—a review. Biometals 18:295–303
Fatt P, Ginsborg BL (1958) The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol 142:516–543
Foster MC, Leapman RD, Li MX, Atwater I (1993) Elemental composition of secretory granules in pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Biophys J 64:525–532
Frederickson CJ, Giblin LJ, Krężel A, McAdoo DJ, Muelle RN, Zeng Y, Balaji RV, Masalha R, Thompson RB, Fierke CA, Sarvey JM, de Valdenebro M, Prough DS, Zornow MH (2006) Concentrations of extracellular free zinc (pZn)e in the central nervous system during simple anesthetization, ischemia and reperfusion. Exp Neurol 198:285–293
Frederickson CJ, Koh J-Y, Bush AI (2005) The neurobiology of zinc in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:449–462
Gee KR, Zhou Z-L, Qian W-J, Kennedy R (2002) Detection and imaging of zinc secretion from pancreatic β-cells using a new fluorescent zinc indicator. J Am Chem Soc 124:776–778
Grimm C, Kraft R, Sauerbruch S, Schultz G, Harteneck C (2003) Molecular and functional characterization of the melastatin-related cation channel TRPM3. J Biol Chem 278:21493–21501
Gyulkhandanyan AV, Lee SC, Bikopoulos G, Dai F, Wheeler MB (2006) The Zn2+-transporting pathways in pancreatic β-cells: a role for the L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channel. J Biol Chem 281:9361–9372
Hille B (2001) Ion channels of excitable membranes. 3rd ed. Sinauer, Sunderland
Hu H, Bandell M, Petrus MJ, Zhu MX, Patapoutian A (2009) Zinc activates damage-sensing TRPA1 ion channels. Nat Chem Biol 5:183–190
Hutton JC, Penn EJ, Peshavaria M (1983) Low-molecular-weight constituents of isolated insulin-secretory granules. Bivalent cations, adenine nucleotides and inorganic phosphate. Biochem J 210:297–305
Inoue K, Branigan D, Xiong Z-G (2010) Zinc-induced neurotoxicity mediated by transient receptor potential melastatin 7 channels. J Biol Chem 285:7430–7439
Kay AR (2004) Detecting and minimizing zinc contamination in physiological solutions. BMC Physiol 4:4
Komatsu K, Kikuchi K, Kojima H, Urano Y, Nagano T (2005) Selective zinc sensor molecules with various affinities for Zn2+, revealing dynamics and regional distribution of synaptically released Zn2+ in hippocampal slices. J Am Chem Soc 127:10197–10204
Lee N, Chen J, Sun L, Wu S, Gray KR, Rich A, Huang M, Lin J-H, Feder JN, Janovitz EB, Levesque PC, Blanar MA (2003) Expression and characterization of human transient receptor potential melastatin 3 (hTRPM3). J Biol Chem 278:20890–20897
Lemaire K, Ravier MA, Schraenen A, Creemers JWM, de Plas RV, Granvik M, Lommel LV, Waelkens E, Chimienti F, Rutter GA, Gilon P, in't Veld PA, Schuit FC (2009) Insulin crystallization depends on zinc transporter ZnT8 expression, but is not required for normal glucose homeostasis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14872–14877
Li M, Jiang J, Yue L (2006) Functional characterization of homo- and heteromeric channel kinases TRPM6 and TRPM7. J Gen Physiol 127:525–537
Monteilh-Zoller MK, Hermosura MC, Nadler MJS, Scharenberg AM, Penner R, Fleig A (2003) TRPM7 provides an ion channel mechanism for cellular entry of trace metal ions. J Gen Physiol 121:49–60
Nadler MJ, Hermosura MC, Inabe K, Perraud AL, Zhu Q, Stokes AJ, Kurosaki T, Kinet JP, Penner R, Scharenberg AM, Fleig A (2001) LTRPC7 is a Mg.ATP-regulated divalent cation channel required for cell viability. Nature 411:590–595
Nicolson TJ, Bellomo EA, Wijesekara N, Loder MK, Baldwin JM, Gyulkhandanyan AV, Koshkin V, Tarasov AI, Carzaniga R, Kronenberger K, Taneja TK, da Silva Xavier G, Libert S, Froguel P, Scharfmann R, Stetsyuk V, Ravassard P, Parker H, Gribble FM, Reimann F, Sladek R, Hughes SJ, Johnson PRV, Masseboeuf M, Burcelin R, Baldwin SA, Liu M, Lara-Lemus R, Arvan P, Schuit FC, Wheeler MB, Chimienti F, Rutter GA (2009) Insulin storage and glucose homeostasis in mice null for the granule zinc transporter ZnT8 and studies of the type 2 diabetes-associated variants. Diabetes 58:2070–2083
Nilius B, Owsianik G, Voets T, Peters JA (2007) Transient receptor potential cation channels in disease. Physiol Rev 87:165–217
Oberwinkler J, Lis A, Giehl KM, Flockerzi V, Philipp SE (2005) Alternative splicing switches the divalent cation selectivity of TRPM3 channels. J Biol Chem 280:22540–22548
Oberwinkler J, Philipp SE (2007) TRPM3. Handb Exp Pharmacol 179:253–267
Owsianik G, Talavera K, Voets T, Nilius B (2006) Permeation and selectivity of TRP channels. Annu Rev Physiol 68:685–717
de Peretti E, Mappus E (1983) Pattern of plasma pregnenolone sulfate levels in humans from birth to adulthood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57:550–556
Pound LD, Sarkar SA, Benninger RKP, Wang Y, Suwanichkul A, Shadoan MK, Printz RL, Oeser JK, Lee CE, Piston DW, McGuinness OP, Hutton JC, Powell DR, O'Brien RM (2009) Deletion of the mouse Slc30a8 gene encoding zinc transporter-8 results in impaired insulin secretion. Biochem J 421:371–376
Priel T, Hershfinkel M (2006) Zinc influx and physiological consequences in the β-insulinoma cell line, Min6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:205–212
Qian W-J, Gee KR, Kennedy RT (2003) Imaging of Zn2+ release from pancreatic β-cells at the level of single exocytotic events. Anal Chem 75:3468–3475
Ramsey IS, Delling M, Clapham DE (2006) An introduction to TRP channels. Annu Rev Physiol 68:619–647
Robinson LK, Hurley LS (1981) Effect of maternal zinc deficiency of food restriction on rat fetal pancreas. 2. Insulin and glucagon. J Nutr 111:869–877
Schlingmann KP, Waldegger S, Konrad M, Chubanov V, Gudermann T (2007) TRPM6 and TRPM7—gatekeepers of human magnesium metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:813–821
Schmitz C, Perraud A-L, Johnson CO, Inabe K, Smith MK, Penner R, Kurosaki T, Fleig A, Scharenberg AM (2003) Regulation of vertebrate cellular Mg2+ homeostasis by TRPM7. Cell 114:191–200
Stokes CL, Rinzel J (1993) Diffusion of extracellular K+ can synchronize bursting oscillations in a model islet of Langerhans. Biophys J 65:597–607
Søndergaard LG, Stoltenberg M, Doering P, Flyvbjerg A, Rungby J (2006) Zinc ions in the endocrine and exocrine pancreas of zinc deficient rats. Histol Histopathol 21:619–625
Takahashi N, Kishimoto T, Nemoto T, Kadowaki T, Kasai H (2002) Fusion pore dynamics and insulin granule exocytosis in the pancreatic islet. Science 297:1349–1352
Venkatachalam K, Montell C (2007) TRP channels. Annu Rev Biochem 76:387–417
Vignali S, Leiss V, Karl R, Hofmann F, Welling A (2006) Characterization of voltage-dependent sodium and calcium channels in mouse pancreatic A- and B-cells. J Physiol 572:691–706
Wagner TFJ, Loch S, Lambert S, Straub I, Mannebach S, Mathar I, Düfer M, Lis A, Flockerzi V, Philipp SE, Oberwinkler J (2008) Transient receptor potential M3 channels are ionotropic steroid receptors in pancreatic β cells. Nat Cell Biol 10:1421–1430
Zalewski PD, Millard SH, Forbes IJ, Kapaniris O, Slavotinek A, Betts WH, Ward AD, Lincoln SF, Mahadevan I (1994) Video image analysis of labile zinc in viable pancreatic islet cells using a specific fluorescent probe for zinc. J Histochem Cytochem 42:877–884
Zhao J, Bertoglio BA, Gee KR, Kay AR (2008) The zinc indicator FluoZin-3 is not perturbed significantly by physiological levels of calcium or magnesium. Cell Calcium 44:422–426
Acknowledgments
We thank Sandra Plant, Melanie Portz, Heidi Löhr, and Martin Simon-Thomas for excellent technical support. We also thank Oleksandr Rizun for critically reading the manuscript and Dr. Veit Flockerzi for his support during this study. This work was financially supported by the DFG (Emmy Noether Program and GK 1326), HOMFOR, and Forschungskommission der Universität des Saarlandes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Thomas F.J. Wagner, Anna Drews, Sabine Loch, Florian Mohr, Sachar Lambert, and Johannes Oberwinkler are members of the Emmy Noether Research Group in the Institut für Experimentelle und Klinische Pharmakologie und Toxikologie, Universitätsklinikum des Saarlandes.
Anna Drews and Sabine Loch contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, T.F.J., Drews, A., Loch, S. et al. TRPM3 channels provide a regulated influx pathway for zinc in pancreatic beta cells. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 460, 755–765 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-010-0838-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-010-0838-9