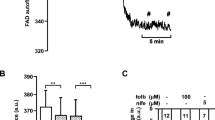
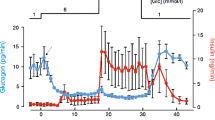
Abstract
Pancreatic beta-cells of sulfonylurea receptor type 1 knock-out (SUR1−/−) mice exhibit an oscillating membrane potential (V m) demonstrating that hyper-polarisation occurs despite the lack of KATP channels. We hypothesize that glucose activates the Na+/K+-ATPase thus increasing a hyper-polarising current. Elevating glucose in SUR1−/− beta-cells resulted in a transient fall in V m and [Ca2+]c independent of sarcoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-activated ATPase (SERCA) activation. This was not affected by K+ channel blockade but inhibited by ATP depletion and by ouabain. Increasing glucose also reduced [Na+]c, an effect reversed by ouabain. Exogenously applied insulin decreased [Na+]c and hyper-polarised V m. Inhibiting insulin signalling in SUR1−/− beta-cells blunted the glucose-induced decrease of [Ca2+]c. Tolbutamide (1 mmol/l) disclosed the SERCA-independent effect of glucose on [Ca2+]c in wild-type beta-cells. The data show that in SUR1−/− beta-cells, glucose activates the Na+/K+-ATPase presumably by increasing [ATP]c. Insulin can also stimulate the pump and potentiate the effect of glucose. Pathways involving the pump may thus serve as potential drug targets in certain metabolic disorders.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]c :
-
Cytosolic free calcium concentration
- V m :
-
Plasma membrane potential
- KIR6.2:
-
Inward rectifying K+ channel type 6.2
- SUR1:
-
Sulfonylurea receptor type 1
- KATP channel:
-
ATP-dependent K+ channel
References
Ashcroft SJ, Weerasinghe LC, Randle PJ (1973) Interrelationship of islet metabolism, adenosine triphosphate content and insulin release. Biochem J 132:223–231
Barg S, Galvanovskis J, Göpel SO, Rorsman P, Eliasson L (2000) Tight coupling between electrical activity and exocytosis in mouse glucagon-secreting alpha-cells. Diabetes 49:1500–1510
Bokvist K, Rorsman P, Smith PA (1990a) Block of ATP-regulated and Ca2+-activated K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells by external tetraethylammonium and quinine. J Physiol 423:327–342
Bokvist K, Rorsman P, Smith PA (1990b) Effects of external tetraethylammonium ions and quinine on delayed rectifying K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol 423:311–325
Borge PD, Moibi J, Greene SR, Trucco M, Young RA, Gao Z, Wolf BA (2002) Insulin receptor signaling and sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase in beta-cells. Diabetes 51(Suppl 3):S427–S433
Clarke RJ, Kane DJ (2007) Two gears of pumping by the sodium pump. Biophys J 93:4187–4196
Darbon P, Tscherter A, Yvon C, Streit J (2003) Role of the electrogenic Na/K pump in disinhibition-induced bursting in cultured spinal networks. J Neurophysiol 90:3119–3129
Doliba NM, Qin W, Vatamaniuk MZ, Buettger CW, Collins HW, Magnuson MA, Kaestner KH, Wilson DF, Carr RD, Matschinsky FM (2006) Cholinergic regulation of fuel-induced hormone secretion and respiration of SUR1−/− mouse islets. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291:E525–E535
Drews G, Zempel G, Krippeit-Drews P, Britsch S, Busch GL, Kaba NK, Lang F (1998) Ion channels involved in insulin release are activated by osmotic swelling of pancreatic B-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1370:8–16
Düfer M, Haspel D, Krippeit-Drews P, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J, Drews G (2004) Oscillations of membrane potential and cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in SUR1−/− beta-cells. Diabetologia 47:488–498
Düfer M, Haspel D, Krippeit-Drews P, Kelm M, Ranta F, Nitschke R, Ullrich S, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J, Drews G (2007) The KATP channel is critical for calcium sequestration into non-ER compartments in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 20:65–74
Dunne MJ, Cosgrove KE, Shepherd RM, Aynsley-Green A, Lindley KJ (2004) Hyperinsulinism in infancy: from basic science to clinical disease. Physiol Rev 84:239–275
Elmi A, Idahl LA, Sandström PE, Sehlin J (2000) D-glucose stimulates the Na+/K+ pump in mouse pancreatic islet cells. Int J Exp Diabetes Res 1:155–164
Ewart HS, Klip A (1995) Hormonal regulation of the Na+-K+-ATPase: mechanisms underlying rapid and sustained changes in pump activity. Am J Physiol 269:C295–C311
Grapengiesser E, Gylfe E, Hellman B (1988) Dual effect of glucose on cytoplasmic Ca2+ in single pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 150:419–425
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Haspel D, Krippeit-Drews P, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J, Drews G, Düfer M (2005) Crosstalk between membrane potential and cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in beta-cells from Sur1−/− mice. Diabetologia 48:913–921
Herchuelz A, Diaz-Horta O, van Eylen F (2002) Na/Ca exchange and Ca2+ homeostasis in the pancreatic beta-cell. Diabetes Metab 28:3S54–3S60 discussion 3S108–112
Humphrey PA, Lüpfert C, Apell HJ, Cornelius F, Clarke RJ (2002) Mechanism of the rate-determining step of the Na+,K+-ATPase pump cycle. Biochemistry 41:9496–9507
Henquin JC, Meissner HP (1982) The electrogenic sodium-potassium pump of mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol 332:529–552
Iannello S, Milazzo P, Belfiore F (2007) Animal and human tissue Na,K-ATPase in normal and insulin-resistant states: regulation, behaviour and interpretative hypothesis on NEFA effects. Obes Rev 8:231–251
Jakab M, Grundbichler M, Benicky J, Ravasio A, Chwatal S, Schmidt S, Strbak V, Fürst J, Paulmichl M, Ritter M (2006) Glucose induces anion conductance and cytosol-to-membrane transposition of ICln in INS-1E rat insulinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 18:21–34
Khan FA, Goforth PB, Zhang M, Satin LS (2001) Insulin activates ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. Diabetes 50:2192–2198
Krippeit-Drews P, Düfer M, Drews G (2000) Parallel oscillations of intracellular calcium activity and mitochondrial membrane potential in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267:179–183
Leibiger IB, Leibiger B, Berggren PO (2002) Insulin feedback action on pancreatic beta-cell function. FEBS Lett 532:1–6
Meissner HP, Schmelz H (1974) Membrane potential of beta-cells in pancreatic islets. Pflügers Arch 351:195–206
Miki T, Nagashima K, Tashiro F et al (1998) Defective insulin secretion and enhanced insulin action in KATP channel-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:10402–10406
Nadal A, Quesada I, Soria B (1999) Homologous and heterologous asynchronicity between identified α-, β- and δ-cells within intact islets of Langerhans in the mouse. J Physiol 517:85–93
Nakazaki M, Crane A, Hu M, Seghers V, Ullrich S, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J (2002) cAMP-activated protein kinase-independent potentiation of insulin secretion by cAMP is impaired in SUR1 null islets. Diabetes 51:3440–3449
Nenquin M, Szollosi A, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J, Henquin JC (2004) Both triggering and amplifying pathways contribute to fuel-induced insulin secretion in the absence of sulfonylurea receptor-1 in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem 279:32316–32324
Noble D, Herchuelz A (2007) Role of Na/Ca exchange and the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in cell function. Conference on Na/Ca exchange. EMBO Rep 8:228–232
Nunemaker CS, Zhang M, Satin LS (2004) Insulin feedback alters mitochondrial activity through an ATP-sensitive K+ channel-dependent pathway in mouse islets and beta-cells. Diabetes 53:1765–1772
Owada S, Larsson O, Arkhammar P, Katz AI, Chibalin AV, Berggren PO, Bertorello AM (1999) Glucose decreases Na+,K+-ATPase activity in pancreatic beta-cells. An effect mediated via Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 and protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem 274:2000–2008
Persaud SJ, Asare-Anane H, Jones PM (2002) Insulin receptor activation inhibits insulin secretion from human islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett 510:225–228
Plant TD (1988) Properties and calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium currents in cultured mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol 404:731–747
Ribalet B, Beigelman PM (1980) Calcium action potentials and potassium permeability activation in pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol 239:C124–C133
Ribalet B, Beigelman PM (1982) Effects of sodium on beta-cell electrical activity. Am J Physiol 242:C296–C303
Ribalet B, Mirell CJ, Johnson DG, Levin SR (1996) Sulfonylurea binding to a low-affinity site inhibits the Na/K-ATPase and the KATP channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Gen Physiol 107:231–241
Roe MW, Lancaster ME, Mertz RJ, Worley JF 3rd, Dukes ID (1993) Voltage-dependent intracellular calcium release from mouse islets stimulated by glucose. J Biol Chem 268:9953–9956
Satoh H, Hayashi H, Noda N, Terada H, Kobayashi A, Yamashita Y, Kawai T, Hirano M, Yamazaki N (1991) Quantification of intracellular free sodium ions by using a new fluorescent indicator, sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate in guinea pig myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 175:611–616
Schulze DU, Düfer M, Wieringa B, Krippeit-Drews P, Drews G (2007) An adenylate kinase is involved in KATP channel regulation of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetologia 50:2126–2134
Seghers V, Nakazaki M, DeMayo F, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J (2000) SUR1 knockout mice. A model for KATP channel-independent regulation of insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 275:9270–9277
Shiota C, Larsson O, Shelton KD, Shiota M, Efanov AM, Hoy M, Lindner J, Kooptiwut S, Juntti-Berggren L, Gromada J, Berggren PO, Magnuson MA (2002) Sulfonylurea receptor type 1 knock-out mice have intact feeding-stimulated insulin secretion despite marked impairment in their response to glucose. J Biol Chem 277:37176–37183
Soltoff SP, Mandel LJ (1984) Active ion transport in the renal proximal tubule. III. The ATP dependence of the Na pump. J Gen Physiol 84:643–662
Sweeney G, Klip A (1998) Regulation of the Na+/K+-ATPase by insulin: why and how? Mol Cell Biochem 182:121–133
Sweeney G, Klip A (2001) Mechanisms and consequences of Na+,K+-pump regulation by insulin and leptin. Cell Mol Biol 47:363–372
Szollosi A, Nenquin M, Henquin JC (2007) Overnight culture unmasks glucose-induced insulin secretion in mouse islets lacking ATP-sensitive K+ channels by improving the triggering Ca2+ signal. J Biol Chem 282:14768–14776
Tarasov AI, Girard CA, Ashcroft FM (2006) ATP sensitivity of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in intact and permeabilized pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 55:2446–2454
Ullrich S, Zhang Y, Avram D, Ranta F, Kuhl D, Häring HU, Lang F (2007) Dexamethasone increases Na+/K+ ATPase activity in insulin secreting cells through SGK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:662–667
Vague P, Coste TC, Jannot MF, Raccah D, Tsimaratos M (2004) C-peptide, Na+,K+-ATPase, and diabetes. Exp Diabesity Res 5:37–50
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the DFG Dr225/6-3 (gd) and DU425/1-2 (md), the NIH grant DK044311 and JDRF 1-2005-750 (jb) and the Thrasher Foundation (lab).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Düfer, M., Haspel, D., Krippeit-Drews, P. et al. Activation of the Na+/K+-ATPase by insulin and glucose as a putative negative feedback mechanism in pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 457, 1351–1360 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0592-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0592-4