Abstract.
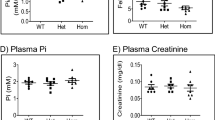
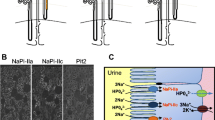
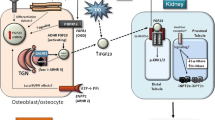
Over the past decade, three classes of Na/Pi cotransporters have been identified in mammalian kidney. The type IIa Na/Pi cotransporter, Npt2, is the most abundant and is expressed in the brush-border membrane of renal proximal tubular cells where the bulk of filtered inorganic phosphate (Pi) is reabsorbed. Disruption of the Npt2 gene in mice underscored the importance of Npt2 in the overall maintenance of Pi homeostasis and demonstrated that Npt2 is the target for regulation of proximal tubular Pi reabsorption by parathyroid hormone and dietary Pi. The regulation is post-transcriptional and largely occurs by brush-border membrane retrieval and insertion of Npt2 protein. Of great interest is the recent identification of novel Pi regulating genes, PHEX and FGF23, that play a role in the pathophysiology of inherited (X-linked hypophosphatemia and autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets) and acquired (oncogenic hypophosphatemic rickets) disorders characterized by renal Pi wasting and associated skeletal abnormalities. Studies are currently underway to elucidate the molecular basis for impaired renal Pi reabsorption in these disorders and to determine the precise physiological role of PHEX and FGF-23 in the regulation of Pi homeostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tenenhouse, H.S., Sabbagh, Y. Novel phosphate-regulating genes in the pathogenesis of renal phosphate wasting disorders. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 444, 317–326 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0839-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0839-4